KTM03 type speed control for three-phase half-controlled rectifier circuit
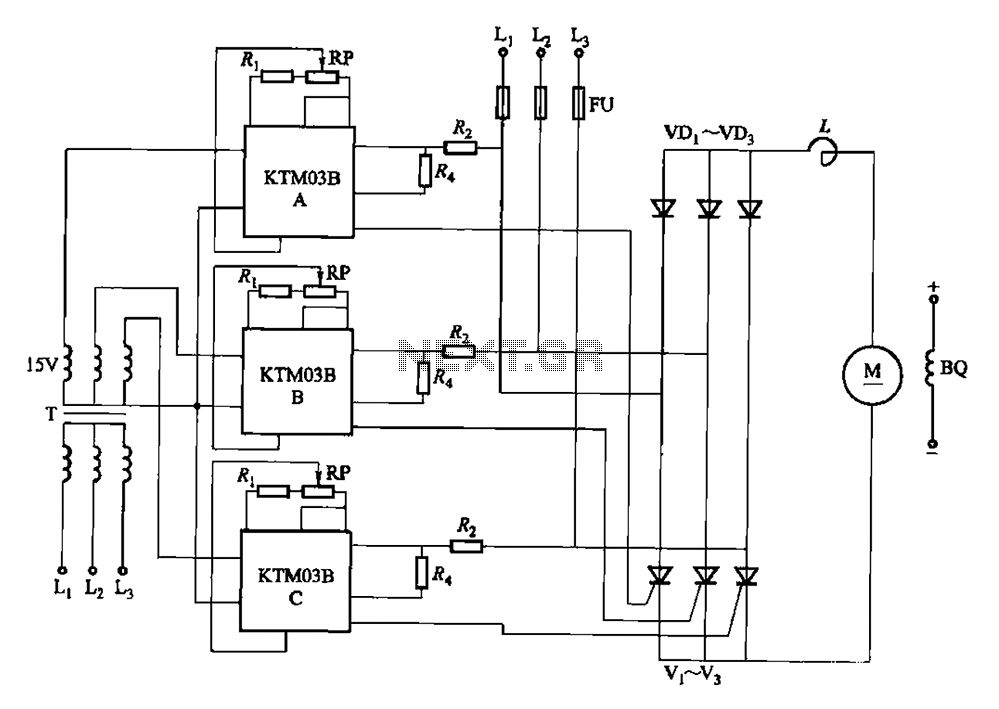
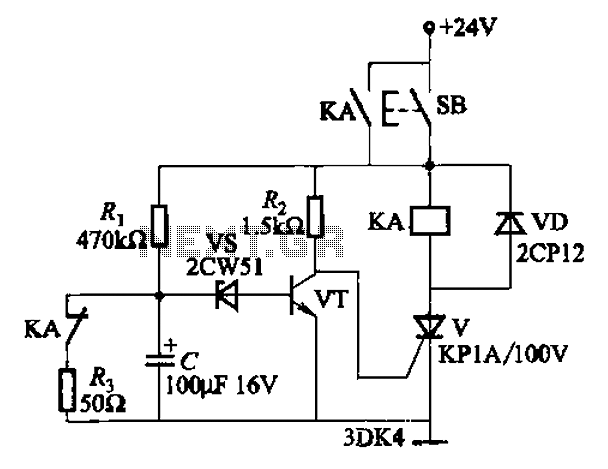
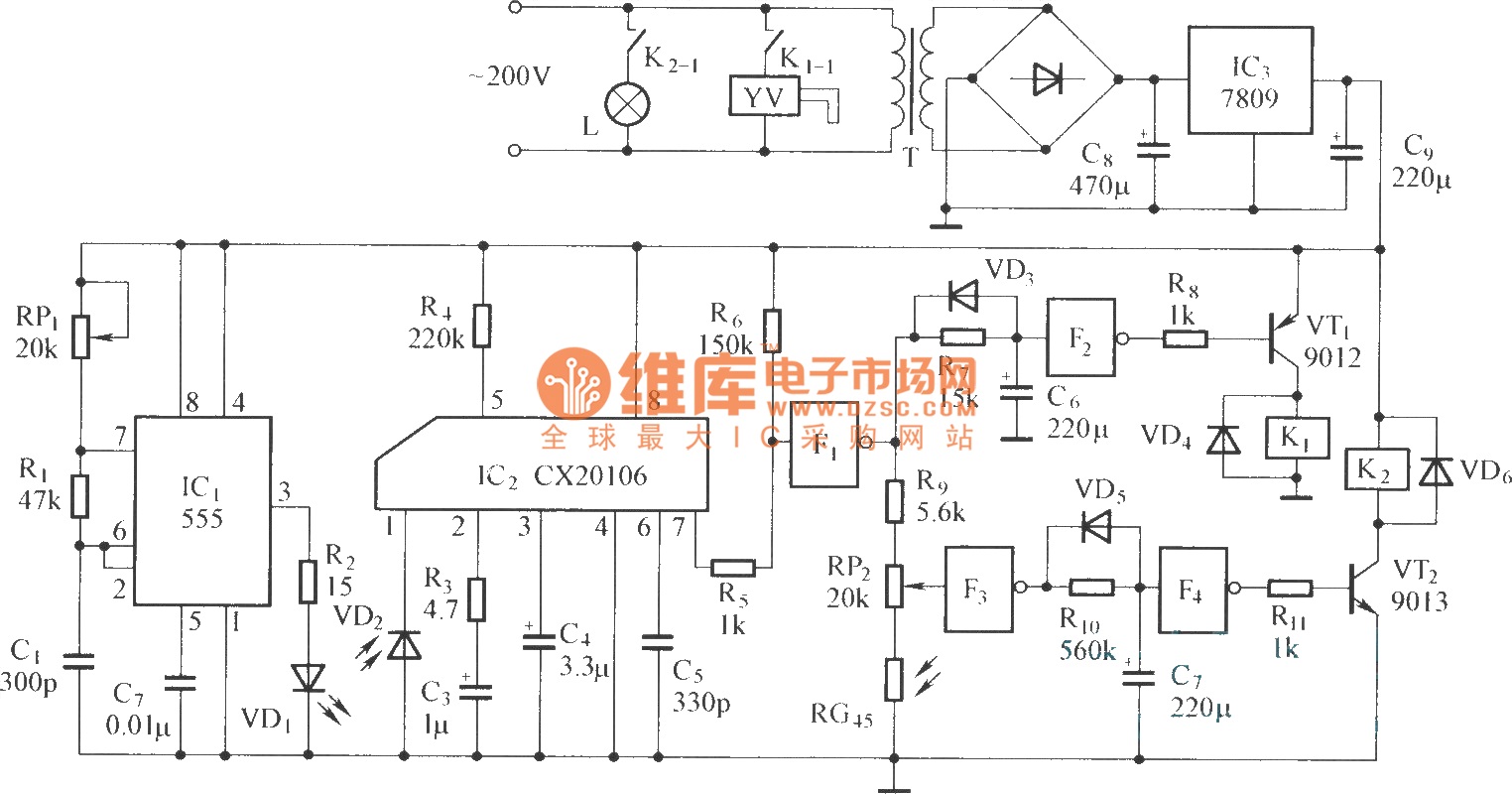
Adjusting the phase potentiometer RP can change the conduction angle of each corresponding thyristor (V1-V). This adjustment alters the voltage applied across the load.
The circuit utilizes a phase control technique to manage the power delivered to a load by varying the conduction angle of thyristors. Each thyristor (V1, V2, etc.) is connected in a configuration that allows for independent control via a potentiometer, specifically RP. By rotating the potentiometer, the phase angle at which each thyristor begins to conduct can be modified.
When the phase angle is adjusted, the point in the AC waveform at which the thyristor turns on is shifted. This results in a change in the effective voltage applied to the load. A smaller conduction angle allows the thyristor to conduct for a shorter duration within each AC cycle, reducing the average voltage and current delivered to the load. Conversely, a larger conduction angle increases the duration of conduction, thereby increasing the average voltage and current.
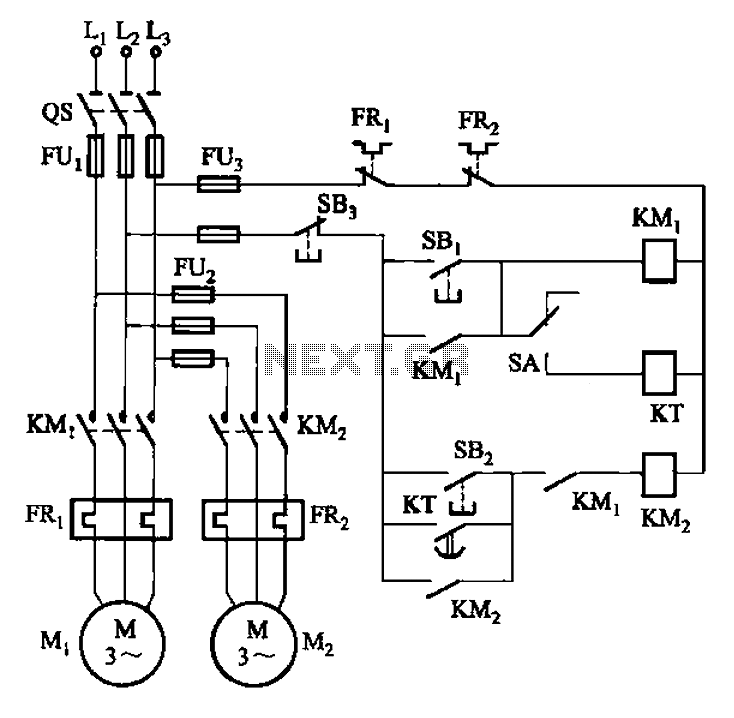
This method is commonly employed in applications such as light dimmers, motor speed controls, and temperature controllers where precise control of power is required. The design must ensure that the thyristors are capable of handling the load's voltage and current ratings, and appropriate heat sinking may be necessary to dissipate heat generated during operation. Additionally, snubber circuits may be included to protect the thyristors from voltage spikes and to improve the overall reliability of the circuit.
Overall, the ability to adjust the conduction angle through the phase potentiometer provides a versatile means of controlling power delivery in various electronic applications.Adjusting the phase potentiometer RP, can change each corresponding thyristor vl-V. Conduction angle, thereby changing the applied voltage across the load size.
The circuit utilizes a phase control technique to manage the power delivered to a load by varying the conduction angle of thyristors. Each thyristor (V1, V2, etc.) is connected in a configuration that allows for independent control via a potentiometer, specifically RP. By rotating the potentiometer, the phase angle at which each thyristor begins to conduct can be modified.
When the phase angle is adjusted, the point in the AC waveform at which the thyristor turns on is shifted. This results in a change in the effective voltage applied to the load. A smaller conduction angle allows the thyristor to conduct for a shorter duration within each AC cycle, reducing the average voltage and current delivered to the load. Conversely, a larger conduction angle increases the duration of conduction, thereby increasing the average voltage and current.
This method is commonly employed in applications such as light dimmers, motor speed controls, and temperature controllers where precise control of power is required. The design must ensure that the thyristors are capable of handling the load's voltage and current ratings, and appropriate heat sinking may be necessary to dissipate heat generated during operation. Additionally, snubber circuits may be included to protect the thyristors from voltage spikes and to improve the overall reliability of the circuit.
Overall, the ability to adjust the conduction angle through the phase potentiometer provides a versatile means of controlling power delivery in various electronic applications.Adjusting the phase potentiometer RP, can change each corresponding thyristor vl-V. Conduction angle, thereby changing the applied voltage across the load size.