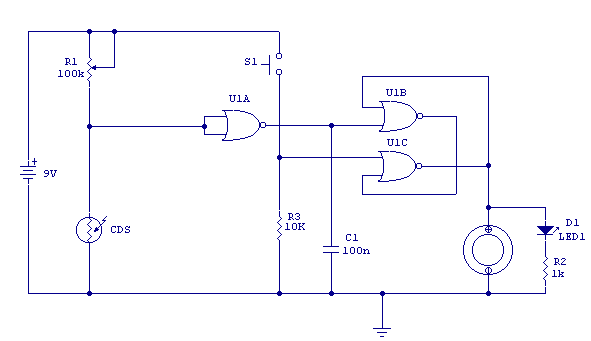
Micropower monostable circuit diagram
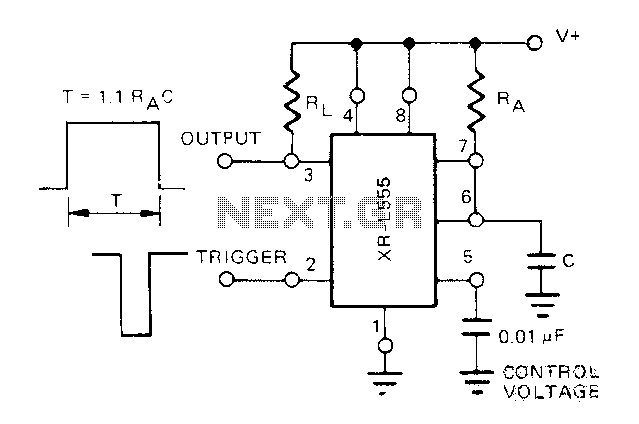
The Exars XR-L555 circuit has a typical power consumption of 900 W and operates with a power supply voltage of 5V. It is a micro-power circuit that can be used as a direct replacement for the standard 555 timer. The delay is controlled by an external resistor (RA) and capacitor (C), which determine the duration of the output pulse.
The Exars XR-L555 is a versatile timer circuit designed for low-power applications. With a power consumption of 900 W, it is optimized for efficiency, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The circuit operates at a supply voltage of 5V, allowing it to be integrated into various electronic systems that require a reliable timing mechanism.
The XR-L555 functions similarly to the classic 555 timer, providing the same timing capabilities with enhanced performance characteristics. The timing interval is adjustable through the selection of an external resistor (RA) and capacitor (C). The relationship between these components is defined by the formula:
\[ T = 1.1 \times RA \times C \]
where \( T \) is the output pulse duration. By varying the values of RA and C, users can precisely control the timing behavior of the circuit, making it suitable for applications such as pulse width modulation, timer delays, and oscillators.
In addition to its basic timing functions, the XR-L555 may also include features such as a low-power sleep mode, which further enhances its efficiency in power-sensitive applications. The micro-power design ensures that the circuit consumes minimal energy during operation, making it an ideal choice for portable and battery-operated devices.
Overall, the Exars XR-L555 circuit combines the familiar functionality of the traditional 555 timer with modern enhancements that cater to low-power requirements, providing a reliable and flexible solution for a wide range of electronic timing applications.Exars XR-L555 circuit typical power consumption is 900 W, the power supply voltage of 5V, micro-power circuit, XR-L555 can be used directly in place of the 555 timer. Delay by an external resistor and a capacitor (RA and C) control, delay determines the duration of the output pulse.
The Exars XR-L555 is a versatile timer circuit designed for low-power applications. With a power consumption of 900 W, it is optimized for efficiency, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The circuit operates at a supply voltage of 5V, allowing it to be integrated into various electronic systems that require a reliable timing mechanism.
The XR-L555 functions similarly to the classic 555 timer, providing the same timing capabilities with enhanced performance characteristics. The timing interval is adjustable through the selection of an external resistor (RA) and capacitor (C). The relationship between these components is defined by the formula:
\[ T = 1.1 \times RA \times C \]
where \( T \) is the output pulse duration. By varying the values of RA and C, users can precisely control the timing behavior of the circuit, making it suitable for applications such as pulse width modulation, timer delays, and oscillators.
In addition to its basic timing functions, the XR-L555 may also include features such as a low-power sleep mode, which further enhances its efficiency in power-sensitive applications. The micro-power design ensures that the circuit consumes minimal energy during operation, making it an ideal choice for portable and battery-operated devices.
Overall, the Exars XR-L555 circuit combines the familiar functionality of the traditional 555 timer with modern enhancements that cater to low-power requirements, providing a reliable and flexible solution for a wide range of electronic timing applications.Exars XR-L555 circuit typical power consumption is 900 W, the power supply voltage of 5V, micro-power circuit, XR-L555 can be used directly in place of the 555 timer. Delay by an external resistor and a capacitor (RA and C) control, delay determines the duration of the output pulse.