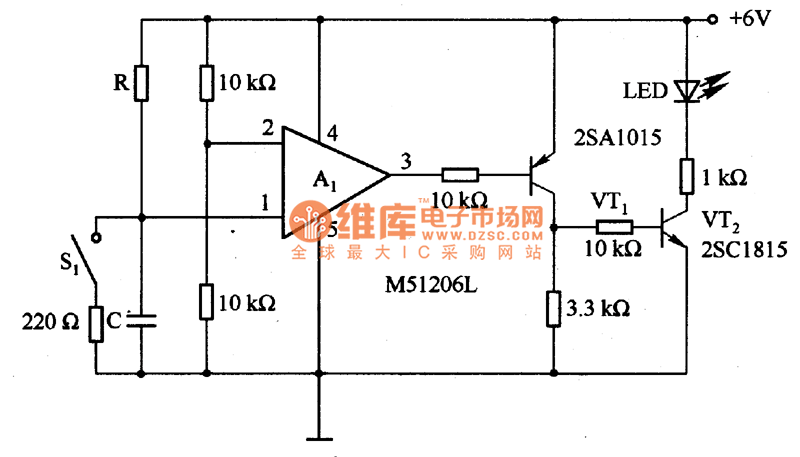
Miniature Beeping Circuit
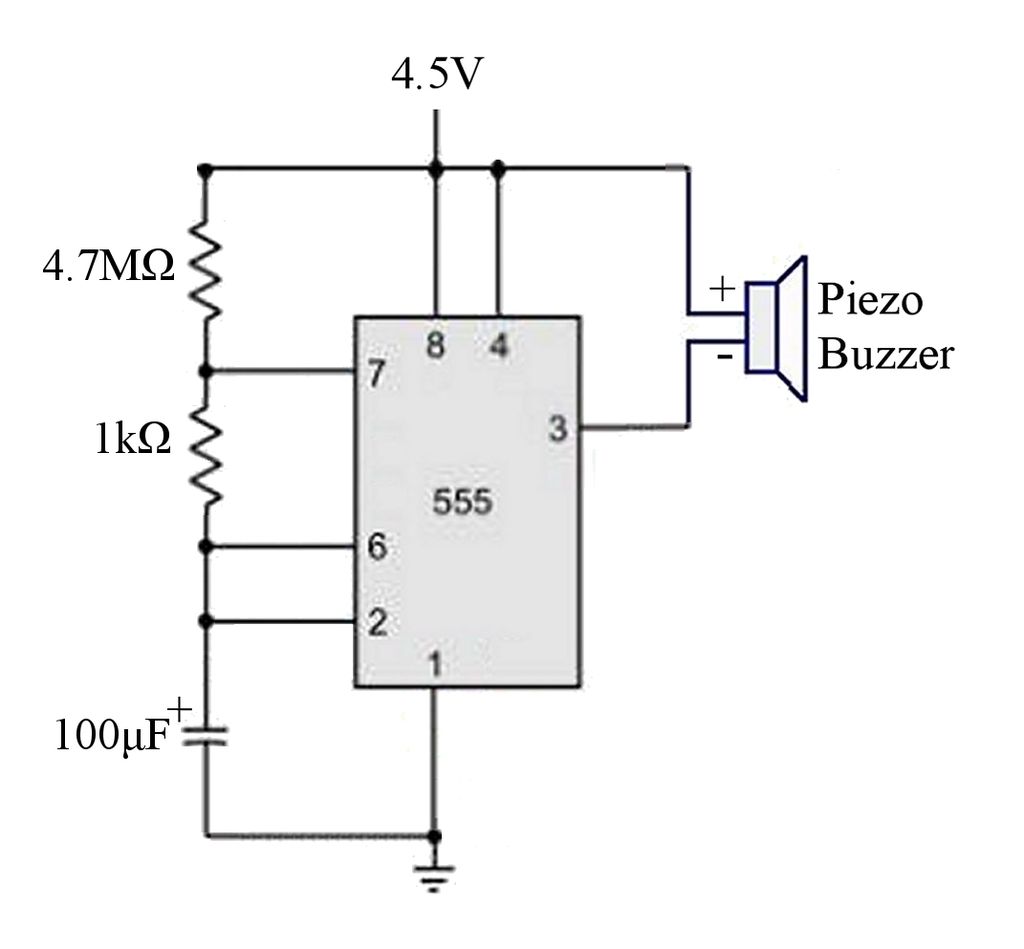
The circuit is a basic 555 timer circuit in astable mode. In this configuration, the integrated circuit (IC) generates a brief pulse to the buzzer at regular intervals.
The 555 timer in astable mode operates as an oscillator, producing a continuous square wave output without requiring any external triggering. In this configuration, the circuit consists of a 555 timer IC, resistors, a capacitor, and a buzzer.
The timing components, typically two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C1), determine the frequency of the output pulse. The frequency (f) and duty cycle (D) of the output waveform can be calculated using the formulas:
f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2R2) * C1)
D = (R2 / (R1 + 2R2)) * 100%
Where:
- R1 is connected between the discharge pin (Pin 7) and Vcc (positive supply voltage).
- R2 is connected between the discharge pin (Pin 7) and the threshold pin (Pin 6).
- C1 is connected between the threshold pin (Pin 6) and ground.
The output from the 555 timer is taken from the output pin (Pin 3), which drives the buzzer. The buzzer will sound each time the output pin transitions from low to high, producing an audible beep at the defined intervals.
For practical implementation, it is important to select appropriate resistor and capacitor values to achieve the desired timing characteristics. Additionally, the power supply voltage should be compatible with the 555 timer specifications, typically ranging from 4.5V to 15V.
By adjusting R1, R2, and C1, the circuit can be customized for various applications, such as alarms, timers, or sound indicators, making it a versatile choice for basic timing and sound generation tasks.The circuit is a basic 555 timer circuit in astable mode. In this configuration the IC sends a brief pulse to the buzzer every few minutes. The values.. 🔗 External reference
The 555 timer in astable mode operates as an oscillator, producing a continuous square wave output without requiring any external triggering. In this configuration, the circuit consists of a 555 timer IC, resistors, a capacitor, and a buzzer.
The timing components, typically two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C1), determine the frequency of the output pulse. The frequency (f) and duty cycle (D) of the output waveform can be calculated using the formulas:
f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2R2) * C1)
D = (R2 / (R1 + 2R2)) * 100%
Where:
- R1 is connected between the discharge pin (Pin 7) and Vcc (positive supply voltage).
- R2 is connected between the discharge pin (Pin 7) and the threshold pin (Pin 6).
- C1 is connected between the threshold pin (Pin 6) and ground.
The output from the 555 timer is taken from the output pin (Pin 3), which drives the buzzer. The buzzer will sound each time the output pin transitions from low to high, producing an audible beep at the defined intervals.
For practical implementation, it is important to select appropriate resistor and capacitor values to achieve the desired timing characteristics. Additionally, the power supply voltage should be compatible with the 555 timer specifications, typically ranging from 4.5V to 15V.
By adjusting R1, R2, and C1, the circuit can be customized for various applications, such as alarms, timers, or sound indicators, making it a versatile choice for basic timing and sound generation tasks.The circuit is a basic 555 timer circuit in astable mode. In this configuration the IC sends a brief pulse to the buzzer every few minutes. The values.. 🔗 External reference