Ni-Cd battery charger circuit
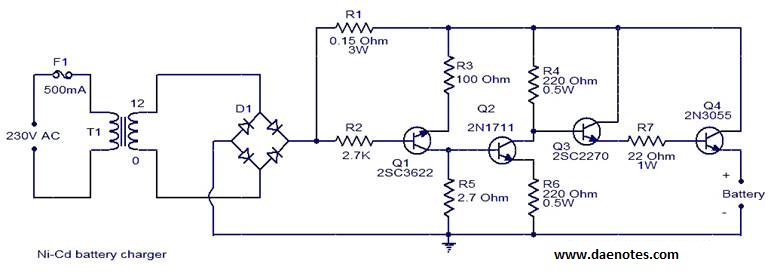
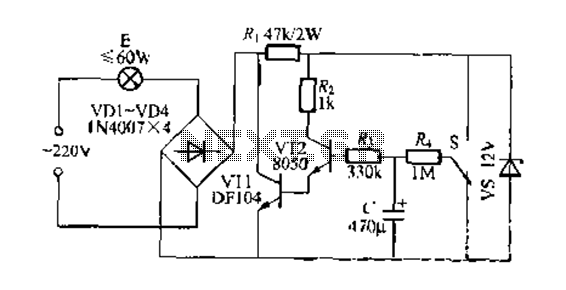
This circuit is primarily designed for charging 12V Ni-Cd battery packs. However, it can also be used to charge 6V and 9V battery packs with slight modifications.
The circuit operates by utilizing a power supply that provides the necessary voltage and current for charging the batteries. The main components typically include a transformer, a bridge rectifier, a filtering capacitor, and a voltage regulator, along with necessary protection diodes and resistors.
The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a level suitable for charging the batteries. The bridge rectifier converts the AC voltage to DC, which is essential for battery charging. The filtering capacitor smooths out the rectified DC voltage, reducing ripple and providing a more stable output.
For charging 12V Ni-Cd batteries, the circuit ensures that the voltage across the battery terminals does not exceed the maximum charging voltage of approximately 14.4V. This is crucial to prevent overcharging, which can lead to battery damage. The voltage regulator can be adjusted to provide the appropriate output voltage for 6V and 9V battery packs, ensuring compatibility with different battery configurations.
Additionally, incorporating a charging indicator LED can provide visual feedback on the charging status. A current limiting resistor may also be included to prevent excessive current flow during the initial charging phase, which can be particularly important for older or partially discharged batteries.
Overall, this circuit offers versatility in charging various Ni-Cd battery packs, with the potential for further enhancements to improve efficiency and safety during the charging process.This circuit can be primarily used for charging 12V Ni-Cd battery packs. Any way 6V and 9V battery packs can be also charged by using this circuit a little.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing a power supply that provides the necessary voltage and current for charging the batteries. The main components typically include a transformer, a bridge rectifier, a filtering capacitor, and a voltage regulator, along with necessary protection diodes and resistors.
The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a level suitable for charging the batteries. The bridge rectifier converts the AC voltage to DC, which is essential for battery charging. The filtering capacitor smooths out the rectified DC voltage, reducing ripple and providing a more stable output.
For charging 12V Ni-Cd batteries, the circuit ensures that the voltage across the battery terminals does not exceed the maximum charging voltage of approximately 14.4V. This is crucial to prevent overcharging, which can lead to battery damage. The voltage regulator can be adjusted to provide the appropriate output voltage for 6V and 9V battery packs, ensuring compatibility with different battery configurations.
Additionally, incorporating a charging indicator LED can provide visual feedback on the charging status. A current limiting resistor may also be included to prevent excessive current flow during the initial charging phase, which can be particularly important for older or partially discharged batteries.
Overall, this circuit offers versatility in charging various Ni-Cd battery packs, with the potential for further enhancements to improve efficiency and safety during the charging process.This circuit can be primarily used for charging 12V Ni-Cd battery packs. Any way 6V and 9V battery packs can be also charged by using this circuit a little.. 🔗 External reference