Overtone crystal oscillator
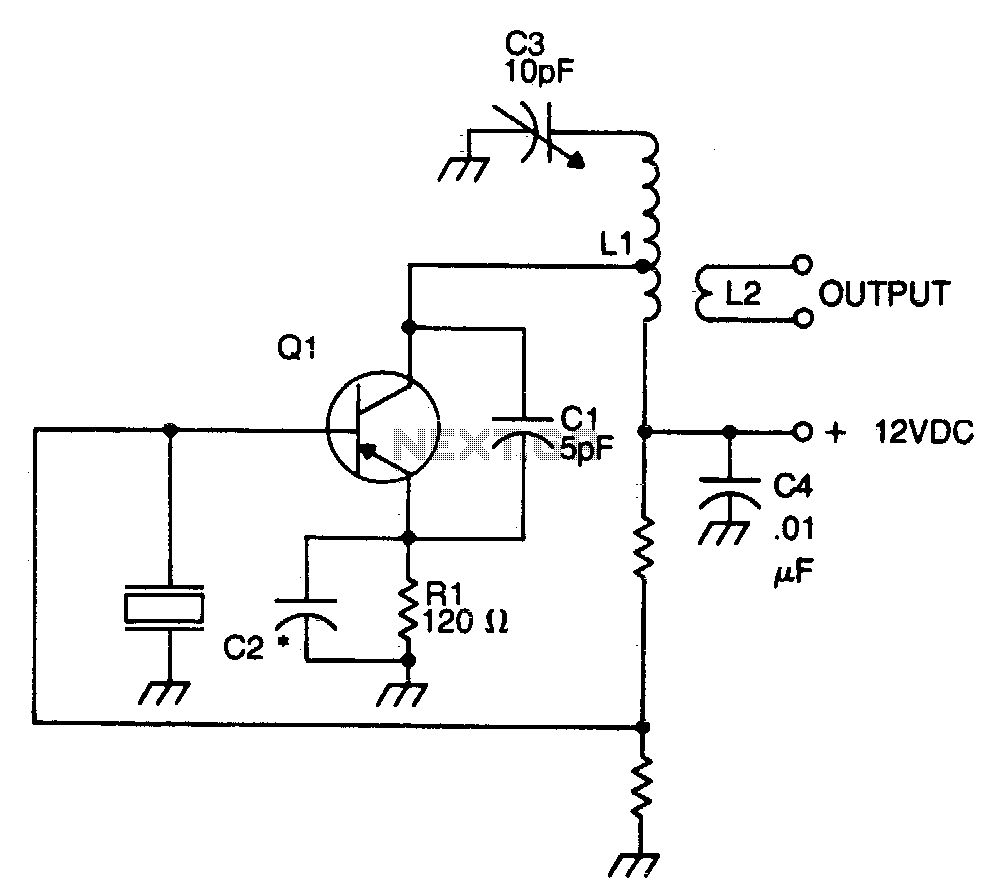
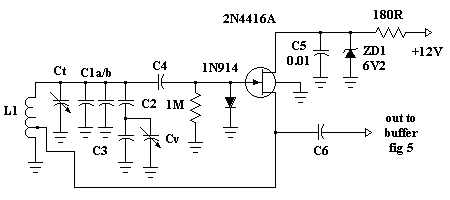
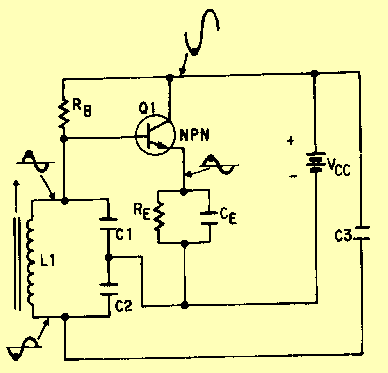
The crystal element in this circuit is connected directly between the base and ground. Capacitor C1 is utilized to enhance feedback due to the internal capacitances of the transistor. This capacitor should be positioned as close as possible to the transistor's case. The LC tank circuit in the collector of the transistor is tuned to the overtone frequency of the crystal. The emitter resistor capacitor must exhibit a capacitive reactance of approximately 90 ohms at the operational frequency. The tap on inductor L1 is employed to match the impedance of the transistor's collector. In most instances, the optimal placement of this tap is roughly one-third from the cold end of the coil. The positioning of this tap represents a compromise between stability and maximum power output. The output signal is extracted from a link coupling coil, L2, which functions through transformer action.
The circuit utilizes a crystal oscillator configuration, where the crystal serves as a frequency-determining element, establishing stable oscillation at its resonant frequency. The connection of the crystal between the base and ground provides a negative feedback mechanism essential for maintaining oscillation. Capacitor C1 is crucial for improving the feedback loop, compensating for the inherent capacitances present in the transistor, which can affect oscillation stability and performance. Its placement is critical; positioning it close to the transistor minimizes parasitic inductance and capacitance, thereby enhancing circuit performance.
The LC tank circuit, consisting of an inductor and capacitor, is designed to resonate at the overtone frequency of the crystal, ensuring that the oscillator operates efficiently at the desired frequency. The emitter resistor capacitor combination is designed to present a specific capacitive reactance, approximately 90 ohms, at the intended operating frequency. This value is essential for optimal performance, as it influences the gain and stability of the oscillator.
Inductor L1 features a tap that serves to match the load impedance at the collector of the transistor. This tap's placement is a critical design consideration, typically positioned about one-third from the cold end of the coil. This location is a strategic compromise, balancing the need for stability against the desire for maximum power output. The output signal is derived from the link coupling coil, L2, which operates based on transformer principles, allowing for efficient signal transfer from the oscillator circuit to the load while preserving the integrity of the signal waveform.The crystal element in this circuit is connected directly between the base and ground. Capacitor Cl is used to improve the feedback due to the internal capacitances of the transistor. This capacitor should be mounted as close as possible to the case of the transistor. The LC tank circuit in the collector of the transistor is tuned to the overtone frequency of the crystal. The emitter resistor capacitor must have a capacitive reactance of approximately 90 ohms at the frequency of operation.
The tap on inductor Ll is used to match the impedance of the collector of the transistor In most cases, the optimum placement of this tap is approximately one-third from the cold end of the coil. The placement of this tap is a trade-off between stability and maximum power output. The output signal is taken from a link coupling coil, L2, and operates by transformer action.
The circuit utilizes a crystal oscillator configuration, where the crystal serves as a frequency-determining element, establishing stable oscillation at its resonant frequency. The connection of the crystal between the base and ground provides a negative feedback mechanism essential for maintaining oscillation. Capacitor C1 is crucial for improving the feedback loop, compensating for the inherent capacitances present in the transistor, which can affect oscillation stability and performance. Its placement is critical; positioning it close to the transistor minimizes parasitic inductance and capacitance, thereby enhancing circuit performance.
The LC tank circuit, consisting of an inductor and capacitor, is designed to resonate at the overtone frequency of the crystal, ensuring that the oscillator operates efficiently at the desired frequency. The emitter resistor capacitor combination is designed to present a specific capacitive reactance, approximately 90 ohms, at the intended operating frequency. This value is essential for optimal performance, as it influences the gain and stability of the oscillator.
Inductor L1 features a tap that serves to match the load impedance at the collector of the transistor. This tap's placement is a critical design consideration, typically positioned about one-third from the cold end of the coil. This location is a strategic compromise, balancing the need for stability against the desire for maximum power output. The output signal is derived from the link coupling coil, L2, which operates based on transformer principles, allowing for efficient signal transfer from the oscillator circuit to the load while preserving the integrity of the signal waveform.The crystal element in this circuit is connected directly between the base and ground. Capacitor Cl is used to improve the feedback due to the internal capacitances of the transistor. This capacitor should be mounted as close as possible to the case of the transistor. The LC tank circuit in the collector of the transistor is tuned to the overtone frequency of the crystal. The emitter resistor capacitor must have a capacitive reactance of approximately 90 ohms at the frequency of operation.
The tap on inductor Ll is used to match the impedance of the collector of the transistor In most cases, the optimum placement of this tap is approximately one-third from the cold end of the coil. The placement of this tap is a trade-off between stability and maximum power output. The output signal is taken from a link coupling coil, L2, and operates by transformer action.