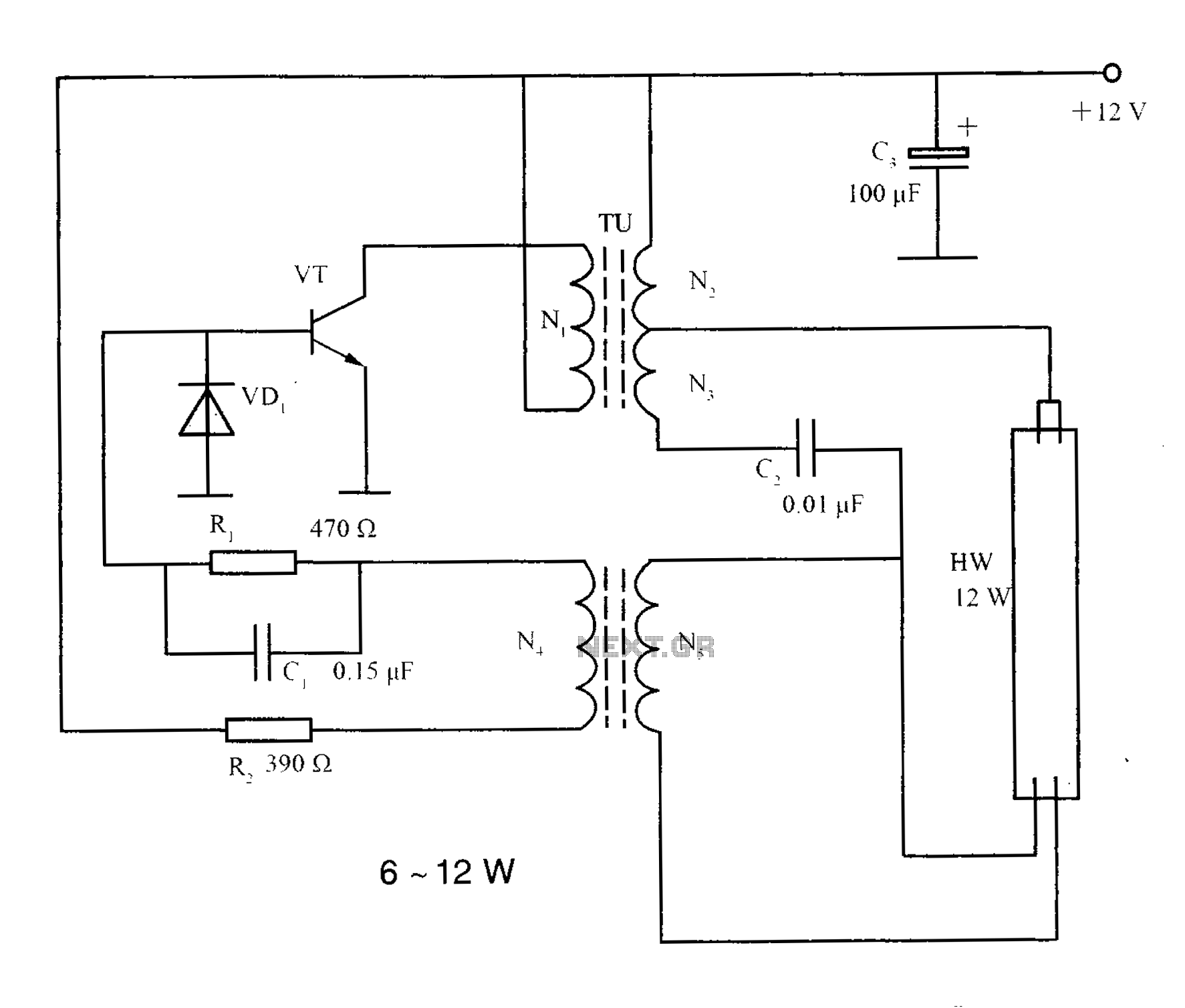
inverter circuits
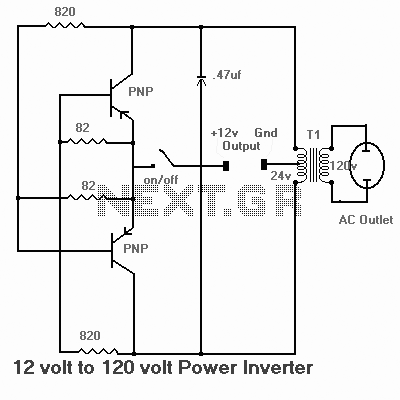
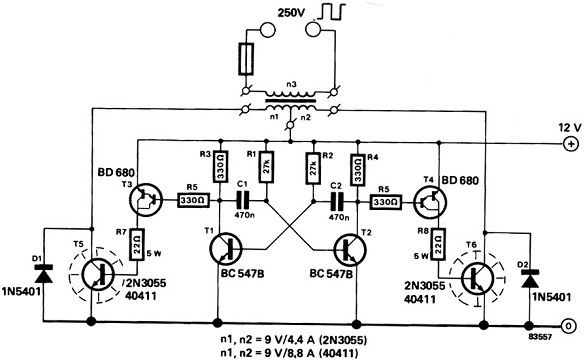
Some good inverter circuits I found oscillate at approximately 50 to 60 Hz. They are likely capable of handling up to two amps; any more than that will cause them to automatically shut off. If there are questions, please leave them in the comment box or email me.
Inverter circuits are essential components in various applications, converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). The typical frequency of operation for these circuits is between 50 Hz and 60 Hz, which aligns with standard power supply frequencies used in many regions worldwide. The inverter circuits discussed are designed to handle loads up to two amps, making them suitable for low to moderate power applications.
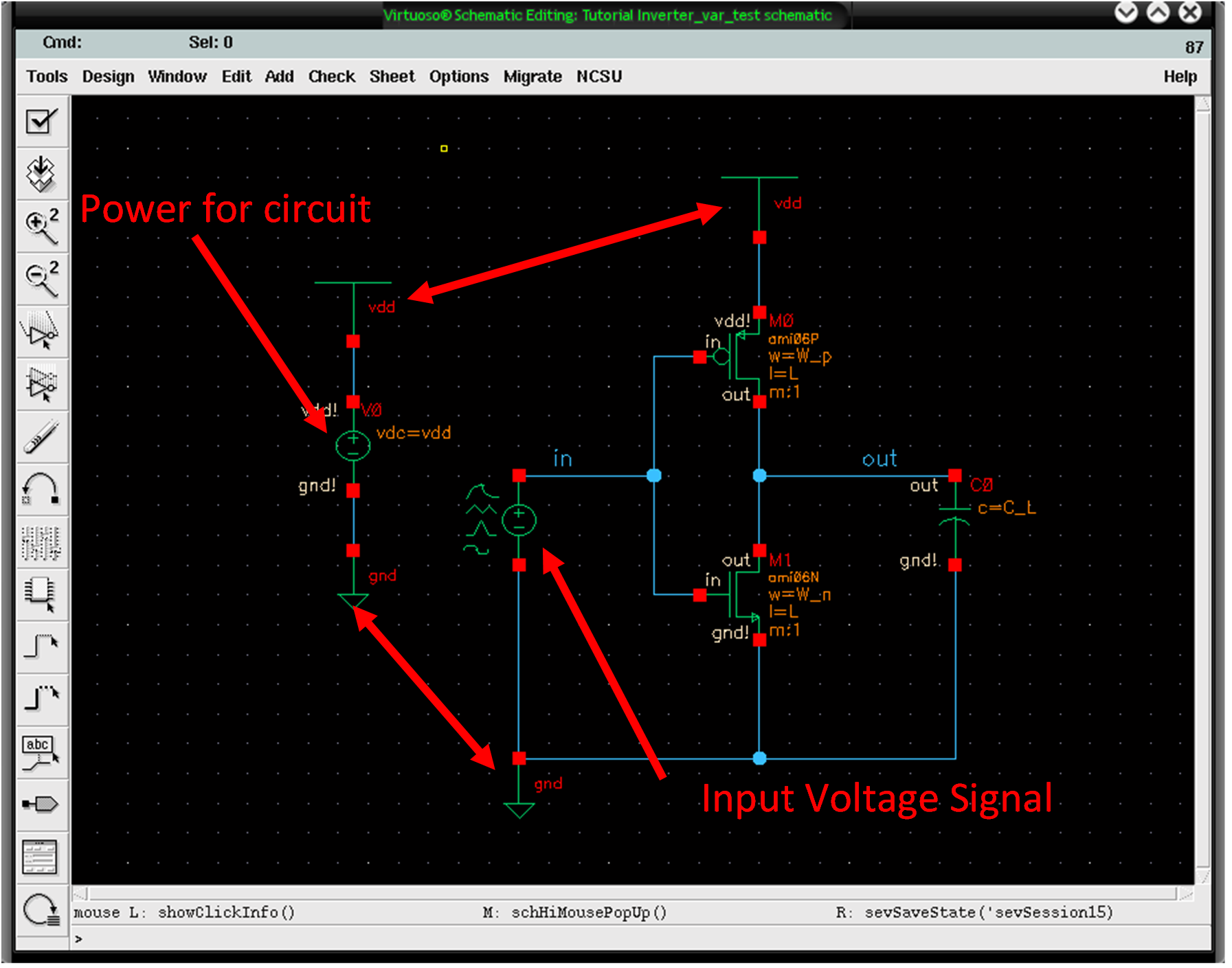
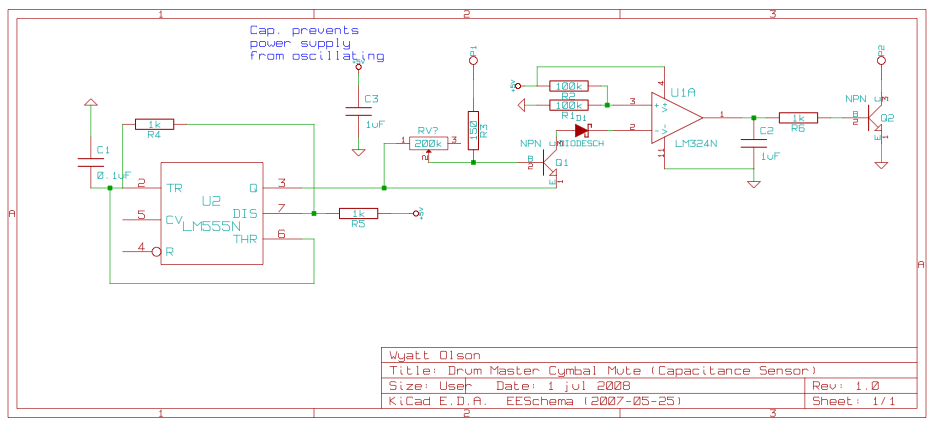
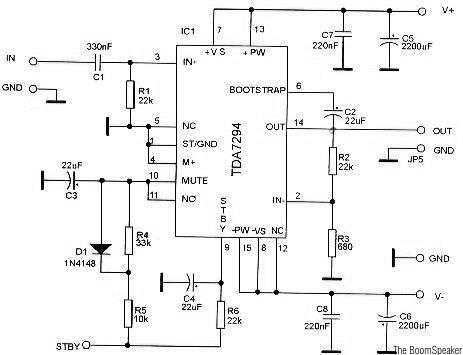
The design of these inverters typically involves a few critical components: a DC power source, oscillators, switching devices (such as transistors or MOSFETs), and a transformer. The oscillator generates a square wave signal at the desired frequency. This square wave is then used to turn the switching devices on and off, creating an alternating current output. The transformer steps up or steps down the voltage as needed while isolating the load from the DC source.
Protection mechanisms are often integrated into inverter designs to prevent overheating and overcurrent conditions. When the load exceeds the two-amp threshold, the inverter automatically shuts off to protect the circuit from damage. This feature is crucial for maintaining the reliability and longevity of the inverter.
Inverter circuits can be applied in various scenarios, including powering small household appliances, charging batteries, and providing emergency backup power. Understanding the specifications and limitations of these circuits allows for effective integration into electronic systems, ensuring optimal performance and safety.Some good inverter circuits I fond they, oscillate at about 50 to 60Hz. They will probably handle up to about two amps any more and the will auto shut off. Have questions ask me leave your questions in the comment box or email me at ericgoodchild@yahoo. com 🔗 External reference
Inverter circuits are essential components in various applications, converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). The typical frequency of operation for these circuits is between 50 Hz and 60 Hz, which aligns with standard power supply frequencies used in many regions worldwide. The inverter circuits discussed are designed to handle loads up to two amps, making them suitable for low to moderate power applications.
The design of these inverters typically involves a few critical components: a DC power source, oscillators, switching devices (such as transistors or MOSFETs), and a transformer. The oscillator generates a square wave signal at the desired frequency. This square wave is then used to turn the switching devices on and off, creating an alternating current output. The transformer steps up or steps down the voltage as needed while isolating the load from the DC source.
Protection mechanisms are often integrated into inverter designs to prevent overheating and overcurrent conditions. When the load exceeds the two-amp threshold, the inverter automatically shuts off to protect the circuit from damage. This feature is crucial for maintaining the reliability and longevity of the inverter.
Inverter circuits can be applied in various scenarios, including powering small household appliances, charging batteries, and providing emergency backup power. Understanding the specifications and limitations of these circuits allows for effective integration into electronic systems, ensuring optimal performance and safety.Some good inverter circuits I fond they, oscillate at about 50 to 60Hz. They will probably handle up to about two amps any more and the will auto shut off. Have questions ask me leave your questions in the comment box or email me at ericgoodchild@yahoo. com 🔗 External reference