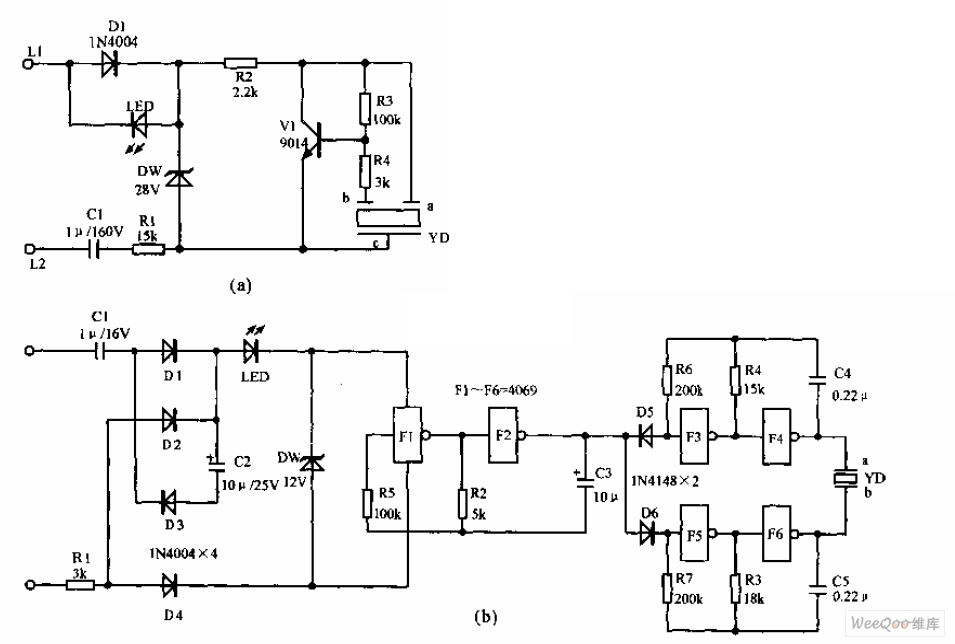
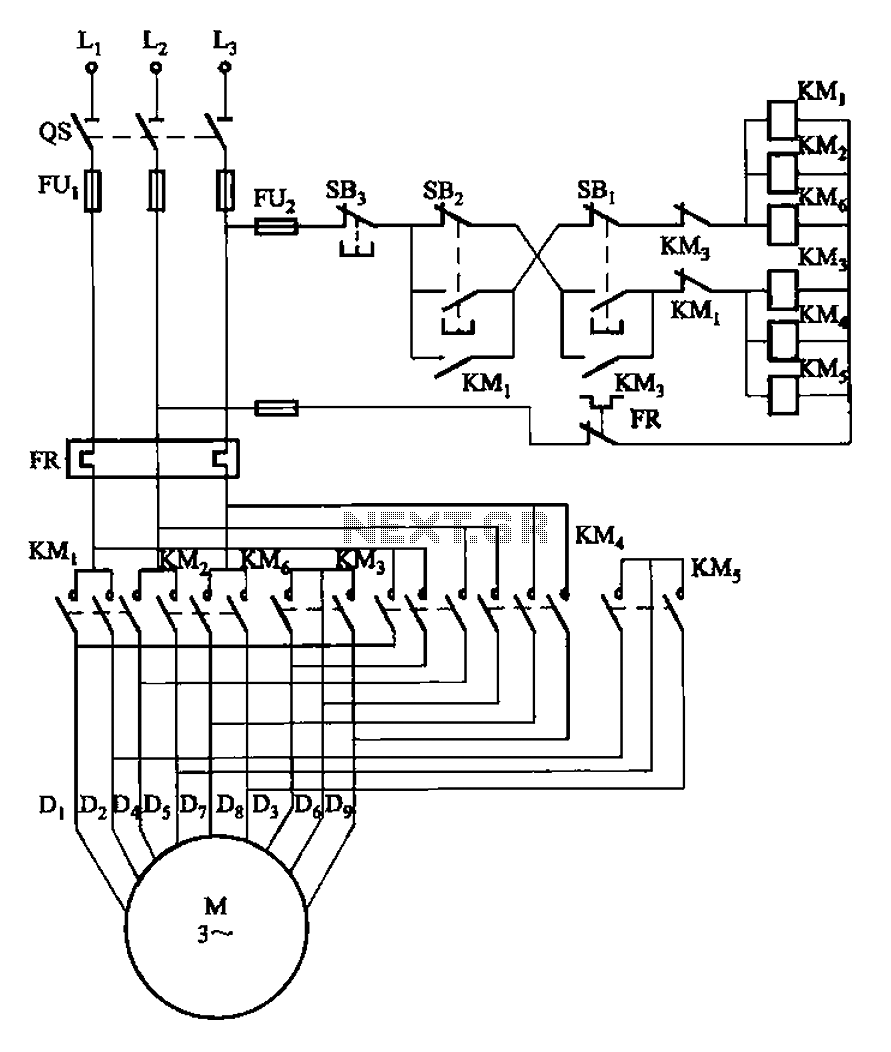
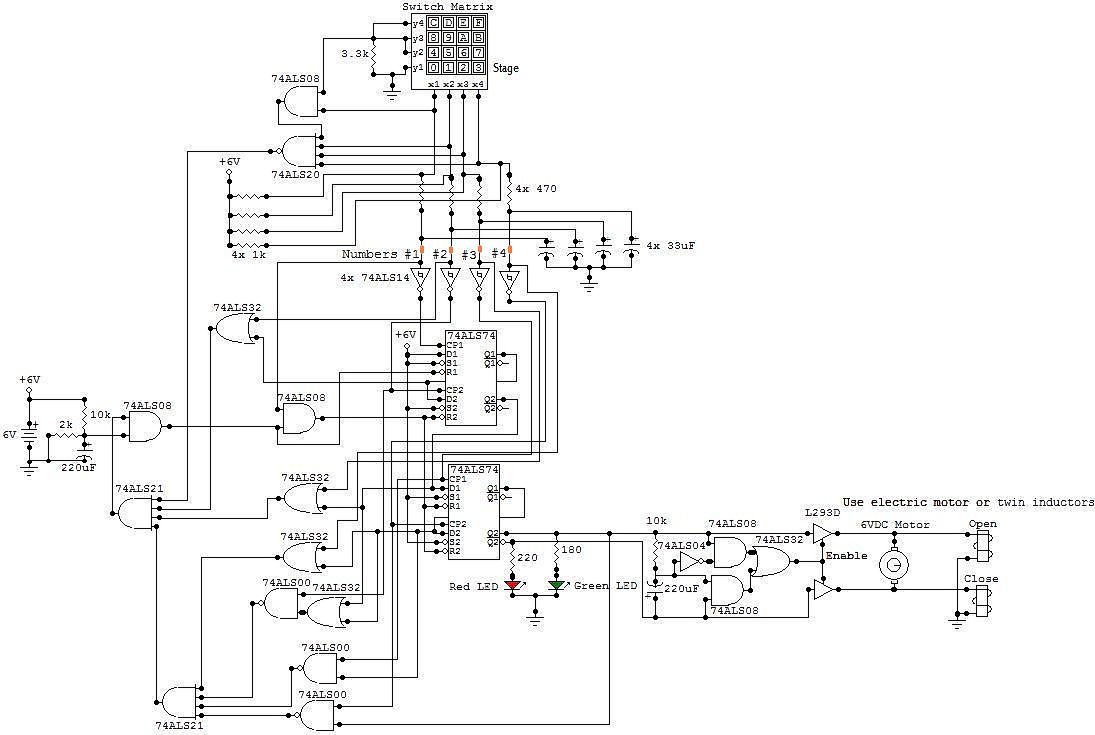
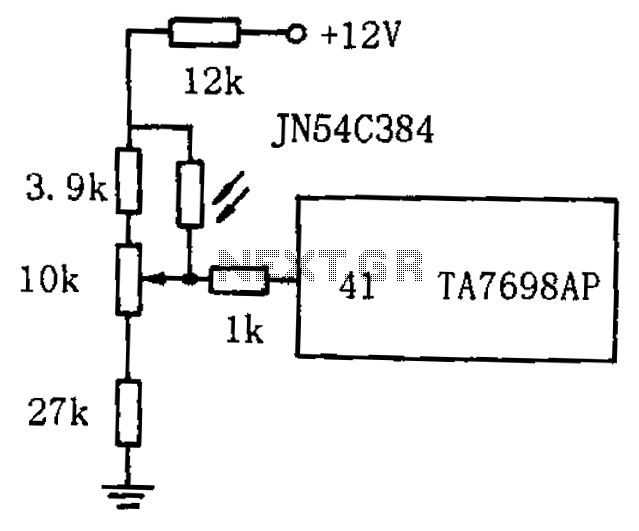
One of the high-pressure sensing alarm circuit
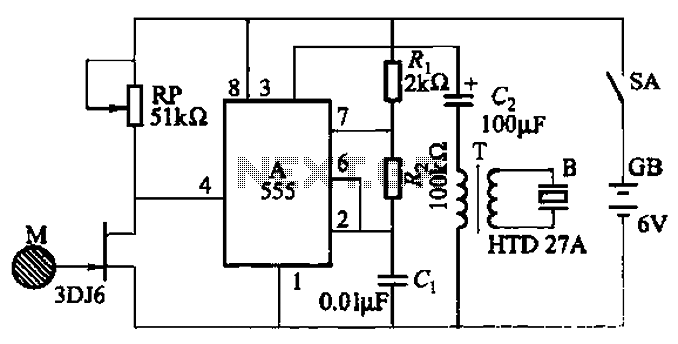
The circuit utilizes a 555 integrated circuit (IC) configured as a non-stable multivibrator. When a sensor detects proximity to a high-voltage electrified body, a piezoelectric ceramic sheet generates an alarm. Additionally, when in proximity to a high-frequency electric field, it produces a vibrating sound, and when near an electrostatic field, it emits a sound resembling a flute.
The described circuit employs a 555 timer IC in a non-stable multivibrator configuration to create an audio alert system responsive to specific electric fields. The circuit is designed to monitor the proximity of high-voltage sources and generate audible signals through a piezoelectric transducer.
In this configuration, the 555 timer operates continuously in a state of oscillation, producing a square wave output. The frequency of oscillation can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values connected to the 555 timer. The output from the timer is fed into a piezoelectric ceramic sheet, which converts the electrical signals into sound.
When the sensor is activated by detecting a high-voltage electrified body, the output of the 555 timer changes, triggering the piezoelectric element to emit a loud alarm sound. This serves as an immediate warning signal.
In addition, the circuit is sensitive to varying electric fields. When the sensor detects a high-frequency electric field, the output frequency of the 555 timer increases, causing the piezoelectric element to produce a vibrating sound. Conversely, when the sensor is near an electrostatic field, the output alters to create a sound that resembles a flute, adding a distinct tonal quality to the alarm system.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines the functionalities of proximity sensing and sound generation, providing a versatile alert mechanism for high-voltage environments.By the 555 IC A composed of a non-steady-state self-excited multivibrator. When the sensor very close to the high-voltage electrified body, the piezoelectric ceramic sheet B out alarm. When it is close to the frequency electric field, cricket issue vibrato; close when the electrostatic field, emit electrical flute-like sound straight.
The described circuit employs a 555 timer IC in a non-stable multivibrator configuration to create an audio alert system responsive to specific electric fields. The circuit is designed to monitor the proximity of high-voltage sources and generate audible signals through a piezoelectric transducer.
In this configuration, the 555 timer operates continuously in a state of oscillation, producing a square wave output. The frequency of oscillation can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values connected to the 555 timer. The output from the timer is fed into a piezoelectric ceramic sheet, which converts the electrical signals into sound.
When the sensor is activated by detecting a high-voltage electrified body, the output of the 555 timer changes, triggering the piezoelectric element to emit a loud alarm sound. This serves as an immediate warning signal.
In addition, the circuit is sensitive to varying electric fields. When the sensor detects a high-frequency electric field, the output frequency of the 555 timer increases, causing the piezoelectric element to produce a vibrating sound. Conversely, when the sensor is near an electrostatic field, the output alters to create a sound that resembles a flute, adding a distinct tonal quality to the alarm system.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines the functionalities of proximity sensing and sound generation, providing a versatile alert mechanism for high-voltage environments.By the 555 IC A composed of a non-steady-state self-excited multivibrator. When the sensor very close to the high-voltage electrified body, the piezoelectric ceramic sheet B out alarm. When it is close to the frequency electric field, cricket issue vibrato; close when the electrostatic field, emit electrical flute-like sound straight.