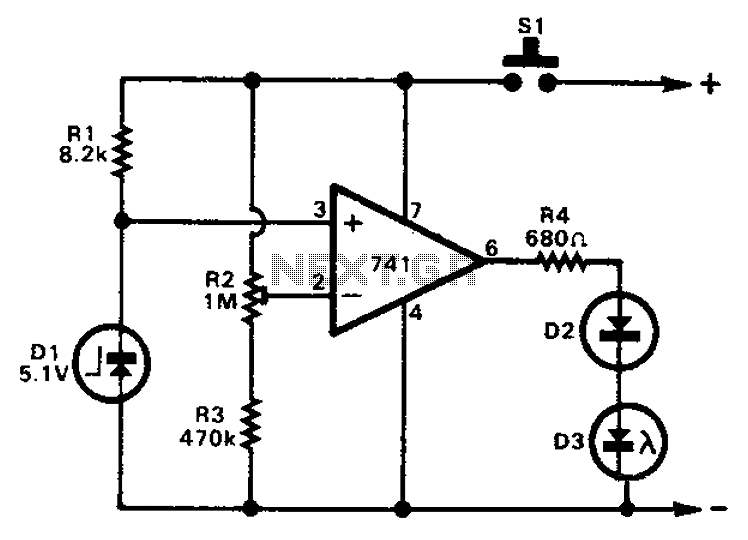
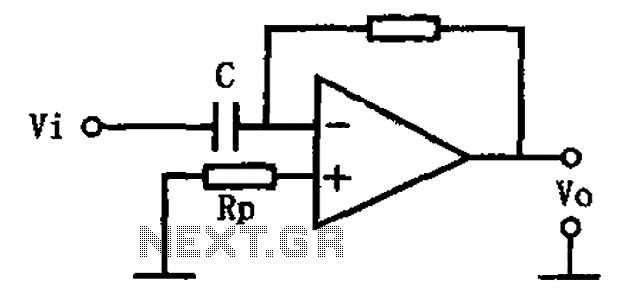
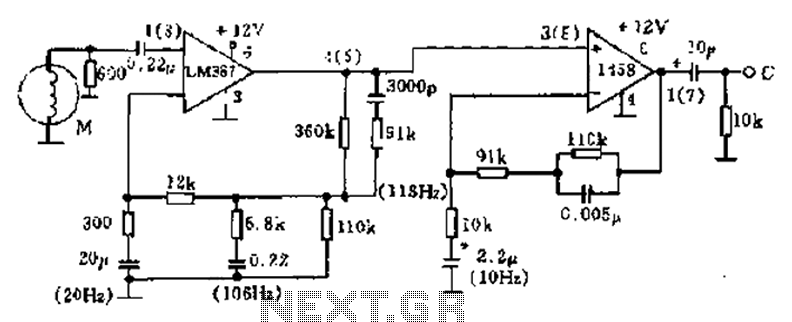
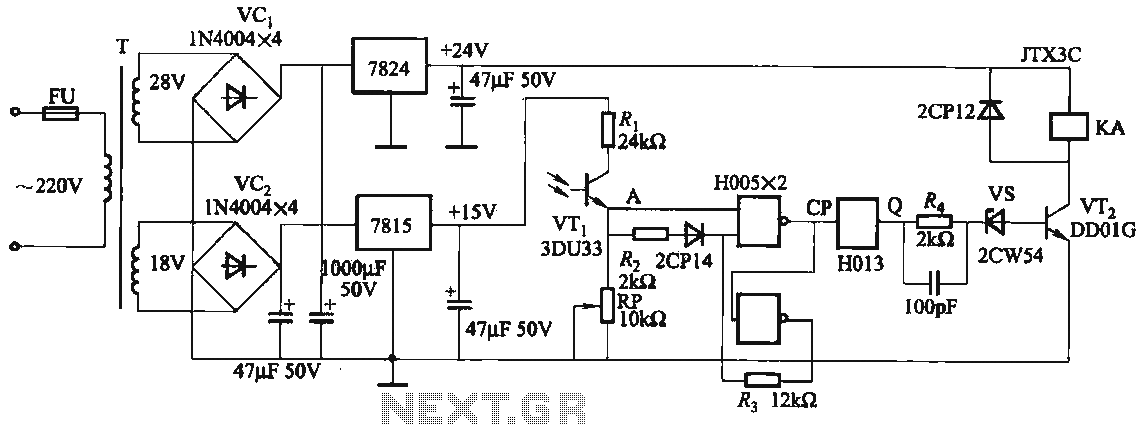
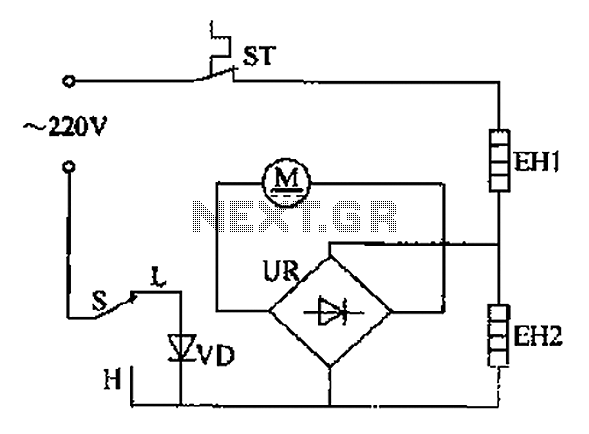
Light sensor switch circuit
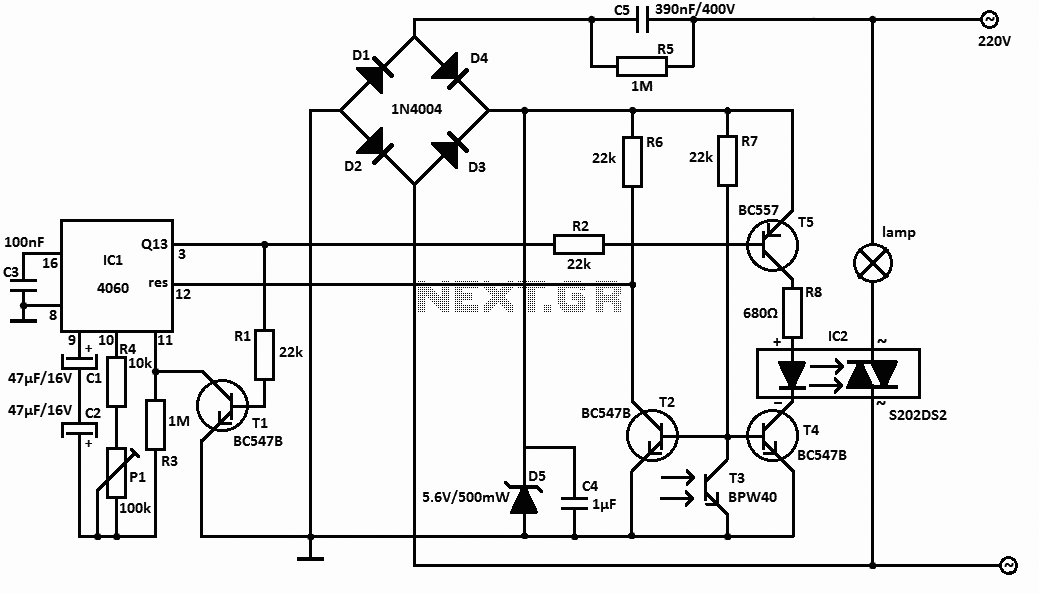
This light sensor switch circuit enables the automatic activation of a lamp when ambient light levels decrease, such as during nightfall. The duration for which the lamp remains on can be adjusted using potentiometer P1, with a range of 1 to 5 hours.
The light sensor switch circuit typically employs a light-dependent resistor (LDR) to detect ambient light levels. When the light intensity falls below a predetermined threshold, the LDR's resistance increases, triggering a transistor or relay to close the circuit and turn on the lamp.
The circuit consists of several key components: the LDR, a potentiometer (P1) for time adjustment, a timing capacitor, and a resistor to set the timing interval. The timing capacitor, in conjunction with the resistor, determines how long the lamp stays illuminated after the LDR detects low light levels.
When designing the circuit, it is essential to select an appropriate transistor or relay that can handle the lamp's load. The output stage is typically connected to the lamp via a relay to ensure safe operation, especially if the lamp operates at mains voltage.
To enhance the functionality of the circuit, a diode can be included across the relay coil to protect against back EMF when the relay is switched off. Additionally, an LED indicator may be added to show when the circuit is active, providing a visual confirmation of operation.
Overall, this light sensor switch circuit is a practical solution for automating lighting in response to changing ambient light conditions, making it suitable for outdoor lighting, garden lights, or any application where automatic light control is desired.This light sensor switch circuit allows the automatic connection of a lamp when the light is low (at nightfall) and will maintain the lamp ON for a certain period of time. This time can be adjusted with P1 between 1 and 5 hours. The switch.. 🔗 External reference
The light sensor switch circuit typically employs a light-dependent resistor (LDR) to detect ambient light levels. When the light intensity falls below a predetermined threshold, the LDR's resistance increases, triggering a transistor or relay to close the circuit and turn on the lamp.
The circuit consists of several key components: the LDR, a potentiometer (P1) for time adjustment, a timing capacitor, and a resistor to set the timing interval. The timing capacitor, in conjunction with the resistor, determines how long the lamp stays illuminated after the LDR detects low light levels.
When designing the circuit, it is essential to select an appropriate transistor or relay that can handle the lamp's load. The output stage is typically connected to the lamp via a relay to ensure safe operation, especially if the lamp operates at mains voltage.
To enhance the functionality of the circuit, a diode can be included across the relay coil to protect against back EMF when the relay is switched off. Additionally, an LED indicator may be added to show when the circuit is active, providing a visual confirmation of operation.
Overall, this light sensor switch circuit is a practical solution for automating lighting in response to changing ambient light conditions, making it suitable for outdoor lighting, garden lights, or any application where automatic light control is desired.This light sensor switch circuit allows the automatic connection of a lamp when the light is low (at nightfall) and will maintain the lamp ON for a certain period of time. This time can be adjusted with P1 between 1 and 5 hours. The switch.. 🔗 External reference