Mini FM Receiver using TDA7088
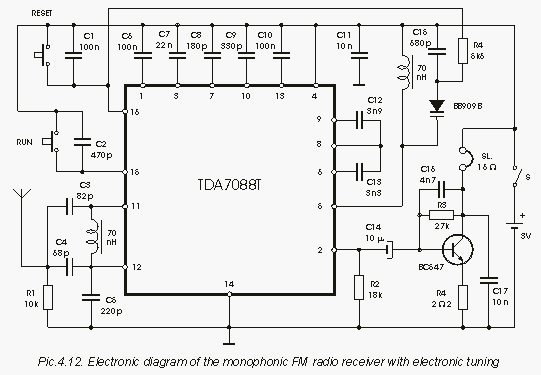
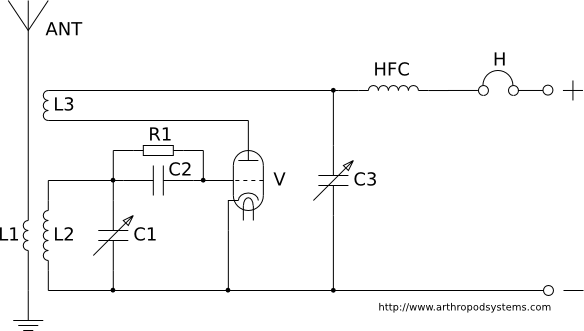
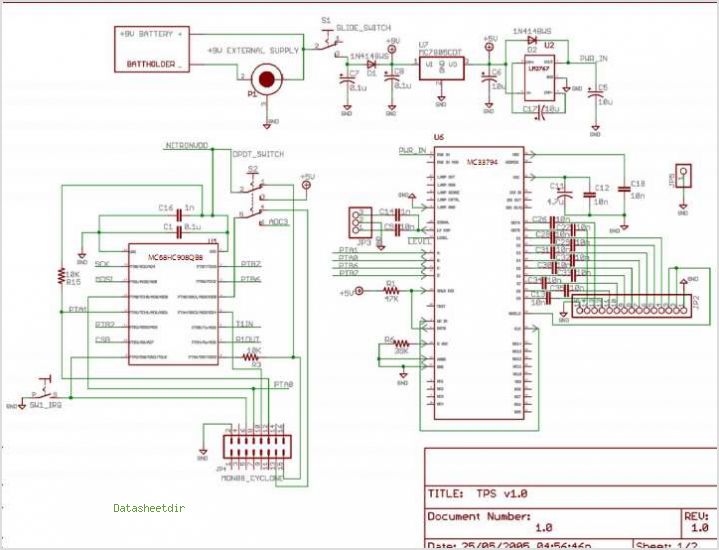
The electronic diagram of the monophonic FM receiver made with TDA7088T is shown on Pic.4.12. If built with SMD components it can be placed in a matchbox, altogether with two button-type batteries. The operating principle of this device is given in the previous chapter. The only thing new is a very simple audio amplifier made with BC547 transistor, which is loaded by cheap 16-Ohm headphones. The telescopic antenna is used, as on Pic.4.8.
The monophonic FM receiver utilizing the TDA7088T IC is designed for compactness and efficiency, making it suitable for portable applications. The integration of surface-mount device (SMD) components allows the entire circuit to fit within a small enclosure, such as a matchbox, enhancing its portability. The device operates on two button-type batteries, providing a convenient power source for mobile use.
The TDA7088T serves as the heart of the FM receiver, handling frequency demodulation and signal processing. Its design incorporates various stages, including an RF amplifier, a mixer, and a demodulator, which work in tandem to extract audio signals from the received FM broadcast. The schematic likely includes necessary passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors to support the operation of the IC and ensure proper tuning and filtering of the incoming signals.
An important addition to this design is the audio amplifier stage, which utilizes a BC547 transistor. This component functions as a simple yet effective amplifier, boosting the audio signal to a level suitable for driving inexpensive 16-ohm headphones. The choice of a BC547 transistor is advantageous due to its availability, low cost, and adequate performance for audio applications. The amplifier circuit is designed to provide sufficient gain while maintaining audio fidelity, allowing users to enjoy clear sound reproduction from the FM broadcasts.
To enhance reception quality, a telescopic antenna is employed, which can be extended or retracted based on the user's needs. This type of antenna is effective for FM signals and can be adjusted to optimize reception depending on the environment. The overall design prioritizes simplicity and functionality, making it accessible for hobbyists and electronics enthusiasts looking to build their own FM receiver. The combination of compact design, efficient power usage, and straightforward assembly makes this project an excellent introduction to radio frequency electronics.The electronic diagram of the monophonic FM receiver made with TDA7088T is shown on Pic.4.12. If built with SMD components it can be placed in a matchbox, altogether with two button-type batteries. The operating principle of this device is given in the previous chapter. The only thing new is a very simple audio amplifier made with BC547 transistor, which is loaded by cheap 16-Ohm headphones.
The telescopic antenna is used, as on Pic.4.8. 🔗 External reference
The monophonic FM receiver utilizing the TDA7088T IC is designed for compactness and efficiency, making it suitable for portable applications. The integration of surface-mount device (SMD) components allows the entire circuit to fit within a small enclosure, such as a matchbox, enhancing its portability. The device operates on two button-type batteries, providing a convenient power source for mobile use.
The TDA7088T serves as the heart of the FM receiver, handling frequency demodulation and signal processing. Its design incorporates various stages, including an RF amplifier, a mixer, and a demodulator, which work in tandem to extract audio signals from the received FM broadcast. The schematic likely includes necessary passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors to support the operation of the IC and ensure proper tuning and filtering of the incoming signals.
An important addition to this design is the audio amplifier stage, which utilizes a BC547 transistor. This component functions as a simple yet effective amplifier, boosting the audio signal to a level suitable for driving inexpensive 16-ohm headphones. The choice of a BC547 transistor is advantageous due to its availability, low cost, and adequate performance for audio applications. The amplifier circuit is designed to provide sufficient gain while maintaining audio fidelity, allowing users to enjoy clear sound reproduction from the FM broadcasts.
To enhance reception quality, a telescopic antenna is employed, which can be extended or retracted based on the user's needs. This type of antenna is effective for FM signals and can be adjusted to optimize reception depending on the environment. The overall design prioritizes simplicity and functionality, making it accessible for hobbyists and electronics enthusiasts looking to build their own FM receiver. The combination of compact design, efficient power usage, and straightforward assembly makes this project an excellent introduction to radio frequency electronics.The electronic diagram of the monophonic FM receiver made with TDA7088T is shown on Pic.4.12. If built with SMD components it can be placed in a matchbox, altogether with two button-type batteries. The operating principle of this device is given in the previous chapter. The only thing new is a very simple audio amplifier made with BC547 transistor, which is loaded by cheap 16-Ohm headphones.
The telescopic antenna is used, as on Pic.4.8. 🔗 External reference