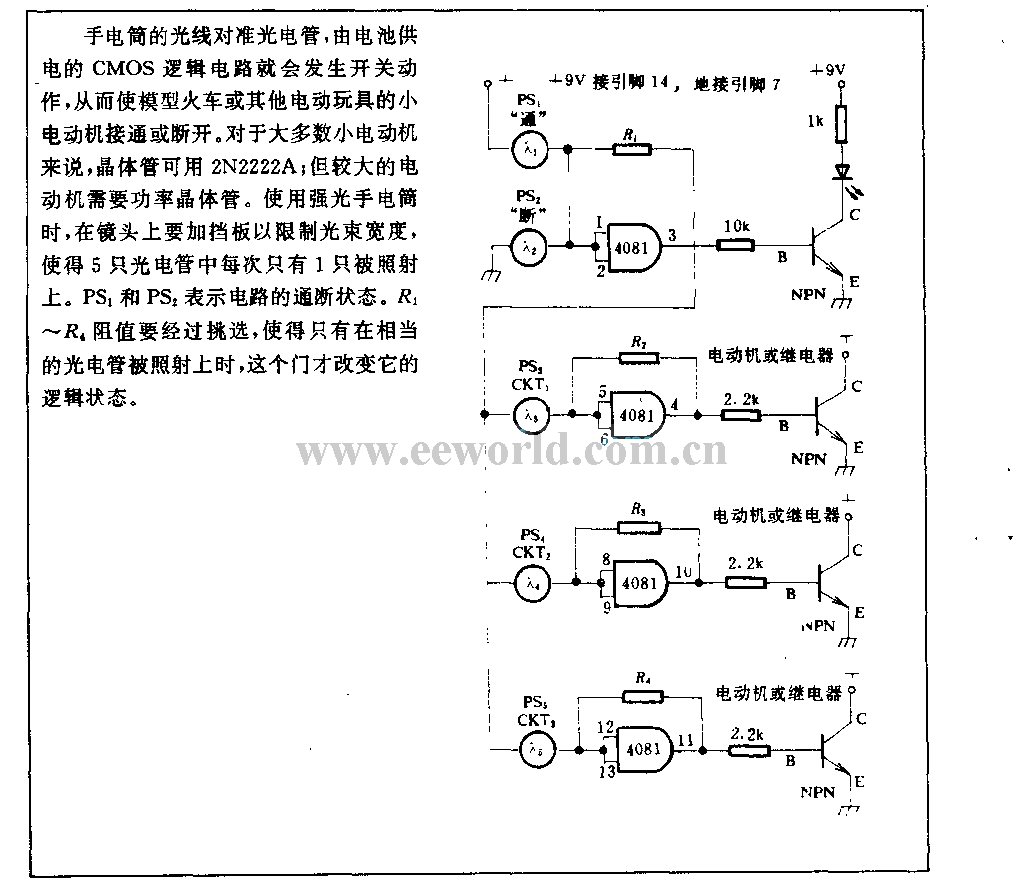
op amp 6 line audio mixer circuit
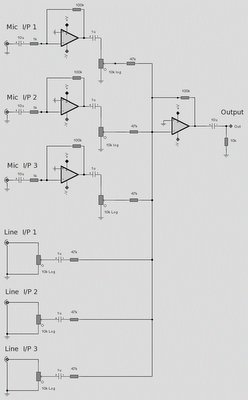
The microphone inputs are amplified approximately 100 times or 40 dB, with the total gain of the mixer, including the summing amplifier, reaching 46 dB. The microphone input is designed for microphones that produce an output of around 2 mV RMS at a distance of 1 meter. Most dynamic microphones conform to this specification. The choice of operational amplifier (op-amp) is not critical in this circuit; bipolar, FET input, or MOS type op-amps can be utilized, such as the 741, LF351, TL061, TL071, CA3140, and others. The power supply consists of a dual positive and negative supply, with two 9-volt batteries suggested as shown above, or a dedicated power supply for extended usage.
The circuit features a microphone preamplifier that increases the low-level audio signal from a dynamic microphone to a usable level for further processing. The input stage employs a high-gain operational amplifier configured in a non-inverting amplifier configuration, providing a gain of 40 dB. This stage is crucial for ensuring that the weak audio signals, typically in the range of 2 mV RMS, are amplified sufficiently to drive subsequent stages without introducing significant noise or distortion.
The total gain of the mixer, which includes the summing amplifier, is designed to achieve an overall amplification of 46 dB. This ensures that the combined audio signals from multiple microphones can be summed effectively while maintaining audio fidelity. The summing amplifier stage is configured to mix the signals from various input channels, allowing for flexible audio routing and control.
The choice of operational amplifiers in this design offers flexibility, as various types can be employed based on availability or specific performance characteristics. The suggested op-amps, including the 741, LF351, TL061, TL071, and CA3140, provide a range of input impedance and noise performance, accommodating different application requirements.
Power supply considerations are vital in audio applications to ensure stable operation. The circuit can be powered by dual 9-volt batteries, which are suitable for portable applications. For longer-term use, a dedicated power supply is recommended to maintain consistent performance without the need for frequent battery replacements. The dual supply configuration allows for proper biasing of the op-amps, ensuring optimal performance across the audio frequency range.
Overall, this circuit design is suitable for various audio applications, including live sound reinforcement and recording, providing a robust solution for microphone signal amplification and mixing.The mic inputs are amplified about 100 times or 40dB, the total gain of the mixer including the summing amplifier is 46dB. The mic input is designed for microphones with outputs of about 2mV RMS at 1 meter. Most dynamic microphones meet this standard. The choice of IC op-amp is not critical in this circuit. Bipolar, FET input or MOS type op-amps c an therefore be used; i. e 741, LF351, TL061, TL071, CA3140 etc. The power supply is a dual positive and negative supply, two 9 Volt batteries may be used as shown above or a power supply is recommended for longer periods of use. 🔗 External reference
The circuit features a microphone preamplifier that increases the low-level audio signal from a dynamic microphone to a usable level for further processing. The input stage employs a high-gain operational amplifier configured in a non-inverting amplifier configuration, providing a gain of 40 dB. This stage is crucial for ensuring that the weak audio signals, typically in the range of 2 mV RMS, are amplified sufficiently to drive subsequent stages without introducing significant noise or distortion.
The total gain of the mixer, which includes the summing amplifier, is designed to achieve an overall amplification of 46 dB. This ensures that the combined audio signals from multiple microphones can be summed effectively while maintaining audio fidelity. The summing amplifier stage is configured to mix the signals from various input channels, allowing for flexible audio routing and control.
The choice of operational amplifiers in this design offers flexibility, as various types can be employed based on availability or specific performance characteristics. The suggested op-amps, including the 741, LF351, TL061, TL071, and CA3140, provide a range of input impedance and noise performance, accommodating different application requirements.
Power supply considerations are vital in audio applications to ensure stable operation. The circuit can be powered by dual 9-volt batteries, which are suitable for portable applications. For longer-term use, a dedicated power supply is recommended to maintain consistent performance without the need for frequent battery replacements. The dual supply configuration allows for proper biasing of the op-amps, ensuring optimal performance across the audio frequency range.
Overall, this circuit design is suitable for various audio applications, including live sound reinforcement and recording, providing a robust solution for microphone signal amplification and mixing.The mic inputs are amplified about 100 times or 40dB, the total gain of the mixer including the summing amplifier is 46dB. The mic input is designed for microphones with outputs of about 2mV RMS at 1 meter. Most dynamic microphones meet this standard. The choice of IC op-amp is not critical in this circuit. Bipolar, FET input or MOS type op-amps c an therefore be used; i. e 741, LF351, TL061, TL071, CA3140 etc. The power supply is a dual positive and negative supply, two 9 Volt batteries may be used as shown above or a power supply is recommended for longer periods of use. 🔗 External reference