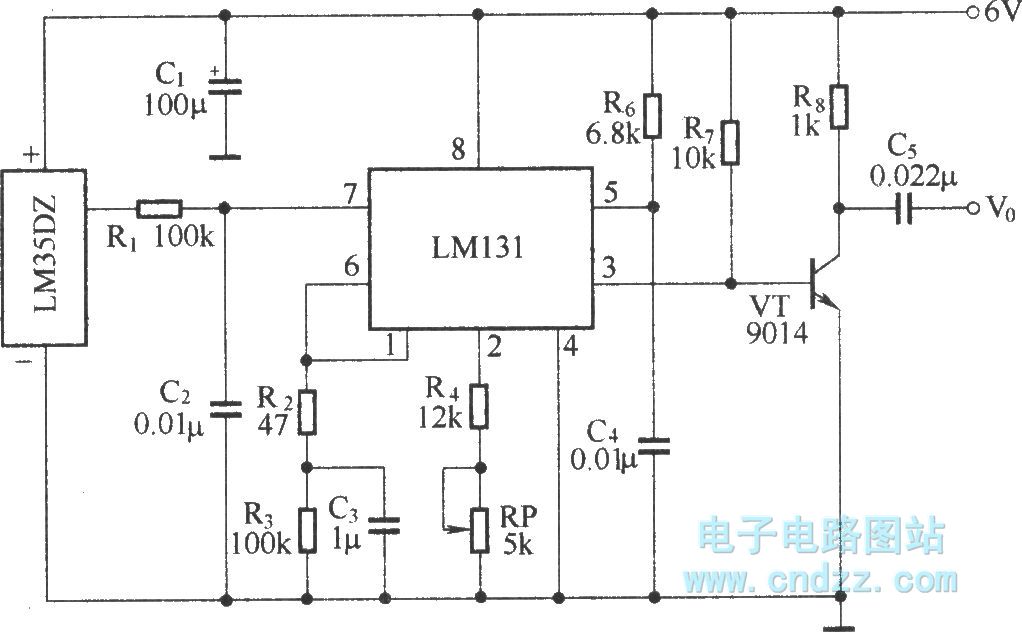
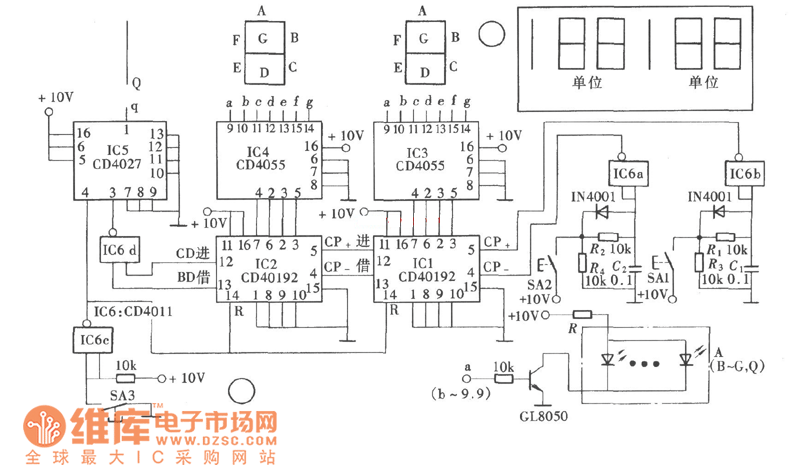
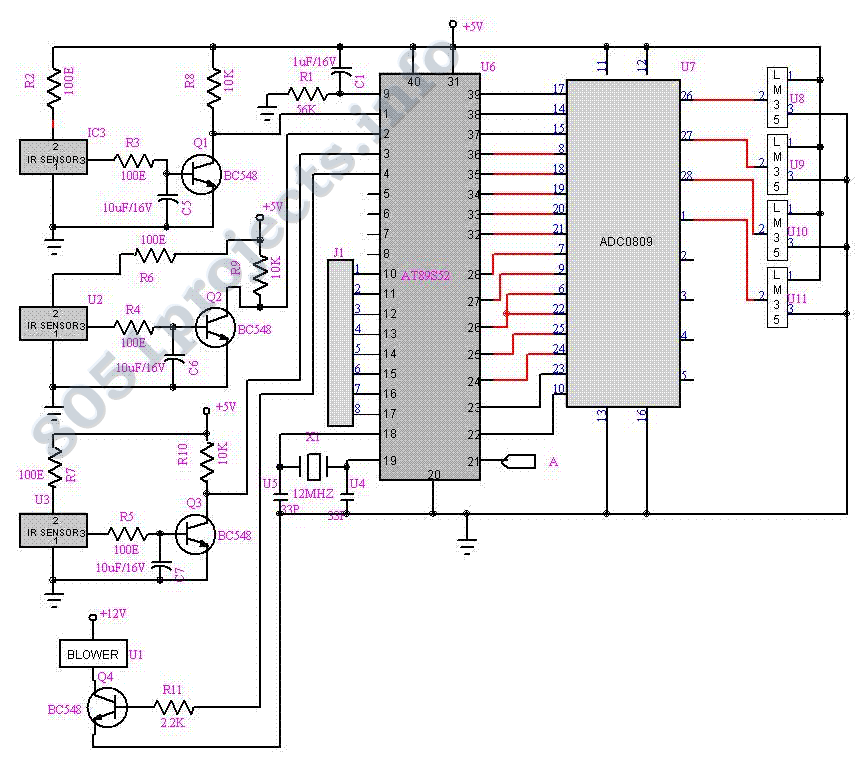
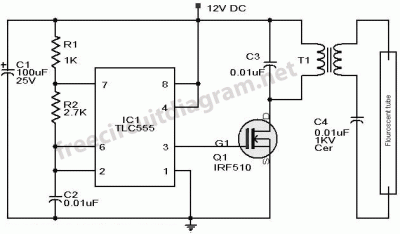
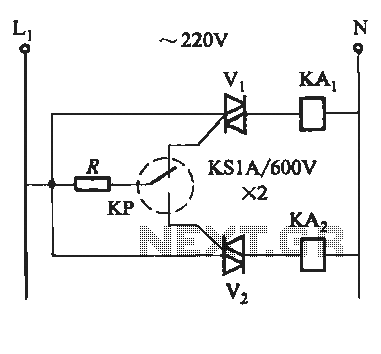
Metal Detector Circuit
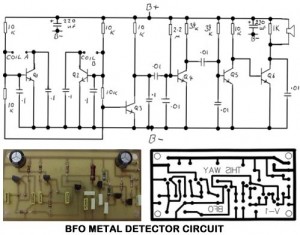
Metal Detector Circuit Overview The metal detector circuit is an electronic circuit that is specifically designed to detect metal that lies deep in the water.
The metal detector circuit operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a coil generates an alternating magnetic field. When metal objects enter this field, they disrupt the magnetic lines of force, inducing a secondary current in the coil. This change is detected and translated into an audible signal or visual indication, alerting the user to the presence of metal.
The circuit typically comprises a transmitter coil, a receiver coil, and associated electronic components. The transmitter coil is powered by an oscillator circuit that generates a high-frequency AC signal. This signal is then fed into the transmitter coil, creating the magnetic field. The receiver coil, positioned close to the transmitter, detects changes in the magnetic field caused by nearby metal objects.
The output from the receiver coil is processed by an amplifier circuit to enhance the signal strength. Subsequently, a demodulator converts the amplified signal into a form suitable for triggering an alarm or indicator, such as a buzzer or LED. The circuit may also include a threshold adjustment feature, allowing the user to set sensitivity levels based on the environment or the type of metal being searched.
In applications where detection is required underwater, the circuit must be waterproofed and designed to withstand harsh conditions. This may involve using specialized enclosures and materials that do not corrode or interfere with the detection process. Furthermore, the power supply for such circuits is often designed to be energy-efficient, utilizing batteries or solar cells to ensure prolonged operational life in remote areas.
Overall, the design of a metal detector circuit for underwater use combines principles of electronics, materials science, and environmental engineering to create an effective tool for locating submerged metallic objects.Metal Detector Circuit Overview The metal detector circuit is an electronic circuit that is specifically designed to detect metal that lies deep in the water. 🔗 External reference
The metal detector circuit operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a coil generates an alternating magnetic field. When metal objects enter this field, they disrupt the magnetic lines of force, inducing a secondary current in the coil. This change is detected and translated into an audible signal or visual indication, alerting the user to the presence of metal.
The circuit typically comprises a transmitter coil, a receiver coil, and associated electronic components. The transmitter coil is powered by an oscillator circuit that generates a high-frequency AC signal. This signal is then fed into the transmitter coil, creating the magnetic field. The receiver coil, positioned close to the transmitter, detects changes in the magnetic field caused by nearby metal objects.
The output from the receiver coil is processed by an amplifier circuit to enhance the signal strength. Subsequently, a demodulator converts the amplified signal into a form suitable for triggering an alarm or indicator, such as a buzzer or LED. The circuit may also include a threshold adjustment feature, allowing the user to set sensitivity levels based on the environment or the type of metal being searched.
In applications where detection is required underwater, the circuit must be waterproofed and designed to withstand harsh conditions. This may involve using specialized enclosures and materials that do not corrode or interfere with the detection process. Furthermore, the power supply for such circuits is often designed to be energy-efficient, utilizing batteries or solar cells to ensure prolonged operational life in remote areas.
Overall, the design of a metal detector circuit for underwater use combines principles of electronics, materials science, and environmental engineering to create an effective tool for locating submerged metallic objects.Metal Detector Circuit Overview The metal detector circuit is an electronic circuit that is specifically designed to detect metal that lies deep in the water. 🔗 External reference