Infrared Remote Tester
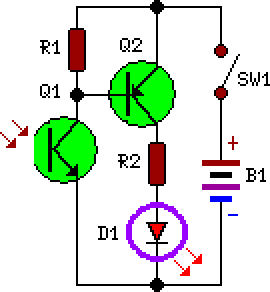
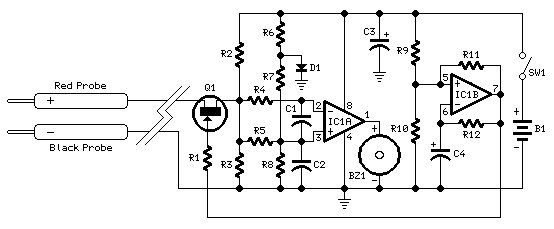
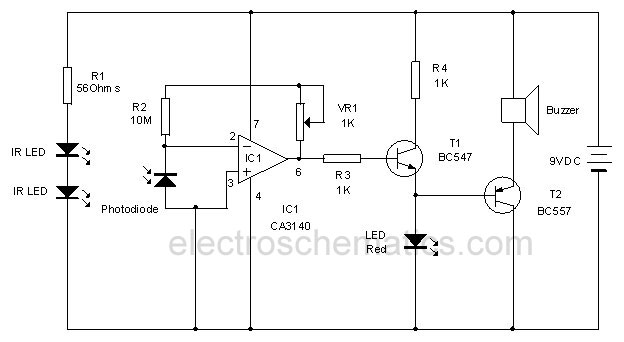
A simple device designed for quickly checking common infrared remote controls can be beneficial for electronics enthusiasts who often need to repair or test these widespread devices. A reliable circuit was created using a few components: the LED will flash when any button on the remote control is pressed. The side of the remote control that contains the infrared emitting diode(s) should be pointed towards the photo transistor (Q1) of the checker circuit; the maximum distance for effective operation should not exceed approximately 20 to 25 cm. The circuit draws less than 1 mA of current when the LED is illuminated and 0 mA when no signal is detected by the photo transistor; thus, switch SW1 can be omitted.
The infrared remote control tester circuit is designed to provide a straightforward method for verifying the functionality of remote controls. The core components include a photo transistor, an LED, and a few passive components such as resistors. When a button on the remote control is pressed, infrared light is emitted from the remote's IR LED. This emitted light is detected by the photo transistor (Q1), which is sensitive to infrared wavelengths.
The circuit operates by converting the infrared light signal into an electrical signal that activates the LED indicator. When the photo transistor receives sufficient infrared light, it allows current to flow, turning on the LED. The flashing of the LED serves as a visual indication that the remote control is functioning properly.
The design emphasizes simplicity and low power consumption, making it ideal for quick checks without the need for complex equipment. With a current draw of less than 1 mA during operation, the circuit is efficient and can be powered by a small battery. The omission of the switch (SW1) is justified by the low power requirements, allowing for a continuous readiness to detect signals without unnecessary components.
To ensure optimal performance, the user should maintain a distance of 20 to 25 cm between the remote control and the tester. This range allows for effective detection while minimizing the effects of ambient light interference. The straightforward nature of this circuit makes it an excellent tool for electronics amateurs and professionals alike, providing a reliable means of troubleshooting and testing infrared remote controls efficiently.A very simple device allowing a quick check of common Infra-red Remote-Controls can be useful to the electronics amateur, frequently asked to repair or test these ubiquitous devices. A reliable circuit was designed with a handful of components: the LED will flash when any of the Remote-Control push buttons will be pressed.
The side of the Remote-C ontrol bearing the IR emitting diode(s) must be directed towards the Photo Transistor (Q1) of the checker circuit: maximum distance should not exceed about 20 - 25cm. Current drawing of the circuit is less than 1mA when the LED illuminates and 0mA when no signal is picked-up by the Photo Transistor: therefore, SW1 can be omitted.
🔗 External reference
The infrared remote control tester circuit is designed to provide a straightforward method for verifying the functionality of remote controls. The core components include a photo transistor, an LED, and a few passive components such as resistors. When a button on the remote control is pressed, infrared light is emitted from the remote's IR LED. This emitted light is detected by the photo transistor (Q1), which is sensitive to infrared wavelengths.
The circuit operates by converting the infrared light signal into an electrical signal that activates the LED indicator. When the photo transistor receives sufficient infrared light, it allows current to flow, turning on the LED. The flashing of the LED serves as a visual indication that the remote control is functioning properly.
The design emphasizes simplicity and low power consumption, making it ideal for quick checks without the need for complex equipment. With a current draw of less than 1 mA during operation, the circuit is efficient and can be powered by a small battery. The omission of the switch (SW1) is justified by the low power requirements, allowing for a continuous readiness to detect signals without unnecessary components.
To ensure optimal performance, the user should maintain a distance of 20 to 25 cm between the remote control and the tester. This range allows for effective detection while minimizing the effects of ambient light interference. The straightforward nature of this circuit makes it an excellent tool for electronics amateurs and professionals alike, providing a reliable means of troubleshooting and testing infrared remote controls efficiently.A very simple device allowing a quick check of common Infra-red Remote-Controls can be useful to the electronics amateur, frequently asked to repair or test these ubiquitous devices. A reliable circuit was designed with a handful of components: the LED will flash when any of the Remote-Control push buttons will be pressed.
The side of the Remote-C ontrol bearing the IR emitting diode(s) must be directed towards the Photo Transistor (Q1) of the checker circuit: maximum distance should not exceed about 20 - 25cm. Current drawing of the circuit is less than 1mA when the LED illuminates and 0mA when no signal is picked-up by the Photo Transistor: therefore, SW1 can be omitted.
🔗 External reference