Mosfet Tester
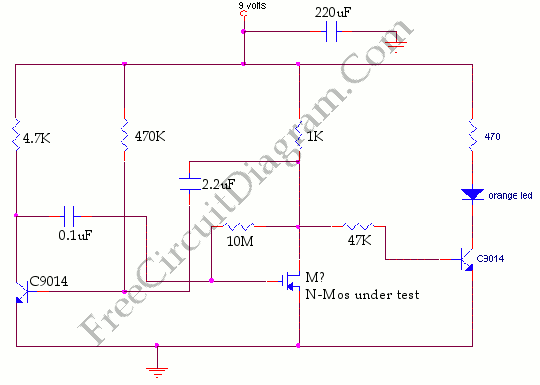
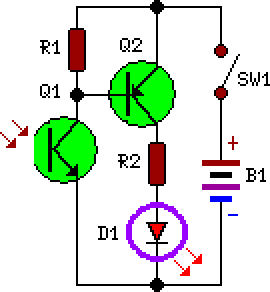
This circuit falls under the category of an astable multivibrator. It is designed to test N-channel MOSFETs, specifically power types such as the IRF830, to determine their functionality.
The astable multivibrator circuit is a type of oscillator that continuously switches between its high and low states without requiring any external triggering. This makes it particularly useful for applications like testing MOSFETs, where a square wave signal is needed to effectively drive the gate of the device under test.
The circuit typically consists of two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C1) connected to an N-channel MOSFET. The resistors are used to set the charging and discharging times of the capacitor, which in turn determines the frequency of the oscillation. The output can be taken from the drain of the MOSFET, which will produce a square wave signal.
When testing an N-channel MOSFET such as the IRF830, the gate of the MOSFET is connected to the output of the astable multivibrator. The square wave signal will turn the MOSFET on and off rapidly. By observing the output at the drain, one can assess whether the MOSFET is functioning properly. If the MOSFET turns on and off in response to the square wave signal, it indicates that the device is operational.
The values of the resistors and capacitor can be adjusted to change the frequency of the output signal, allowing for testing across different operational conditions. Proper selection of these components is crucial for ensuring that the MOSFET is driven adequately within its specified gate threshold voltage range.
This astable multivibrator circuit serves as a simple yet effective means for evaluating the performance of power MOSFETs, providing a visual indication of their operational status through the generated square wave output.This circuit included in the category astable multivibrator. This circuit is used to test? N-Mosfets (the power kind e.g irf830), whether it works or not. If. 🔗 External reference
The astable multivibrator circuit is a type of oscillator that continuously switches between its high and low states without requiring any external triggering. This makes it particularly useful for applications like testing MOSFETs, where a square wave signal is needed to effectively drive the gate of the device under test.
The circuit typically consists of two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C1) connected to an N-channel MOSFET. The resistors are used to set the charging and discharging times of the capacitor, which in turn determines the frequency of the oscillation. The output can be taken from the drain of the MOSFET, which will produce a square wave signal.
When testing an N-channel MOSFET such as the IRF830, the gate of the MOSFET is connected to the output of the astable multivibrator. The square wave signal will turn the MOSFET on and off rapidly. By observing the output at the drain, one can assess whether the MOSFET is functioning properly. If the MOSFET turns on and off in response to the square wave signal, it indicates that the device is operational.
The values of the resistors and capacitor can be adjusted to change the frequency of the output signal, allowing for testing across different operational conditions. Proper selection of these components is crucial for ensuring that the MOSFET is driven adequately within its specified gate threshold voltage range.
This astable multivibrator circuit serves as a simple yet effective means for evaluating the performance of power MOSFETs, providing a visual indication of their operational status through the generated square wave output.This circuit included in the category astable multivibrator. This circuit is used to test? N-Mosfets (the power kind e.g irf830), whether it works or not. If. 🔗 External reference