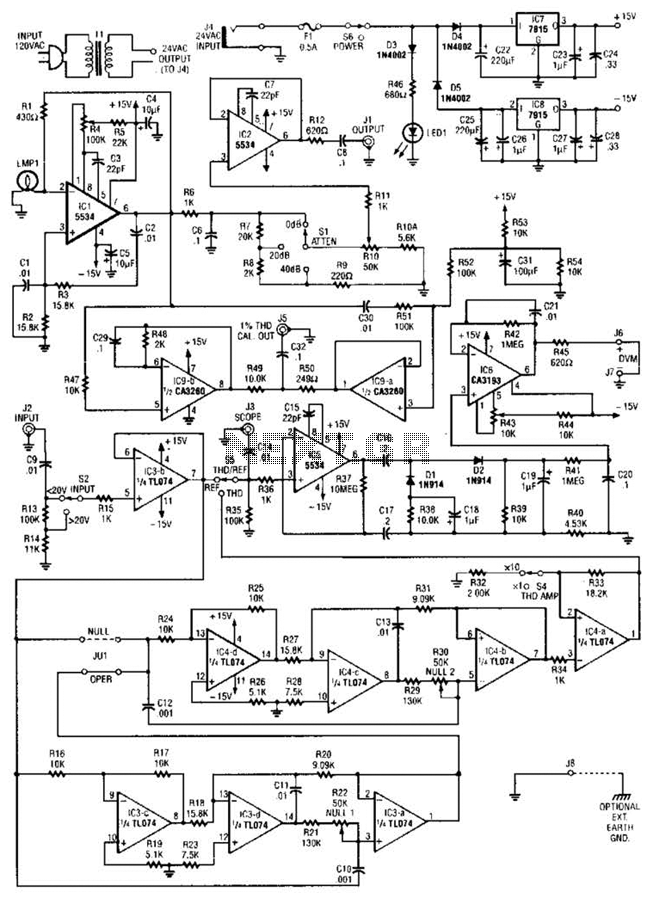
Inductance Meter Circuit
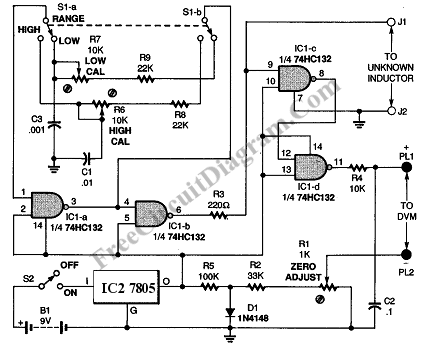
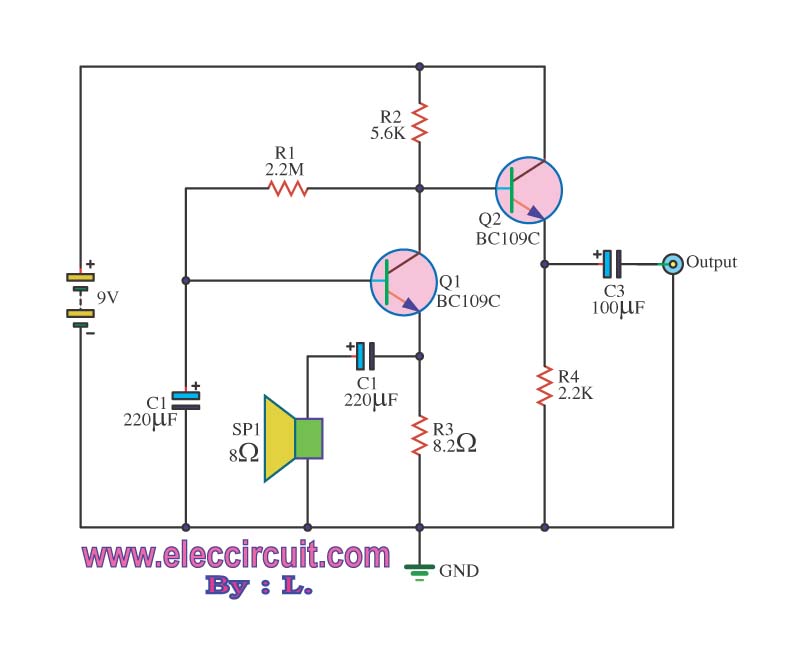
This inductance meter serves as an adapter for a digital voltmeter (DVM), enabling the voltmeter to measure the value of inductors. The inductance meter is particularly useful in designing switch mode power supplies, as it often requires hand-winding coils and measuring inductance through trial and error to achieve the desired value. The schematic diagram of the inductance meter adapter circuit illustrates its functionality, which provides two measurement ranges. The low range measures inductors with values between 3 µH and 500 µH, while the high range measures inductance values from 100 µH to 5 mH. Calibration of this inductance meter adapter involves connecting a digital voltmeter, setting it to the 200 mV range, shorting the test probe, and adjusting the zero (R1) to achieve a zero millivolt reading. For low range calibration, the voltmeter should be set to the low range position and adjusted to the 2 V range. Testing a known inductor of approximately 400 µH requires adjusting the low calibration potentiometer to yield a reading of 1 mV/µH, with a 400 µH inductor resulting in a 400 mV reading. For high range calibration, the range selector must be switched to the high position, using a known inductor of around 5 mH, and adjusting the high calibration potentiometer to provide 100 mV per mH, with a 5 mH inductor giving a 500 mV reading on the DVM.
The inductance meter adapter circuit is designed to enhance the functionality of a standard digital voltmeter, allowing for precise measurement of inductance values essential for various electronic applications. The circuit typically includes a few key components: resistors, capacitors, and a range switch. The resistors are used to set the voltage levels for the low and high ranges, while capacitors may be employed to filter out noise and stabilize the readings.
The schematic diagram is crucial for understanding the interconnections between these components. The circuit may feature a microcontroller or an operational amplifier to process the signals from the inductors being measured. This processing allows for accurate conversion of inductance to a corresponding voltage that can be read by the digital voltmeter.
In practical applications, the inductance meter adapter is invaluable for engineers and hobbyists alike when working with inductors in power supply designs or other electronic circuits. The ability to easily switch between measurement ranges allows for flexibility in testing various inductance values, ensuring that designers can optimize their circuits effectively. The calibration process is straightforward, requiring minimal equipment and ensuring that the measurements are reliable and accurate, which is critical in electronic design and troubleshooting.This inductance meter is actually an adapter to your digital voltmeter (DVM). Using this circuit now your voltmeter is capable of measuring inductor value. Inductance meter is very helpful in designing switch mode power supply, since its often needed to wind the coil by hand and measure the inductance fro trial and error to get the required value. Here is the schematic diagram of the inductance meter adapter circuit: This circuit is designed to provide twi measurement range. The low range will measure inductors with inductance value between 3uH to 500uH, and the high range will measure inductance values between 100uH and 5mH.
To calibrate this inductance meter adapter, connect a digital voltmeter, swith the voltmeter to 200 mV range, short the test probe and adjust the zero (R1) to give zero millivolt reading on your digital voltmeter. To calibrate the low range of this inductance meter adapter, switch the voltmeter to low range position, and select 2 V range for the digital voltmeter.
Test a known inductor that has value around 400uH, adjust the low calibration pot to give correct reading of 1mV / uH. If you use a 400uH inductor then you must adjust the calibration to give exactly a 400mV reading. For high range calibration, switch the range selector to high position and use a known inductor around 5 mH, adjust the high calibration pot to give 100mV per mH.
A 5 mH inductor should give a 500mV reading on your DVM. [Source: Marc Spiwak] 🔗 External reference
The inductance meter adapter circuit is designed to enhance the functionality of a standard digital voltmeter, allowing for precise measurement of inductance values essential for various electronic applications. The circuit typically includes a few key components: resistors, capacitors, and a range switch. The resistors are used to set the voltage levels for the low and high ranges, while capacitors may be employed to filter out noise and stabilize the readings.
The schematic diagram is crucial for understanding the interconnections between these components. The circuit may feature a microcontroller or an operational amplifier to process the signals from the inductors being measured. This processing allows for accurate conversion of inductance to a corresponding voltage that can be read by the digital voltmeter.
In practical applications, the inductance meter adapter is invaluable for engineers and hobbyists alike when working with inductors in power supply designs or other electronic circuits. The ability to easily switch between measurement ranges allows for flexibility in testing various inductance values, ensuring that designers can optimize their circuits effectively. The calibration process is straightforward, requiring minimal equipment and ensuring that the measurements are reliable and accurate, which is critical in electronic design and troubleshooting.This inductance meter is actually an adapter to your digital voltmeter (DVM). Using this circuit now your voltmeter is capable of measuring inductor value. Inductance meter is very helpful in designing switch mode power supply, since its often needed to wind the coil by hand and measure the inductance fro trial and error to get the required value. Here is the schematic diagram of the inductance meter adapter circuit: This circuit is designed to provide twi measurement range. The low range will measure inductors with inductance value between 3uH to 500uH, and the high range will measure inductance values between 100uH and 5mH.
To calibrate this inductance meter adapter, connect a digital voltmeter, swith the voltmeter to 200 mV range, short the test probe and adjust the zero (R1) to give zero millivolt reading on your digital voltmeter. To calibrate the low range of this inductance meter adapter, switch the voltmeter to low range position, and select 2 V range for the digital voltmeter.
Test a known inductor that has value around 400uH, adjust the low calibration pot to give correct reading of 1mV / uH. If you use a 400uH inductor then you must adjust the calibration to give exactly a 400mV reading. For high range calibration, switch the range selector to high position and use a known inductor around 5 mH, adjust the high calibration pot to give 100mV per mH.
A 5 mH inductor should give a 500mV reading on your DVM. [Source: Marc Spiwak] 🔗 External reference