Metronome II
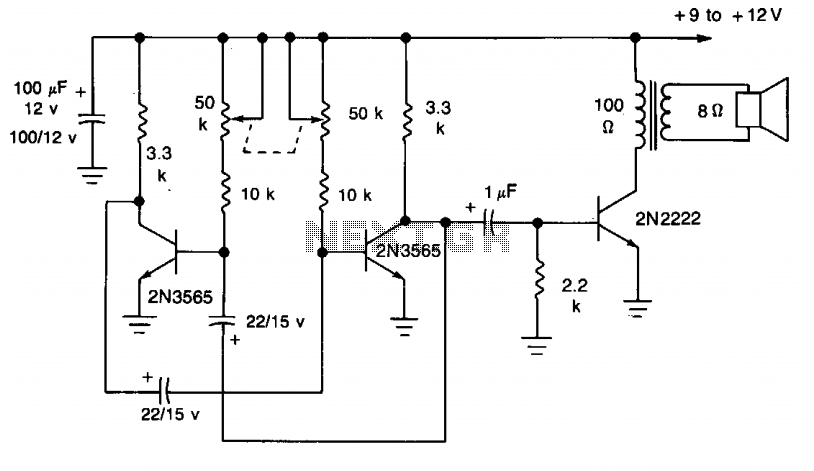
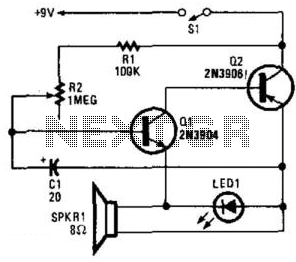
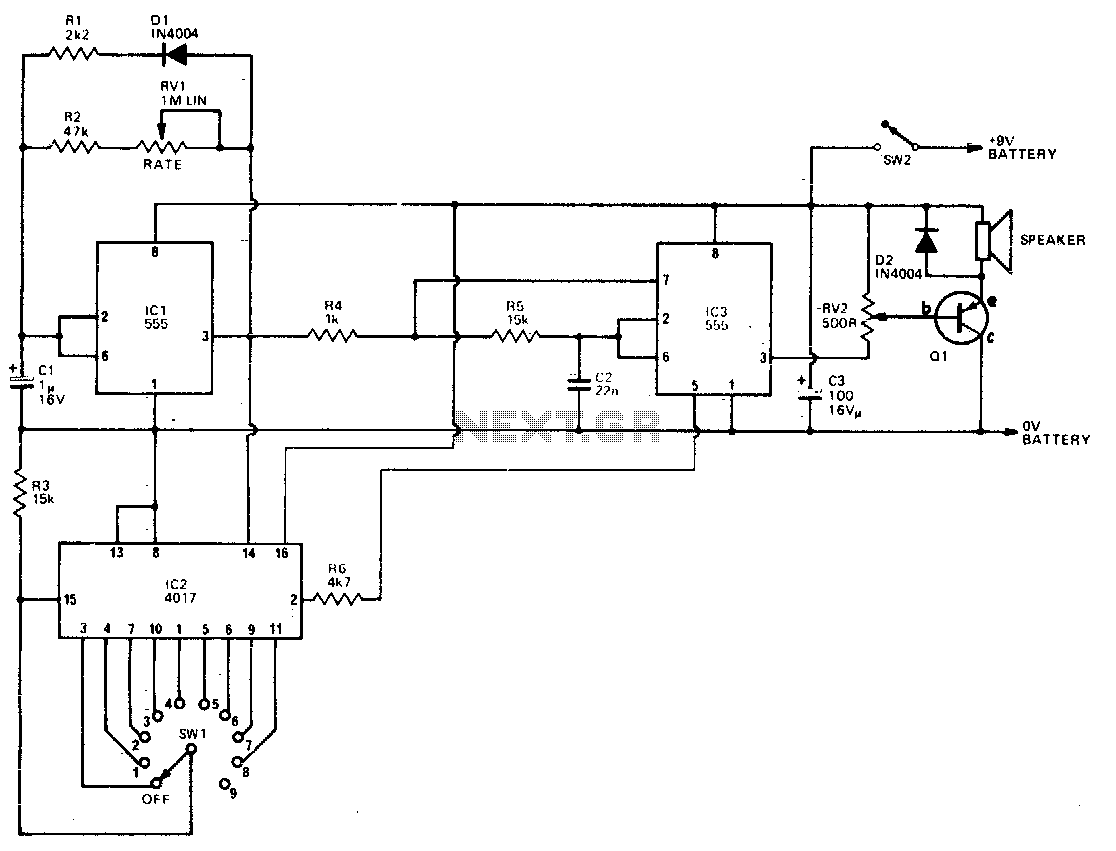
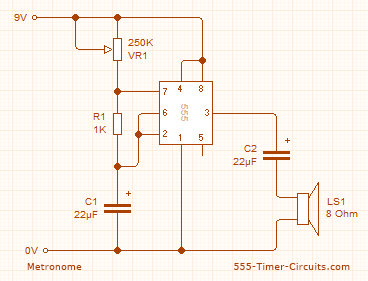
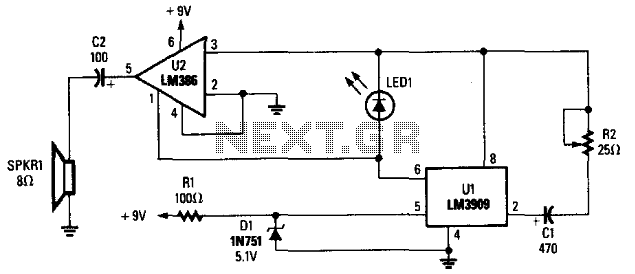
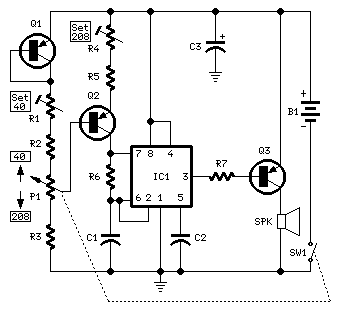
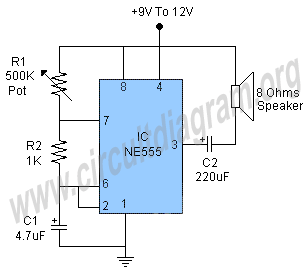
This simple circuit utilizes a multivibrator to generate beats, followed by an audio amplifier stage to enhance the output level. The range of adjustment is approximately from 40 to 200 beats per minute, controlled by a gauged potentiometer.
The described circuit consists of two main functional blocks: a multivibrator and an audio amplifier. The multivibrator, typically configured as an astable multivibrator, produces a square wave output that corresponds to the desired beat frequency. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of resistors and capacitors in the circuit, along with the setting of the potentiometer, which allows for fine-tuning of the output frequency within the specified range of 40 to 200 beats per minute.
The audio amplifier stage is connected to the output of the multivibrator. This stage is designed to amplify the weak square wave signal generated by the multivibrator to a level suitable for driving speakers or other audio output devices. Commonly, an operational amplifier (op-amp) or a dedicated audio amplifier IC is employed for this purpose. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted using feedback resistors, ensuring that the output signal maintains clarity and fidelity without distortion.
Power supply considerations for the circuit are essential, as both the multivibrator and audio amplifier require a stable voltage source to function effectively. Bypass capacitors may be included near the power supply pins of the ICs to filter out any noise and ensure stable operation.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines a multivibrator for beat generation with an audio amplifier for output enhancement, providing a versatile solution for applications requiring adjustable rhythmic sound. The design allows for user-friendly adjustments and can be utilized in various electronic projects, including metronomes, sound effects generators, or rhythm-based applications.This simple circuit uses a multivibrator to generate the beats and a subsequent audio amplifier stage to increase the output level. Range of adjustment is approximately from 40 to 200 beats per minute set by the gauged potentiometer.
The described circuit consists of two main functional blocks: a multivibrator and an audio amplifier. The multivibrator, typically configured as an astable multivibrator, produces a square wave output that corresponds to the desired beat frequency. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of resistors and capacitors in the circuit, along with the setting of the potentiometer, which allows for fine-tuning of the output frequency within the specified range of 40 to 200 beats per minute.
The audio amplifier stage is connected to the output of the multivibrator. This stage is designed to amplify the weak square wave signal generated by the multivibrator to a level suitable for driving speakers or other audio output devices. Commonly, an operational amplifier (op-amp) or a dedicated audio amplifier IC is employed for this purpose. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted using feedback resistors, ensuring that the output signal maintains clarity and fidelity without distortion.
Power supply considerations for the circuit are essential, as both the multivibrator and audio amplifier require a stable voltage source to function effectively. Bypass capacitors may be included near the power supply pins of the ICs to filter out any noise and ensure stable operation.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines a multivibrator for beat generation with an audio amplifier for output enhancement, providing a versatile solution for applications requiring adjustable rhythmic sound. The design allows for user-friendly adjustments and can be utilized in various electronic projects, including metronomes, sound effects generators, or rhythm-based applications.This simple circuit uses a multivibrator to generate the beats and a subsequent audio amplifier stage to increase the output level. Range of adjustment is approximately from 40 to 200 beats per minute set by the gauged potentiometer.