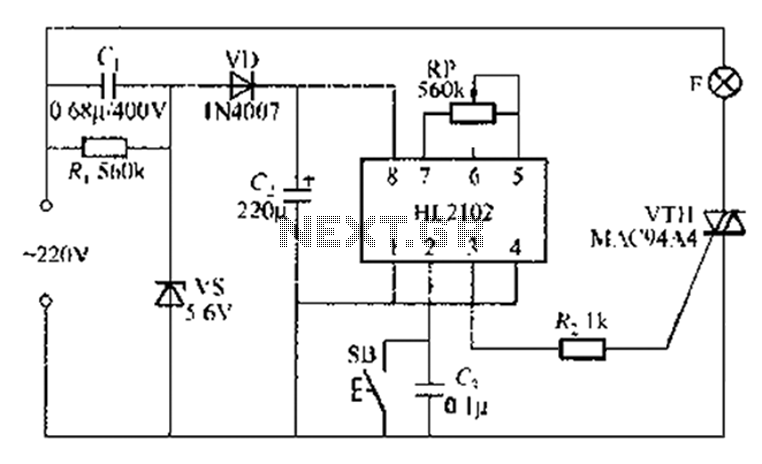
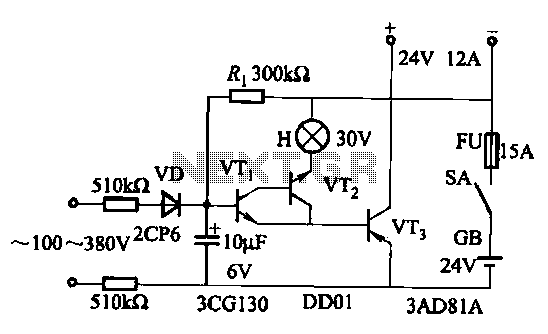
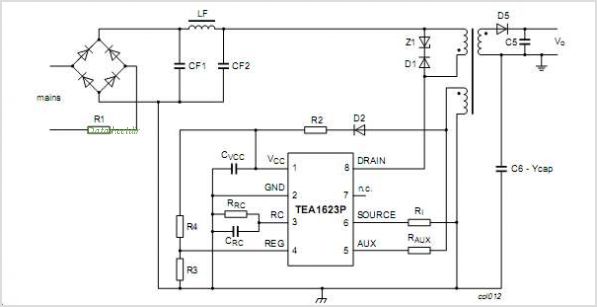
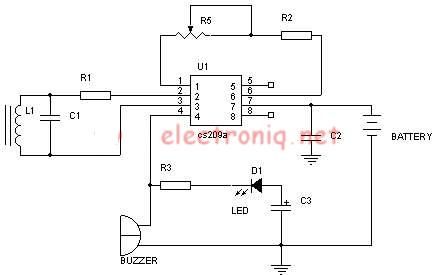
Li Ion Battery Charger Circuit Using IC LP2951
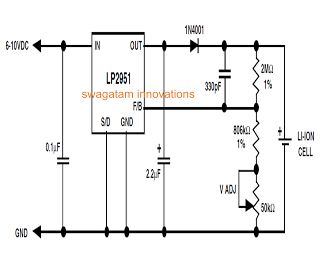
Unlike lead-acid batteries, one advantage of lithium-ion (Li-Ion) batteries is that they can be charged at a 1C rate initially. This means the charging current can be as high as the rated ampere-hour (AH) capacity of the battery at the beginning of the charging process. The design presented in this article can be utilized for charging a single 3.7V Li-Ion cell or a standard cell phone battery externally at a relatively slower rate. In this circuit, the integrated circuit (IC) LP2951 serves as the main active component, chosen for its capability to deliver a very stable output voltage over varying temperatures. Initially, when the discharged cell's voltage is below 4.2V, the IC provides a maximum current of approximately 160mA. Once the terminal voltage of the Li-Ion cell reaches 4.2V, the LP2951 quickly reduces the current to prevent the battery from exceeding this voltage level. The large value resistors included in the circuit ensure that the "OFF" current drain of the battery remains below 2mA, while a 330pF capacitor stabilizes the circuit against unwanted noise generated at the high-impedance feedback node.
The charging circuit for the Li-Ion battery is designed to ensure efficient and safe charging while maintaining the integrity of the battery. The LP2951 voltage regulator is a low-dropout (LDO) linear regulator that provides a regulated output voltage, making it suitable for charging applications where a stable voltage is critical. The ability to charge at a 1C rate allows for rapid charging, which is beneficial in applications where downtime must be minimized.
In the circuit, the inclusion of large value resistors serves a dual purpose. They limit the current when the battery is in the "OFF" state, thereby reducing the self-discharge rate of the battery. This feature is particularly important for maintaining battery health over extended periods of inactivity. The 330pF capacitor plays a crucial role in filtering out high-frequency noise that could interfere with the voltage regulation process. This noise can originate from various sources, including switching power supplies and other electronic components in proximity to the charging circuit.
The charging process begins with the detection of the battery's voltage level. If the voltage is below the threshold of 4.2V, the LP2951 allows maximum current to flow into the battery. As the battery charges and its voltage approaches 4.2V, the LP2951 automatically reduces the current to a safe level. This automatic regulation is vital to prevent overcharging, which can lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan.
Overall, this charging circuit design effectively balances the need for rapid charging with safety and battery longevity. The choice of components and their configuration ensures that the circuit operates within safe parameters while providing reliable performance.Unlike lead acid batteries one good thing about the Li-Ion batteries is that they can be charged at 1C rate initially. It means the charging current may be as high as the rated AH of the battery at the onset. The design presented in this article can be used for charging a single 3. 7V Li-ion cell or a standard cell phone battery externally at a rel atively slower rate. In the given circuit the IC LP2951 becomes the main active component which has been specifically chosen because it is capable of delivering an output voltage thats very stable over temperature. Initially when the particular discharged cell has a voltage level thats below the 4. 2V, the IC generates maximum current to the cell which is around 160mA as discussed above. Once the terminal voltage of the Li-Ion cell reaches the 4. 2V mark, the IC LP2951 instantly inhibits the current so that the battery can longer exceed the 4. 2 V level. The big value resistors included in the circuit ensures the "OFF" current drain of the battery to below 2mA, the 330pF capacitor stabilizes the circuit from unwanted noises created at thehigh-impedance feedback node.
🔗 External reference
The charging circuit for the Li-Ion battery is designed to ensure efficient and safe charging while maintaining the integrity of the battery. The LP2951 voltage regulator is a low-dropout (LDO) linear regulator that provides a regulated output voltage, making it suitable for charging applications where a stable voltage is critical. The ability to charge at a 1C rate allows for rapid charging, which is beneficial in applications where downtime must be minimized.
In the circuit, the inclusion of large value resistors serves a dual purpose. They limit the current when the battery is in the "OFF" state, thereby reducing the self-discharge rate of the battery. This feature is particularly important for maintaining battery health over extended periods of inactivity. The 330pF capacitor plays a crucial role in filtering out high-frequency noise that could interfere with the voltage regulation process. This noise can originate from various sources, including switching power supplies and other electronic components in proximity to the charging circuit.
The charging process begins with the detection of the battery's voltage level. If the voltage is below the threshold of 4.2V, the LP2951 allows maximum current to flow into the battery. As the battery charges and its voltage approaches 4.2V, the LP2951 automatically reduces the current to a safe level. This automatic regulation is vital to prevent overcharging, which can lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan.
Overall, this charging circuit design effectively balances the need for rapid charging with safety and battery longevity. The choice of components and their configuration ensures that the circuit operates within safe parameters while providing reliable performance.Unlike lead acid batteries one good thing about the Li-Ion batteries is that they can be charged at 1C rate initially. It means the charging current may be as high as the rated AH of the battery at the onset. The design presented in this article can be used for charging a single 3. 7V Li-ion cell or a standard cell phone battery externally at a rel atively slower rate. In the given circuit the IC LP2951 becomes the main active component which has been specifically chosen because it is capable of delivering an output voltage thats very stable over temperature. Initially when the particular discharged cell has a voltage level thats below the 4. 2V, the IC generates maximum current to the cell which is around 160mA as discussed above. Once the terminal voltage of the Li-Ion cell reaches the 4. 2V mark, the IC LP2951 instantly inhibits the current so that the battery can longer exceed the 4. 2 V level. The big value resistors included in the circuit ensures the "OFF" current drain of the battery to below 2mA, the 330pF capacitor stabilizes the circuit from unwanted noises created at thehigh-impedance feedback node.
🔗 External reference