IR Remote Control Extender var 5 Circuit
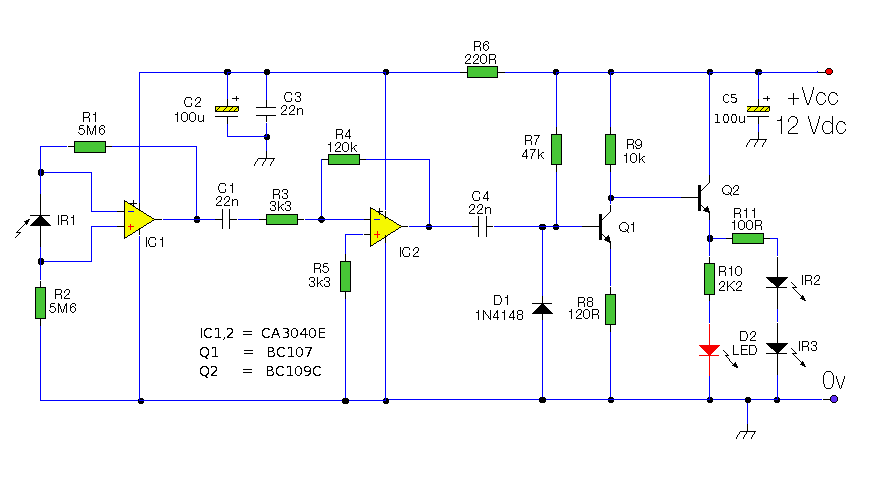
The latest addition to the collection of Infrared (IR) Repeater circuits, the Mark 5, is an enhanced version of the Mark 1 circuit and features an increased range.
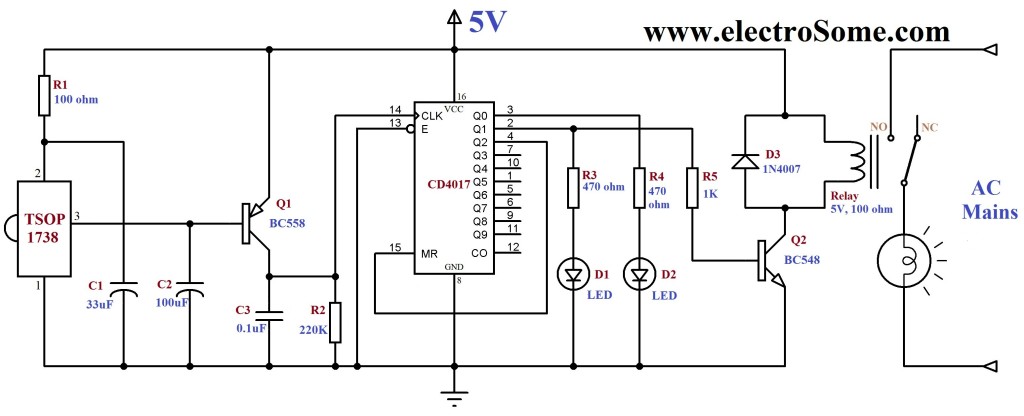
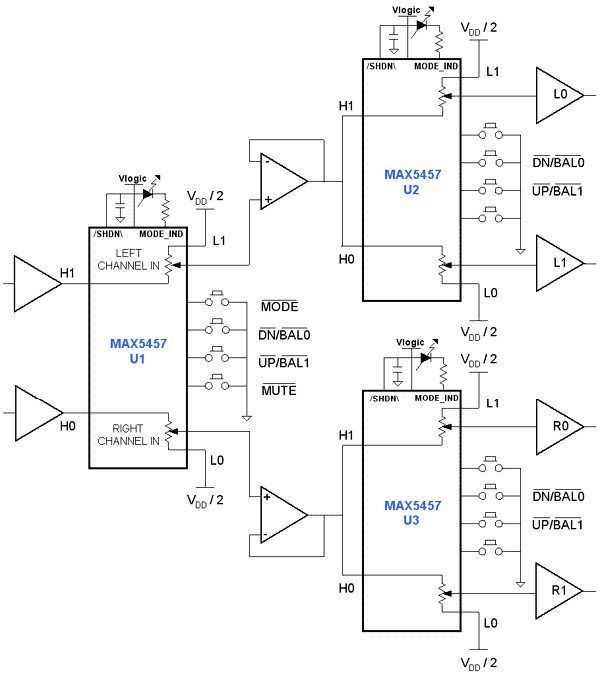
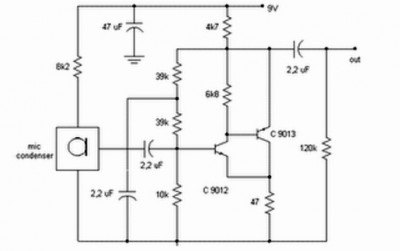
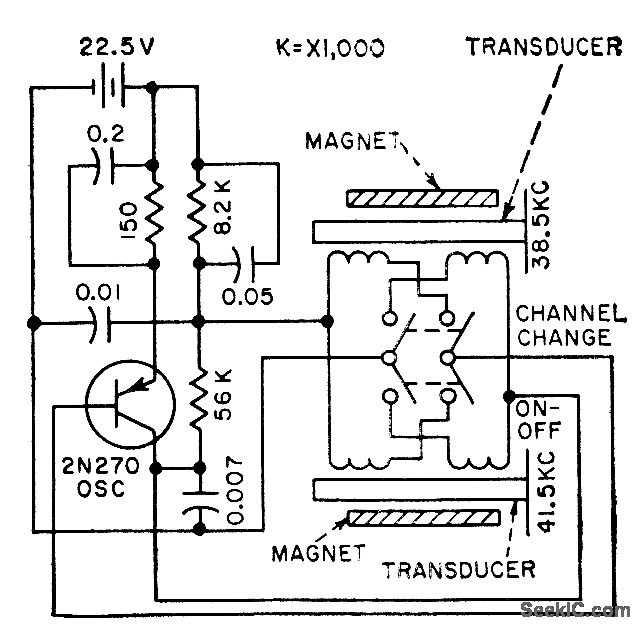
The Mark 5 Infrared Repeater circuit is designed to extend the range of remote control signals, allowing devices to be operated from greater distances or through obstacles. This circuit typically consists of an IR receiver, a microcontroller or amplifier, and an IR transmitter.
The IR receiver detects signals from remote control devices and converts them into electrical signals. These signals are then processed by the microcontroller or amplifier, which boosts the signal strength. The amplified signal is subsequently transmitted by the IR transmitter, which emits infrared light that can be detected by the intended device.
Key components of the Mark 5 circuit may include a photodiode or phototransistor as the IR receiver, a low-noise operational amplifier to enhance the signal, and a high-efficiency IR LED for transmission. The circuit may also incorporate a power supply section, which could utilize a voltage regulator to ensure stable operation.
The enhancements in the Mark 5 over the Mark 1 may include improved sensitivity of the receiver, which allows it to capture weaker signals, and a more robust transmission capability, which increases the effective range. Additionally, adjustments to the circuit layout may reduce interference and improve overall reliability.
This circuit can be utilized in various applications, such as controlling home entertainment systems, HVAC units, or other devices that rely on IR remote controls. The design considerations for the Mark 5 may also include the use of filters to minimize ambient IR noise and optimize performance in diverse environments.The latest addition to my collection of Infra Red (IR) Repeater circuits. The Mark 5 is a much improved version of the Mark 1 circuit and has increased range. 🔗 External reference
The Mark 5 Infrared Repeater circuit is designed to extend the range of remote control signals, allowing devices to be operated from greater distances or through obstacles. This circuit typically consists of an IR receiver, a microcontroller or amplifier, and an IR transmitter.
The IR receiver detects signals from remote control devices and converts them into electrical signals. These signals are then processed by the microcontroller or amplifier, which boosts the signal strength. The amplified signal is subsequently transmitted by the IR transmitter, which emits infrared light that can be detected by the intended device.
Key components of the Mark 5 circuit may include a photodiode or phototransistor as the IR receiver, a low-noise operational amplifier to enhance the signal, and a high-efficiency IR LED for transmission. The circuit may also incorporate a power supply section, which could utilize a voltage regulator to ensure stable operation.
The enhancements in the Mark 5 over the Mark 1 may include improved sensitivity of the receiver, which allows it to capture weaker signals, and a more robust transmission capability, which increases the effective range. Additionally, adjustments to the circuit layout may reduce interference and improve overall reliability.
This circuit can be utilized in various applications, such as controlling home entertainment systems, HVAC units, or other devices that rely on IR remote controls. The design considerations for the Mark 5 may also include the use of filters to minimize ambient IR noise and optimize performance in diverse environments.The latest addition to my collection of Infra Red (IR) Repeater circuits. The Mark 5 is a much improved version of the Mark 1 circuit and has increased range. 🔗 External reference