Inverter

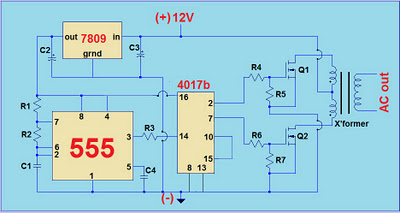
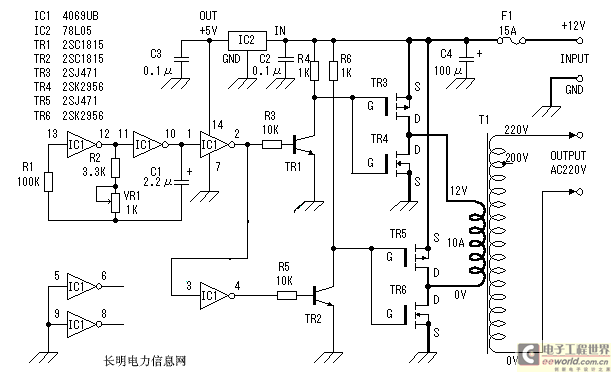
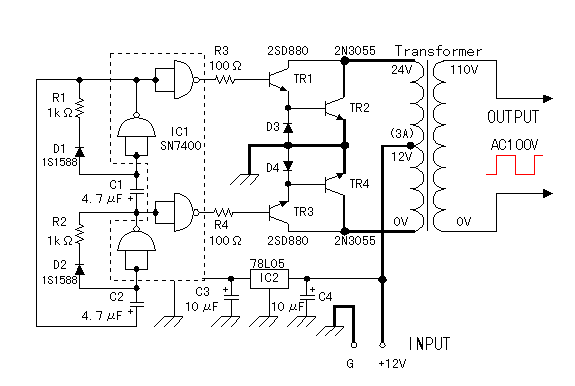
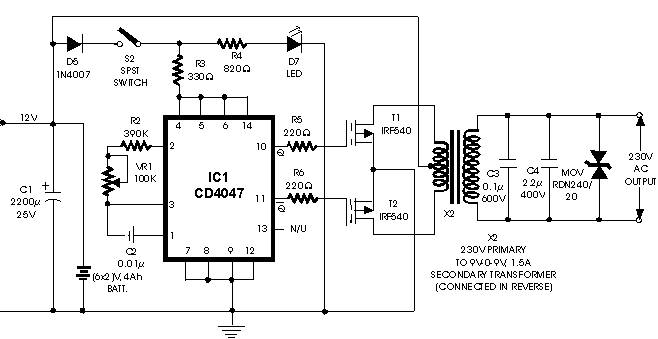
Have you ever wanted to run a TV, stereo or other appliance while on the road or camping? Well, this inverter should solve that problem. It takes 12 VDC and steps it up to 120 VAC. The wattage depends on which transistors you use for Q1 and Q2, as well as how "big" a transformer you use for T1. The inverter can be constructed to supply anywhere from 1 to 1000 (1 KW) watts.
The described inverter circuit is designed to convert a 12 VDC input into a 120 VAC output, making it suitable for powering standard household appliances while away from traditional power sources. The core components of the inverter include two transistors (Q1 and Q2) that function as the primary switching elements. These transistors must be chosen based on their current and voltage ratings, which will ultimately determine the power output capability of the inverter.
The transformer (T1) is another critical component, as it steps up the voltage from the low DC level to the required AC level. The turns ratio of the transformer must be carefully calculated to achieve the desired output voltage. For example, a transformer with a turns ratio of 10:1 would be appropriate for stepping up 12 VDC to approximately 120 VAC. The physical size and power rating of the transformer must also be considered, as these factors will influence the overall efficiency and performance of the inverter.
To enhance performance and reliability, additional components such as diodes for rectification, capacitors for filtering, and resistors for biasing may be included in the circuit design. A suitable control circuit may also be implemented to regulate the switching frequency of the transistors, ensuring stable output voltage and reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Thermal management is another important aspect of the design, as the transistors and transformer can generate significant heat during operation. Adequate heat sinking or cooling mechanisms should be incorporated to prevent overheating and ensure longevity of the components.
Overall, this inverter circuit represents a versatile solution for converting 12 VDC to 120 VAC, with the flexibility to customize the power output based on the specific requirements of the application.Have you ever wanted to run a TV, stereo or other appliance while on the road or camping? Well, this inverter should solve that problem. It takes 12 VDC and steps it up to 120 VAC. The wattage depends on which tansistors you use for Q1 and Q2, as well as how "big" a transformer you use for T1. The inverter can be constructed to supply anywhere from 1 to 1000 (1 KW) watts. 🔗 External reference
The described inverter circuit is designed to convert a 12 VDC input into a 120 VAC output, making it suitable for powering standard household appliances while away from traditional power sources. The core components of the inverter include two transistors (Q1 and Q2) that function as the primary switching elements. These transistors must be chosen based on their current and voltage ratings, which will ultimately determine the power output capability of the inverter.
The transformer (T1) is another critical component, as it steps up the voltage from the low DC level to the required AC level. The turns ratio of the transformer must be carefully calculated to achieve the desired output voltage. For example, a transformer with a turns ratio of 10:1 would be appropriate for stepping up 12 VDC to approximately 120 VAC. The physical size and power rating of the transformer must also be considered, as these factors will influence the overall efficiency and performance of the inverter.
To enhance performance and reliability, additional components such as diodes for rectification, capacitors for filtering, and resistors for biasing may be included in the circuit design. A suitable control circuit may also be implemented to regulate the switching frequency of the transistors, ensuring stable output voltage and reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Thermal management is another important aspect of the design, as the transistors and transformer can generate significant heat during operation. Adequate heat sinking or cooling mechanisms should be incorporated to prevent overheating and ensure longevity of the components.
Overall, this inverter circuit represents a versatile solution for converting 12 VDC to 120 VAC, with the flexibility to customize the power output based on the specific requirements of the application.Have you ever wanted to run a TV, stereo or other appliance while on the road or camping? Well, this inverter should solve that problem. It takes 12 VDC and steps it up to 120 VAC. The wattage depends on which tansistors you use for Q1 and Q2, as well as how "big" a transformer you use for T1. The inverter can be constructed to supply anywhere from 1 to 1000 (1 KW) watts. 🔗 External reference