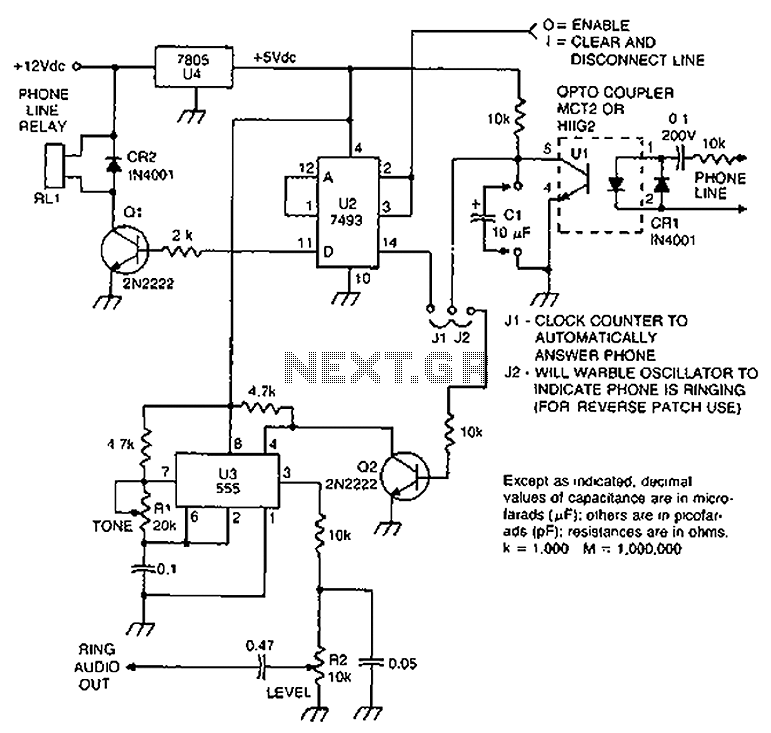
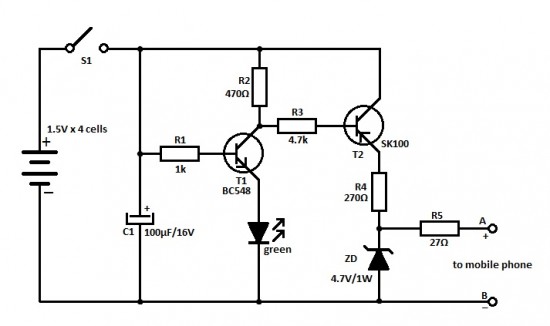
Phone Message Flasher
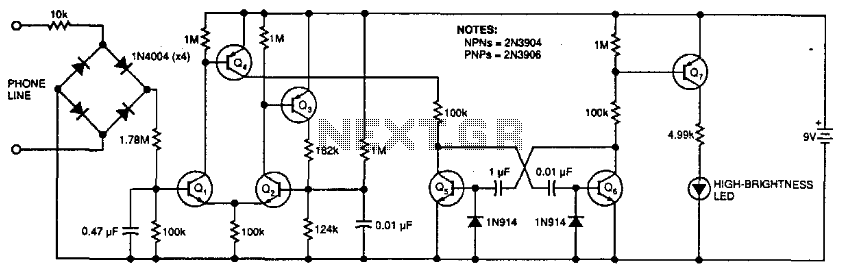
This circuit flashes an LED to indicate that a phone rang during the user's absence. A differential amplifier with hysteresis (Q1, Q2, and Q3) detects high line voltage (ringing), which activates Q4, a multivibrator composed of Q5 and Q6, and subsequently flashes the LED through Q7. Q1 and Q2 remain activated until the phone line voltage drops below 9 V, signaling an off-hook condition.
The circuit utilizes a differential amplifier configured with transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3 to detect the presence of a ringing voltage on the telephone line. The hysteresis feature ensures that the circuit is less sensitive to noise and false triggering, providing reliable detection of ringing signals. When the phone rings, the voltage across the line increases, causing the differential amplifier to output a high signal, which turns on transistor Q4.
Transistor Q4 acts as a switch that enables the multivibrator circuit formed by Q5 and Q6. This multivibrator generates a square wave signal that drives the LED flashing mechanism. The flashing LED serves as a visual indicator that a call was received while the user was away. The LED is connected to transistor Q7, which controls its on/off state based on the output of the multivibrator.
The circuit is designed to maintain the activation of Q1 and Q2 as long as the line voltage remains above 9 V. This feature is crucial as it prevents the circuit from resetting prematurely when the phone is off-hook, ensuring that the LED continues to flash until the user acknowledges the missed call. Once the line voltage drops below the threshold, indicating that the phone is off-hook, Q1 and Q2 turn off, effectively disabling the circuit and stopping the LED from flashing.
This design is particularly useful for users who may not be near their phone when it rings, providing a clear indication of missed calls through the visual feedback of the LED. This circuit flashes an LED to indicate that your phone rang during your absence. A differential amplifier with hyste resis (Ql, Q2, and Q3) detects high line voltage (ringing), which turns on Q4, multivibrator Q5/Q6, and flashes the LED via Q7. Ql and Q2 remain on until the phone-line voltage drops to less than 9 V, which indicates an off-hook condition.
The circuit utilizes a differential amplifier configured with transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3 to detect the presence of a ringing voltage on the telephone line. The hysteresis feature ensures that the circuit is less sensitive to noise and false triggering, providing reliable detection of ringing signals. When the phone rings, the voltage across the line increases, causing the differential amplifier to output a high signal, which turns on transistor Q4.
Transistor Q4 acts as a switch that enables the multivibrator circuit formed by Q5 and Q6. This multivibrator generates a square wave signal that drives the LED flashing mechanism. The flashing LED serves as a visual indicator that a call was received while the user was away. The LED is connected to transistor Q7, which controls its on/off state based on the output of the multivibrator.
The circuit is designed to maintain the activation of Q1 and Q2 as long as the line voltage remains above 9 V. This feature is crucial as it prevents the circuit from resetting prematurely when the phone is off-hook, ensuring that the LED continues to flash until the user acknowledges the missed call. Once the line voltage drops below the threshold, indicating that the phone is off-hook, Q1 and Q2 turn off, effectively disabling the circuit and stopping the LED from flashing.
This design is particularly useful for users who may not be near their phone when it rings, providing a clear indication of missed calls through the visual feedback of the LED. This circuit flashes an LED to indicate that your phone rang during your absence. A differential amplifier with hyste resis (Ql, Q2, and Q3) detects high line voltage (ringing), which turns on Q4, multivibrator Q5/Q6, and flashes the LED via Q7. Ql and Q2 remain on until the phone-line voltage drops to less than 9 V, which indicates an off-hook condition.
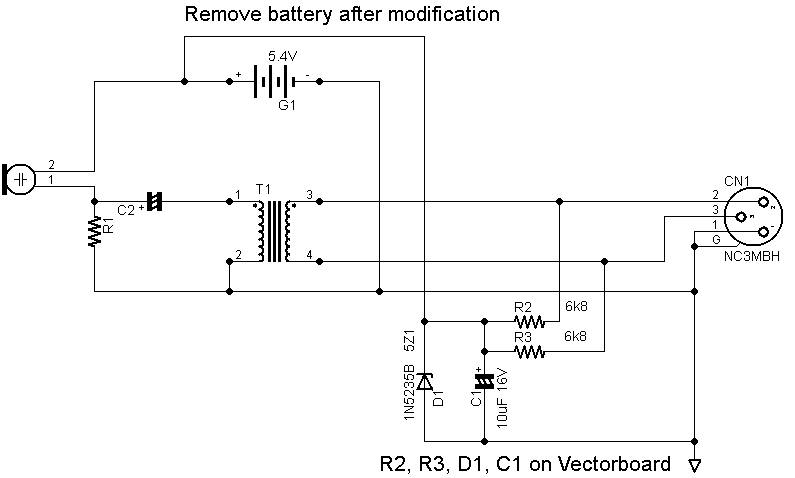
%2B2%2BCH%2Bby%2BIC%2B%2BNE5532%2Bor%2BLF353.jpg)