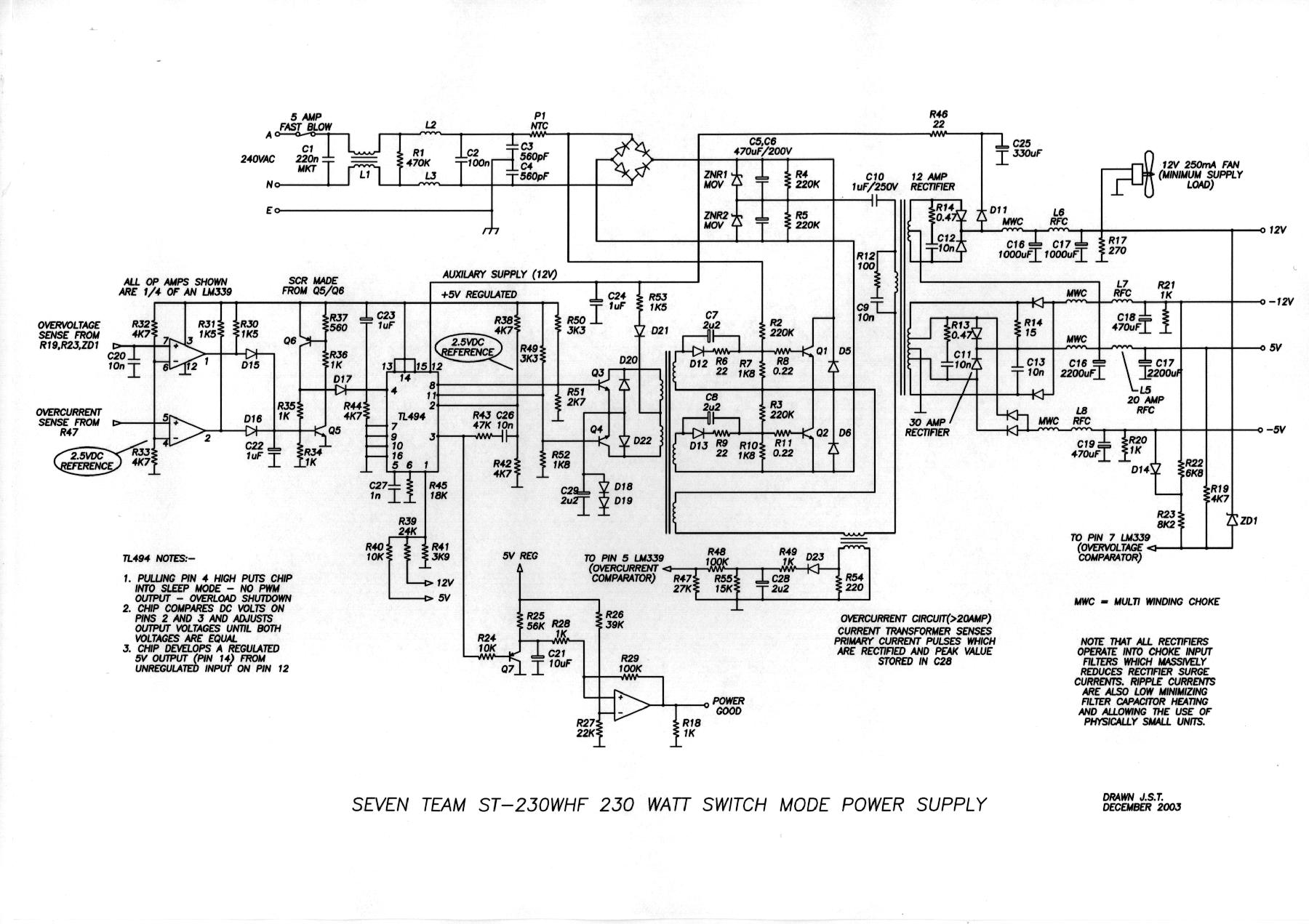
LM12 Simple Power Amplifier
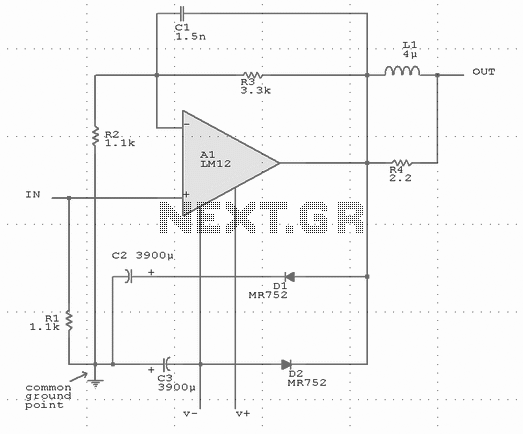
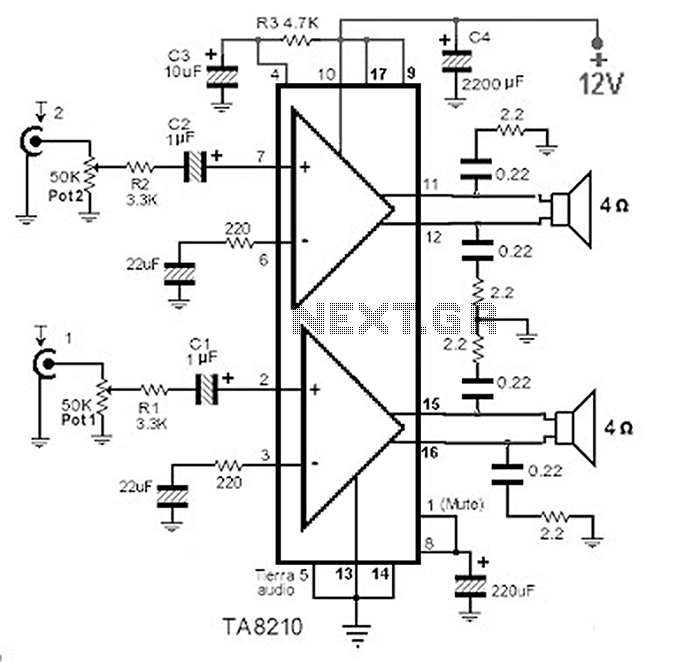
Output-clamp diodes are mandatory because loudspeakers are inductive loads. Output LR isolation is also used because audio amplifiers are usually expected to handle up to 2 mF load capacitance. Large, supply-bypass capacitors located close to the IC are used so that the rectified load current in the supply leads does not get back into the amplifier, increasing high-frequency distortion. More: Single-point grounding for all internal leads plus the signal source and load is recommended to avoid ground loops that can increase distortion.
Output-clamp diodes are essential in audio amplifier circuits to protect against voltage spikes generated by inductive loads such as loudspeakers. When the loudspeaker is turned off or when there is a sudden change in the audio signal, the inductive nature of the loudspeaker can generate back EMF (electromotive force), which can potentially damage the amplifier. The output-clamp diodes are placed in parallel with the load to shunt these voltage spikes safely to ground, thereby protecting the amplifier from excessive voltage.
In addition to the output-clamp diodes, output LR (inductor-resistor) isolation is employed to manage load capacitance, which can be as high as 2 mF in audio applications. This isolation is crucial for maintaining audio fidelity and preventing unwanted interactions between the amplifier and the loudspeaker, which can lead to distortion and degradation of sound quality.
Supply-bypass capacitors play a significant role in stabilizing the power supply to the amplifier. These capacitors are typically large and are placed as close to the integrated circuit (IC) as possible. Their primary function is to filter out high-frequency noise from the power supply and to provide a reservoir of charge that can quickly respond to changes in load current. This arrangement prevents the rectified load current from flowing back into the amplifier's supply leads, which can introduce high-frequency distortion and adversely affect audio performance.
Furthermore, implementing a single-point grounding scheme is recommended for all internal leads, as well as for the signal source and load. This approach minimizes the risk of ground loops, which can introduce unwanted noise and distortion into the audio signal. By ensuring that all grounds converge at a single point, the potential for ground loop interference is significantly reduced, thus enhancing the overall audio quality of the amplifier circuit.Output-clamp diodes are mandatory because loudspeakers are inductive loads. Output LR isolation is also used because audio amplifiers are usually expected to handle up to 2 mF load capacitance. Large, supply-bypass capacitors located close to the IC are used so that the rectified load current in the supply leads does not get back into the amplifier, increasing high-frequency distortion.
Single-point grounding for all internal leads plus the signal source and load is recommended to avoid ground loops that can increase distortion. 🔗 External reference
Output-clamp diodes are essential in audio amplifier circuits to protect against voltage spikes generated by inductive loads such as loudspeakers. When the loudspeaker is turned off or when there is a sudden change in the audio signal, the inductive nature of the loudspeaker can generate back EMF (electromotive force), which can potentially damage the amplifier. The output-clamp diodes are placed in parallel with the load to shunt these voltage spikes safely to ground, thereby protecting the amplifier from excessive voltage.
In addition to the output-clamp diodes, output LR (inductor-resistor) isolation is employed to manage load capacitance, which can be as high as 2 mF in audio applications. This isolation is crucial for maintaining audio fidelity and preventing unwanted interactions between the amplifier and the loudspeaker, which can lead to distortion and degradation of sound quality.
Supply-bypass capacitors play a significant role in stabilizing the power supply to the amplifier. These capacitors are typically large and are placed as close to the integrated circuit (IC) as possible. Their primary function is to filter out high-frequency noise from the power supply and to provide a reservoir of charge that can quickly respond to changes in load current. This arrangement prevents the rectified load current from flowing back into the amplifier's supply leads, which can introduce high-frequency distortion and adversely affect audio performance.
Furthermore, implementing a single-point grounding scheme is recommended for all internal leads, as well as for the signal source and load. This approach minimizes the risk of ground loops, which can introduce unwanted noise and distortion into the audio signal. By ensuring that all grounds converge at a single point, the potential for ground loop interference is significantly reduced, thus enhancing the overall audio quality of the amplifier circuit.Output-clamp diodes are mandatory because loudspeakers are inductive loads. Output LR isolation is also used because audio amplifiers are usually expected to handle up to 2 mF load capacitance. Large, supply-bypass capacitors located close to the IC are used so that the rectified load current in the supply leads does not get back into the amplifier, increasing high-frequency distortion.
Single-point grounding for all internal leads plus the signal source and load is recommended to avoid ground loops that can increase distortion. 🔗 External reference