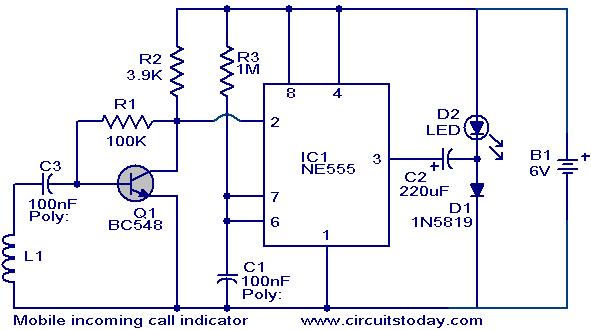
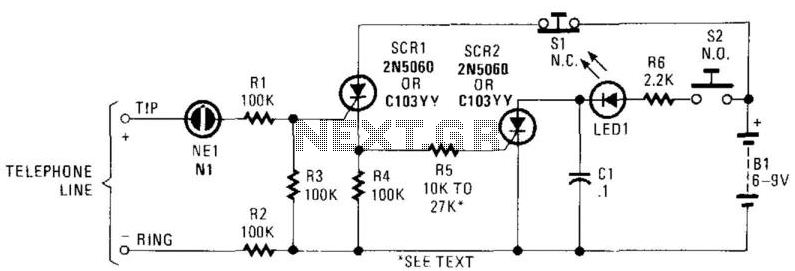
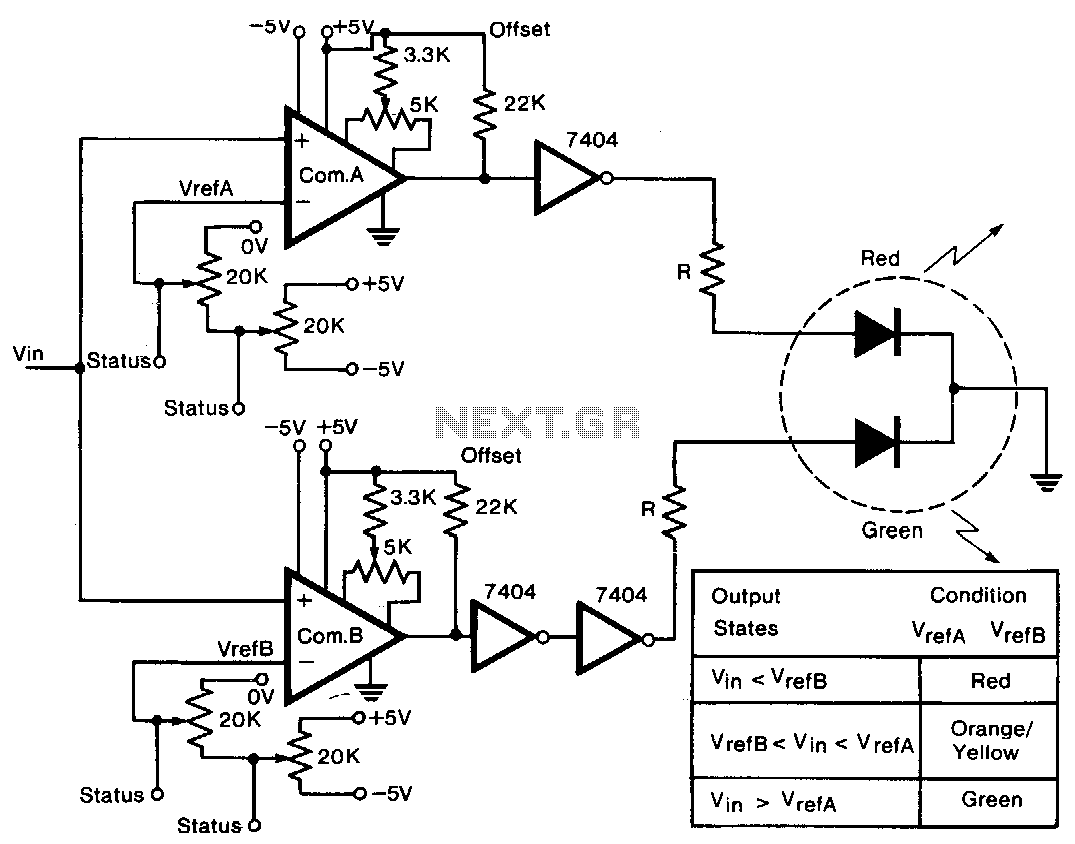
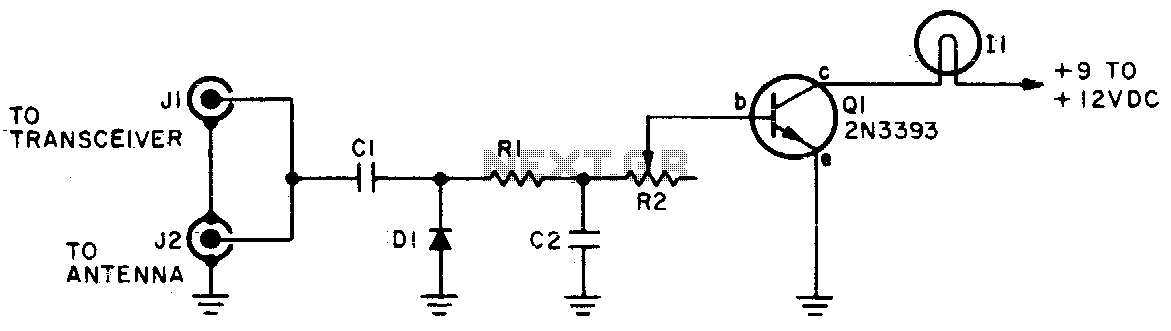
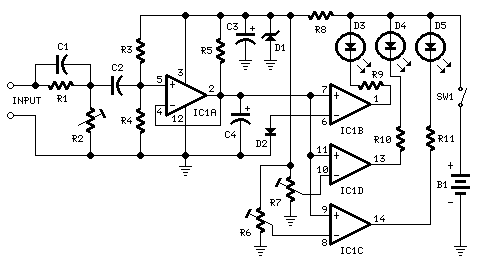
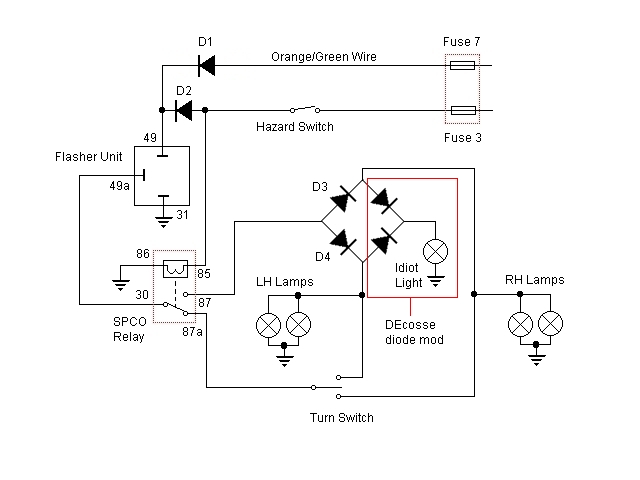
Low-Battery Indicator
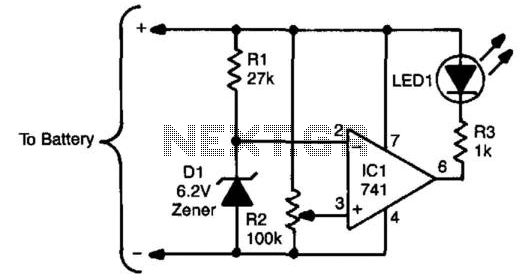
The sensing circuit consists of a 741 op-amp configured as a voltage comparator, utilizing a zener diode as a voltage reference. The op-amp is positioned as a bridge between two resistor ladders; one includes the zener reference, while the other features a high-value linear potentiometer. When the voltage at the wiper of the potentiometer falls below the voltage established by the zener, the output of the op-amp transitions to a low state, activating the LED connected between the op-amp output and Vcc. This circuit can be adapted for battery-powered applications requiring voltages between 6 and 18 V. Adjustments include using a lower-voltage zener diode and a smaller current-limiting resistor for voltages below 9 V, while a larger resistor is necessary for higher voltages.
The described sensing circuit employs a 741 operational amplifier configured as a voltage comparator to monitor voltage levels. The circuit utilizes a zener diode to provide a stable reference voltage, ensuring accurate comparisons against the variable voltage from a high-value linear potentiometer. The potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the input voltage, with the wiper providing a variable voltage that can be adjusted according to the application's requirements.
In operation, the circuit monitors the voltage at the potentiometer's wiper. When this voltage drops below the reference voltage set by the zener diode, the output of the op-amp switches to a low state. This output state is used to drive an LED, which indicates when the monitored voltage has fallen below the desired threshold. The LED is connected between the op-amp output and the positive supply voltage (Vcc), providing a visual indication of the circuit's status.
The design is versatile and can be adapted for various battery-powered applications. The voltage range of 6 to 18 V allows for flexibility in different systems, and the necessary modifications are straightforward. For applications operating below 9 V, a zener diode with a lower breakdown voltage should be selected, along with a corresponding current-limiting resistor to ensure proper LED operation without exceeding the current rating. Conversely, for higher voltage applications, a larger resistor must be chosen to limit the current appropriately, ensuring the longevity of the LED and the integrity of the circuit.
This sensing circuit is suitable for a wide range of applications, including battery monitoring, power supply regulation, and various safety systems that require voltage level monitoring and indication. Its simplicity and adaptability make it a valuable component in electronic design. The sensing circuit consists of a 741 op amp set up as a voltage comparator, using a zener diode as a voltage referen ce. The op amp is inserted as a bridge between two resistance ladders, one which contains the zener reference, and the other a high-value linear potentiometer. When the voltage at the wiper of the potentiometer drops below the voltage set by the zener, the output of the op amp becomes low; that turns on the LED connected between it and Vcc- The circuit can be adapted to work with battery-powered circuits that require between 6 and 18 V; the only changes needed would be a lower-voltage zener and a smaller current-limiting resistor in the case of voltage below 9 V, and a larger resistor for higher voltages.
The described sensing circuit employs a 741 operational amplifier configured as a voltage comparator to monitor voltage levels. The circuit utilizes a zener diode to provide a stable reference voltage, ensuring accurate comparisons against the variable voltage from a high-value linear potentiometer. The potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the input voltage, with the wiper providing a variable voltage that can be adjusted according to the application's requirements.
In operation, the circuit monitors the voltage at the potentiometer's wiper. When this voltage drops below the reference voltage set by the zener diode, the output of the op-amp switches to a low state. This output state is used to drive an LED, which indicates when the monitored voltage has fallen below the desired threshold. The LED is connected between the op-amp output and the positive supply voltage (Vcc), providing a visual indication of the circuit's status.
The design is versatile and can be adapted for various battery-powered applications. The voltage range of 6 to 18 V allows for flexibility in different systems, and the necessary modifications are straightforward. For applications operating below 9 V, a zener diode with a lower breakdown voltage should be selected, along with a corresponding current-limiting resistor to ensure proper LED operation without exceeding the current rating. Conversely, for higher voltage applications, a larger resistor must be chosen to limit the current appropriately, ensuring the longevity of the LED and the integrity of the circuit.
This sensing circuit is suitable for a wide range of applications, including battery monitoring, power supply regulation, and various safety systems that require voltage level monitoring and indication. Its simplicity and adaptability make it a valuable component in electronic design. The sensing circuit consists of a 741 op amp set up as a voltage comparator, using a zener diode as a voltage referen ce. The op amp is inserted as a bridge between two resistance ladders, one which contains the zener reference, and the other a high-value linear potentiometer. When the voltage at the wiper of the potentiometer drops below the voltage set by the zener, the output of the op amp becomes low; that turns on the LED connected between it and Vcc- The circuit can be adapted to work with battery-powered circuits that require between 6 and 18 V; the only changes needed would be a lower-voltage zener and a smaller current-limiting resistor in the case of voltage below 9 V, and a larger resistor for higher voltages.