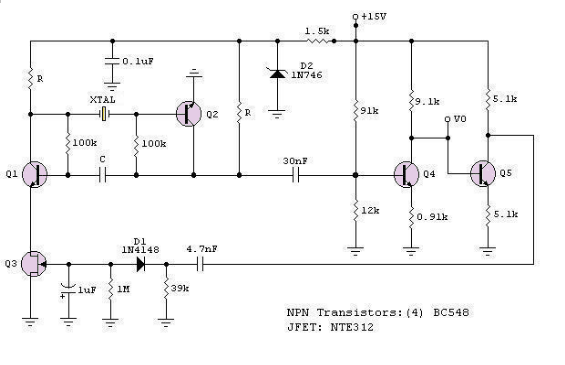
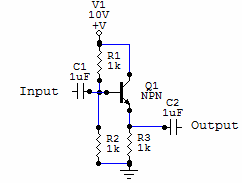
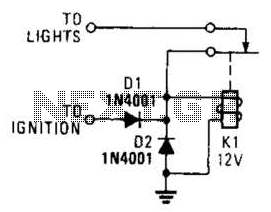
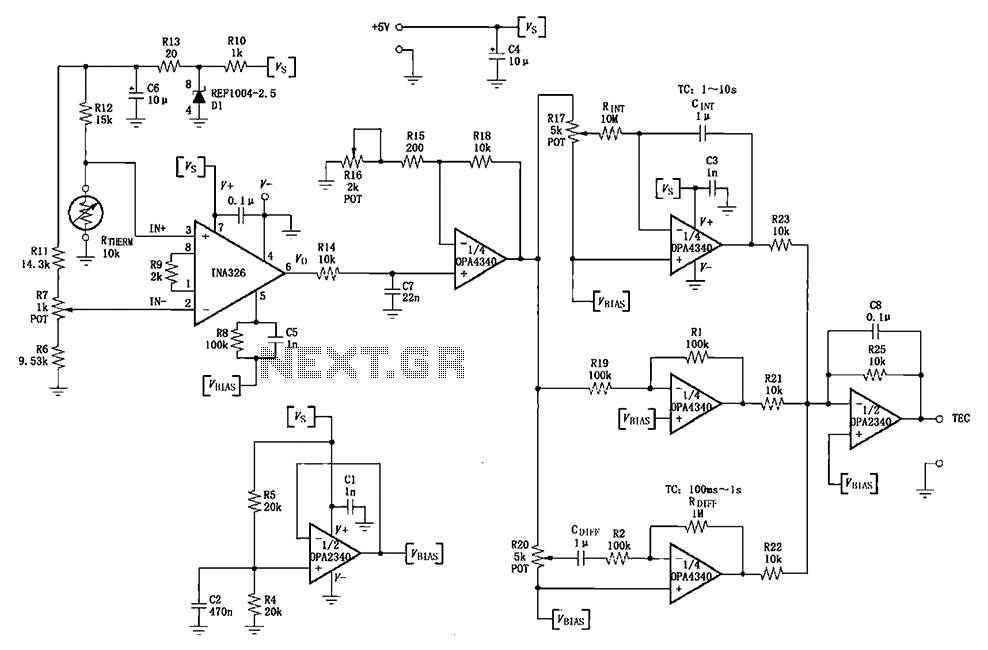
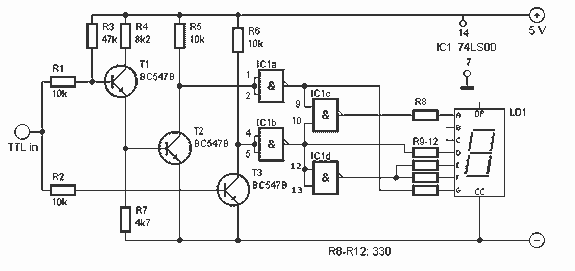
Low Cost Precision Light Control / Dimmer
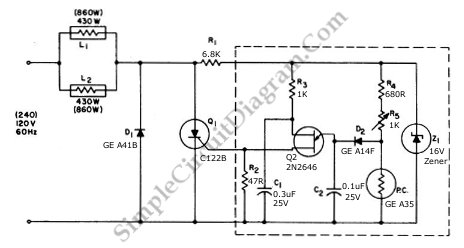
This circuit utilizes a controlled half-plus-fixed half-wave phase control method to regulate an 860-watt lamp load, allowing operation from half to full power.
The circuit employs a phase control technique, which involves adjusting the phase angle of the AC voltage applied to the load. This method is particularly effective for varying the power delivered to resistive loads, such as incandescent lamps. The controlled half-plus-fixed half-wave approach combines elements of both half-wave and full-wave control, providing a smoother transition between power levels and reducing flicker in the lamp output.
The schematic typically includes a triac or a thyristor as the primary switching device, which is triggered at a specific phase angle determined by a control circuit. A zero-crossing detector may be integrated to ensure that the triac is triggered at the optimal point in the AC cycle, minimizing electromagnetic interference and improving efficiency.
Additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and possibly an opto-isolator may be included in the control circuit to provide isolation and to shape the control signal. The use of feedback mechanisms can enhance stability and accuracy in power regulation, ensuring that the lamp load operates effectively across the desired range.
Overall, this circuit design is suitable for applications requiring precise control of incandescent lighting, allowing for energy savings and improved user comfort through adjustable brightness levels.Using a the controlled-half-plus-fixed-half-wave phase control method, this circuit can regulate an 860 a watt lamp load from half to full power. This circuit.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs a phase control technique, which involves adjusting the phase angle of the AC voltage applied to the load. This method is particularly effective for varying the power delivered to resistive loads, such as incandescent lamps. The controlled half-plus-fixed half-wave approach combines elements of both half-wave and full-wave control, providing a smoother transition between power levels and reducing flicker in the lamp output.
The schematic typically includes a triac or a thyristor as the primary switching device, which is triggered at a specific phase angle determined by a control circuit. A zero-crossing detector may be integrated to ensure that the triac is triggered at the optimal point in the AC cycle, minimizing electromagnetic interference and improving efficiency.
Additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and possibly an opto-isolator may be included in the control circuit to provide isolation and to shape the control signal. The use of feedback mechanisms can enhance stability and accuracy in power regulation, ensuring that the lamp load operates effectively across the desired range.
Overall, this circuit design is suitable for applications requiring precise control of incandescent lighting, allowing for energy savings and improved user comfort through adjustable brightness levels.Using a the controlled-half-plus-fixed-half-wave phase control method, this circuit can regulate an 860 a watt lamp load from half to full power. This circuit.. 🔗 External reference