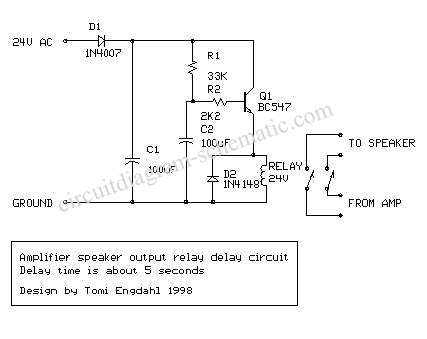
PEAK VOLTMETER FOR NARROW PULSES
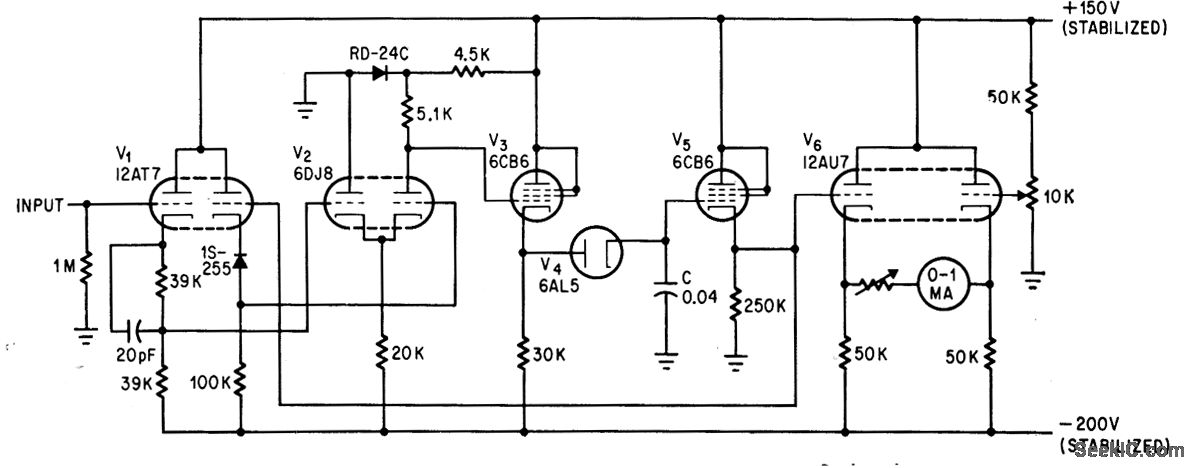
The addition of a dual-triode amplifier (V2) to a conventional peak voltmeter reduces the charging time constant while increasing the available time for measuring peak values. Linearity is maintained up to 40 volts.
The integration of a dual-triode amplifier into a peak voltmeter circuit significantly enhances its performance by optimizing the measurement of transient signals. The dual-triode configuration allows for improved signal amplification, which is crucial for accurately capturing peak voltages in rapidly changing electrical signals.
In this setup, the dual-triode amplifier (V2) serves to minimize the charging time constant of the voltmeter. This reduction is critical because it allows the voltmeter to respond more quickly to changes in voltage, thereby providing a more accurate representation of peak values. The amplifier's design contributes to a high input impedance, which prevents loading effects that could distort the measurement.
The circuit operates effectively within a voltage range of up to 40 volts, maintaining good linearity throughout this range. This characteristic is essential for applications where precise voltage measurements are required, such as in audio electronics or signal processing. The dual-triode configuration ensures that the amplifier can handle variations in input signals without significant distortion, thus preserving the integrity of the measured peak values.
Overall, the enhancement of the peak voltmeter's response through the addition of a dual-triode amplifier exemplifies a practical application of amplifier technology in improving measurement accuracy and speed in electronic instrumentation.Addition of dual-triode amplifier V2 to conventional peak voltmeter reduces charging time constant while increasing available time for measuring peak value. Linearity is good up to 40 v. -M. Uno, Amplifier Improves Peak Voltmeter Response, Electronics, 37:14, p 73. 🔗 External reference
The integration of a dual-triode amplifier into a peak voltmeter circuit significantly enhances its performance by optimizing the measurement of transient signals. The dual-triode configuration allows for improved signal amplification, which is crucial for accurately capturing peak voltages in rapidly changing electrical signals.
In this setup, the dual-triode amplifier (V2) serves to minimize the charging time constant of the voltmeter. This reduction is critical because it allows the voltmeter to respond more quickly to changes in voltage, thereby providing a more accurate representation of peak values. The amplifier's design contributes to a high input impedance, which prevents loading effects that could distort the measurement.
The circuit operates effectively within a voltage range of up to 40 volts, maintaining good linearity throughout this range. This characteristic is essential for applications where precise voltage measurements are required, such as in audio electronics or signal processing. The dual-triode configuration ensures that the amplifier can handle variations in input signals without significant distortion, thus preserving the integrity of the measured peak values.
Overall, the enhancement of the peak voltmeter's response through the addition of a dual-triode amplifier exemplifies a practical application of amplifier technology in improving measurement accuracy and speed in electronic instrumentation.Addition of dual-triode amplifier V2 to conventional peak voltmeter reduces charging time constant while increasing available time for measuring peak value. Linearity is good up to 40 v. -M. Uno, Amplifier Improves Peak Voltmeter Response, Electronics, 37:14, p 73. 🔗 External reference