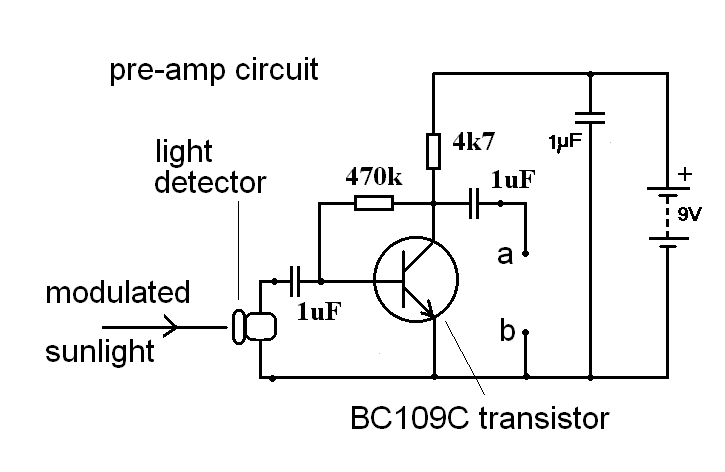
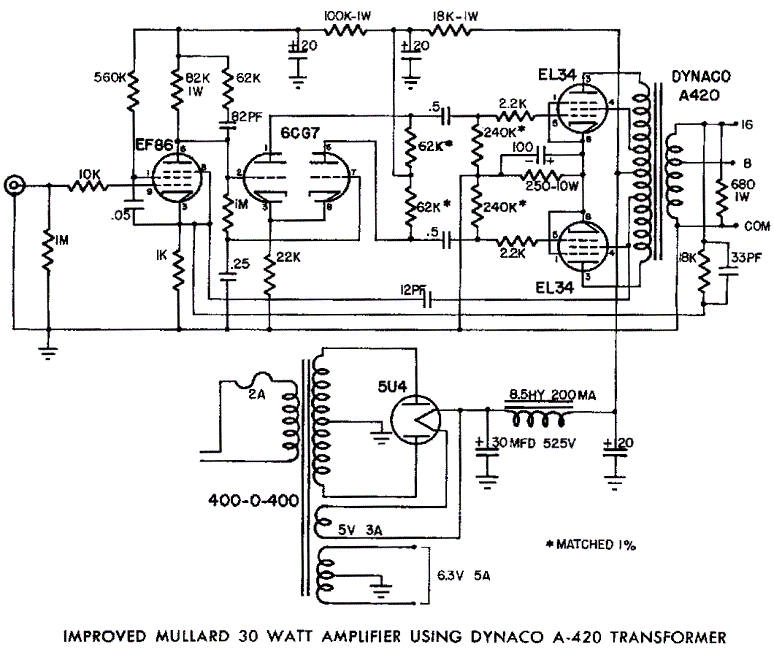
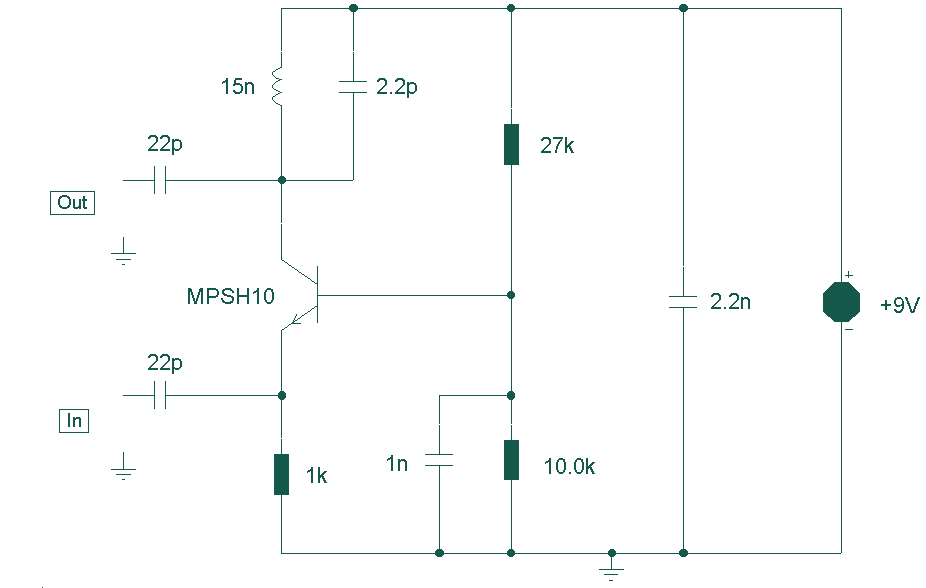
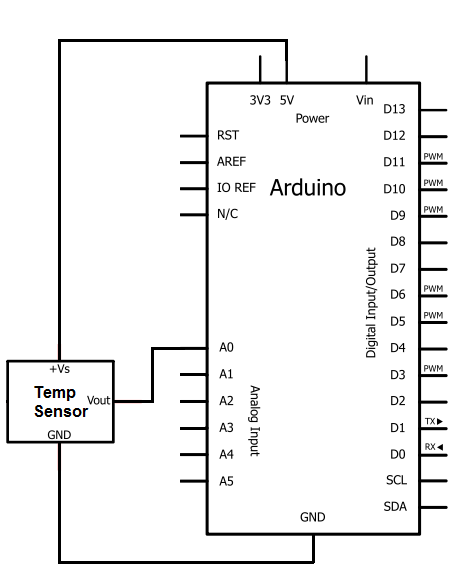
op amp Flow of current in a simple inverting amplifier circuit
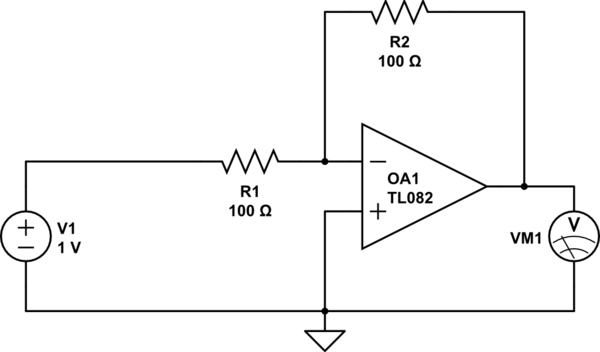
Considering a simple circuit as illustrated below, when the voltage source activates suddenly (changing from 0V to 1V), current will flow through the resistor R1. Assuming an ideal operational amplifier (op-amp) that draws no current, and an ideal voltmeter that also draws no current, the question arises regarding the path of current flow to satisfy Kirchhoff's current law. If the phrase "correctly powered" is interpreted in the context of assuming an ideal op-amp, the critical comment may be retracted; however, it is important to highlight this issue for the benefit of anyone who may later construct actual hardware.
In this scenario, the circuit consists of a voltage source connected to a resistor R1, which is then linked to an ideal op-amp. The op-amp is configured in a non-inverting or inverting configuration, depending on the specific application. The ideal characteristics of the op-amp imply that it has infinite input impedance, resulting in no current entering the input terminals. Consequently, the current flowing through R1 must adhere to Kirchhoff's current law, which states that the sum of currents entering a junction must equal the sum of currents leaving that junction.
When the voltage source transitions from 0V to 1V, a potential difference is established across R1. The current through R1 can be calculated using Ohm's law, where I = V/R, with V being the voltage across R1 and R being the resistance. Given that the op-amp inputs do not draw current, the current flowing through R1 will either flow to the output of the op-amp or through any feedback network connected to the output, depending on the configuration.
For practical applications, it is crucial to consider the limitations of real op-amps and voltmeters, as they do draw some current. This could lead to discrepancies in the behavior of the circuit when transitioning from theoretical assumptions to actual hardware implementation. Understanding these nuances is vital for engineers and designers when developing circuits that utilize op-amps and other components, ensuring that all elements are appropriately accounted for to maintain circuit integrity and performance.Considering a simple circuit like the one below. Let us say that the voltage source suddenly turns on (from 0V to 1V), then current will through through the resistor R1, correct But assuming an ideal op-amp (drawing no current) and an ideal voltmeter (drawing no current), where does the current flow to (in order to satisfy Kirchhoff`s curren t law) If you read "correctly powered" into "assuming an ideal opamp", I have to withdraw my critical comment; I just thought it`s worth pointing out the issue in case the questioner later goes on to build real hardware. 🔗 External reference
In this scenario, the circuit consists of a voltage source connected to a resistor R1, which is then linked to an ideal op-amp. The op-amp is configured in a non-inverting or inverting configuration, depending on the specific application. The ideal characteristics of the op-amp imply that it has infinite input impedance, resulting in no current entering the input terminals. Consequently, the current flowing through R1 must adhere to Kirchhoff's current law, which states that the sum of currents entering a junction must equal the sum of currents leaving that junction.
When the voltage source transitions from 0V to 1V, a potential difference is established across R1. The current through R1 can be calculated using Ohm's law, where I = V/R, with V being the voltage across R1 and R being the resistance. Given that the op-amp inputs do not draw current, the current flowing through R1 will either flow to the output of the op-amp or through any feedback network connected to the output, depending on the configuration.
For practical applications, it is crucial to consider the limitations of real op-amps and voltmeters, as they do draw some current. This could lead to discrepancies in the behavior of the circuit when transitioning from theoretical assumptions to actual hardware implementation. Understanding these nuances is vital for engineers and designers when developing circuits that utilize op-amps and other components, ensuring that all elements are appropriately accounted for to maintain circuit integrity and performance.Considering a simple circuit like the one below. Let us say that the voltage source suddenly turns on (from 0V to 1V), then current will through through the resistor R1, correct But assuming an ideal op-amp (drawing no current) and an ideal voltmeter (drawing no current), where does the current flow to (in order to satisfy Kirchhoff`s curren t law) If you read "correctly powered" into "assuming an ideal opamp", I have to withdraw my critical comment; I just thought it`s worth pointing out the issue in case the questioner later goes on to build real hardware. 🔗 External reference