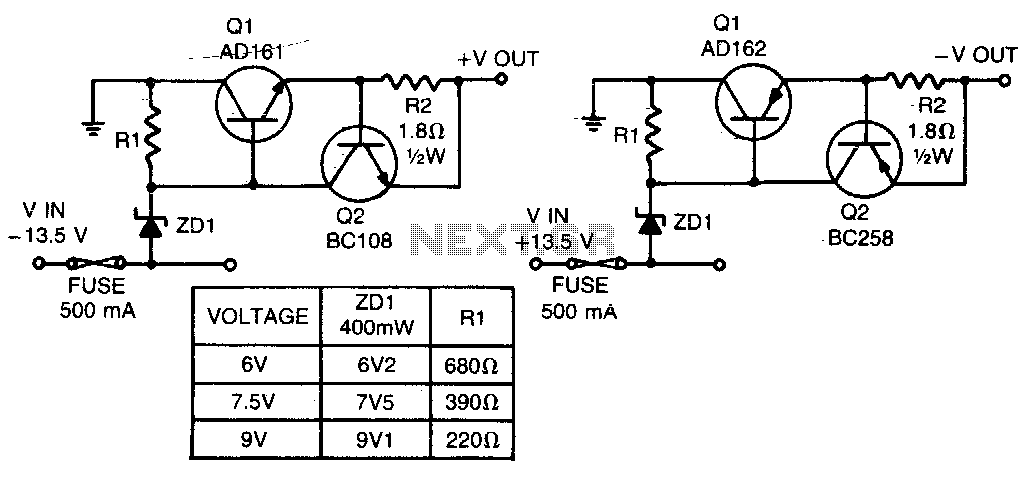
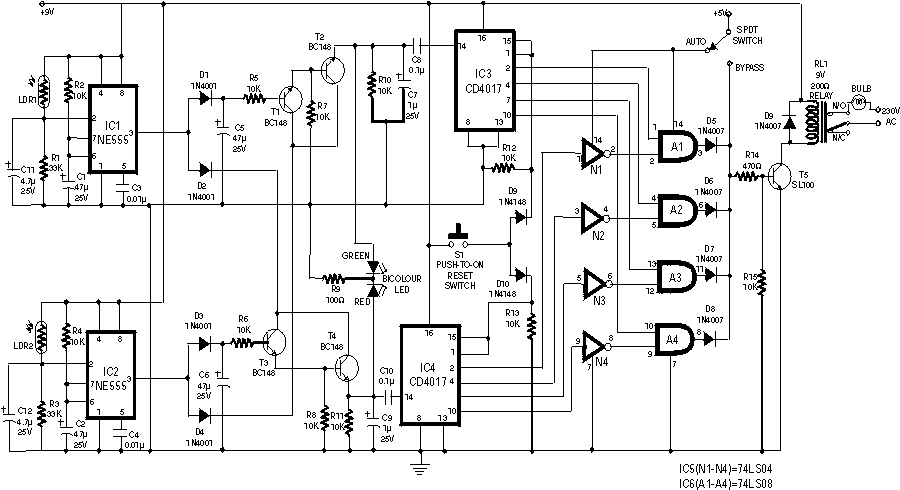
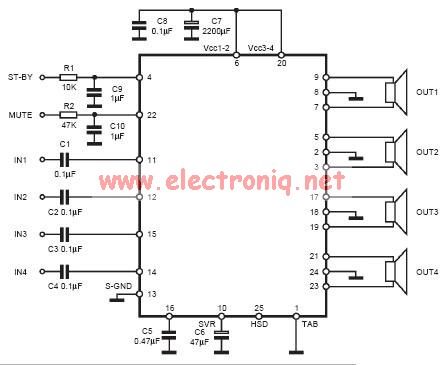
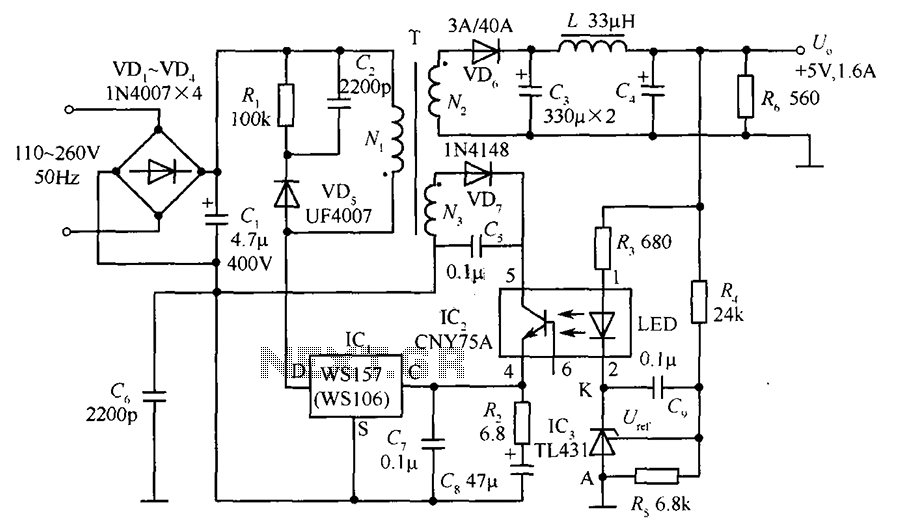
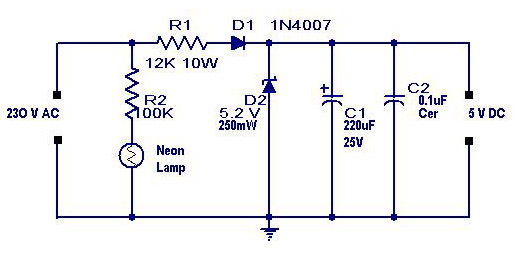
Low Capacitance High Impedance Amplifier Circuit
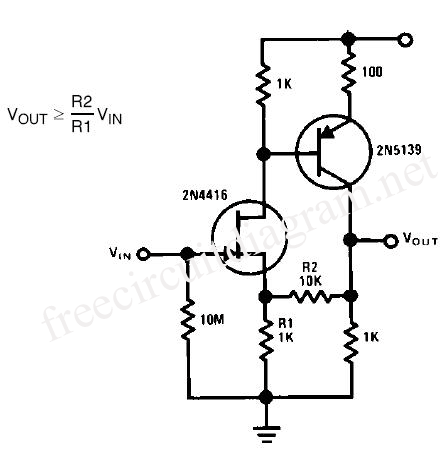
This series-feedback configuration of compounds provides a high input impedance and stable, wide-band gain video amplifier suitable for general-purpose applications. It features low capacitance and high impedance.
The described video amplifier circuit utilizes a series-feedback topology to achieve high input impedance, which is essential for minimizing the loading effect on the preceding stage. This characteristic ensures that the amplifier can interface effectively with a variety of signal sources without degrading the signal integrity. The stability of the amplifier is crucial, particularly in wide-band applications where fluctuations in gain can lead to distortion or signal loss.
The circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) or transistor-based configurations, where feedback is applied to enhance linearity and bandwidth. The low capacitance design is particularly advantageous in high-frequency applications, as it reduces the risk of signal attenuation and phase shifts that can occur due to capacitive loading.
In practical implementations, careful selection of components is necessary to maintain the desired performance. Resistors and capacitors must be chosen to ensure that the amplifier can operate effectively across the intended frequency range while maintaining low noise levels. The layout of the circuit is also critical; minimizing trace lengths and using proper grounding techniques can significantly enhance performance by reducing parasitic capacitance and inductance.
Applications for this type of amplifier include video signal processing, instrumentation, and any scenario where high-speed signal transmission is required. The versatility and reliability of this amplifier make it an essential component in modern electronic systems.This series-feedback series of compounds give a high input impedance and stable, gain wide-band video amplifier for general purpose applications. Low Capacitance, High Impedance, Amplifier Circuit,. 🔗 External reference
The described video amplifier circuit utilizes a series-feedback topology to achieve high input impedance, which is essential for minimizing the loading effect on the preceding stage. This characteristic ensures that the amplifier can interface effectively with a variety of signal sources without degrading the signal integrity. The stability of the amplifier is crucial, particularly in wide-band applications where fluctuations in gain can lead to distortion or signal loss.
The circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) or transistor-based configurations, where feedback is applied to enhance linearity and bandwidth. The low capacitance design is particularly advantageous in high-frequency applications, as it reduces the risk of signal attenuation and phase shifts that can occur due to capacitive loading.
In practical implementations, careful selection of components is necessary to maintain the desired performance. Resistors and capacitors must be chosen to ensure that the amplifier can operate effectively across the intended frequency range while maintaining low noise levels. The layout of the circuit is also critical; minimizing trace lengths and using proper grounding techniques can significantly enhance performance by reducing parasitic capacitance and inductance.
Applications for this type of amplifier include video signal processing, instrumentation, and any scenario where high-speed signal transmission is required. The versatility and reliability of this amplifier make it an essential component in modern electronic systems.This series-feedback series of compounds give a high input impedance and stable, gain wide-band video amplifier for general purpose applications. Low Capacitance, High Impedance, Amplifier Circuit,. 🔗 External reference