Photo interrupter circuit diagram
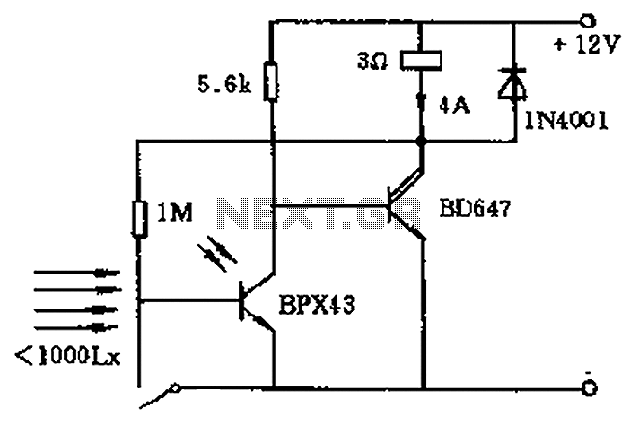
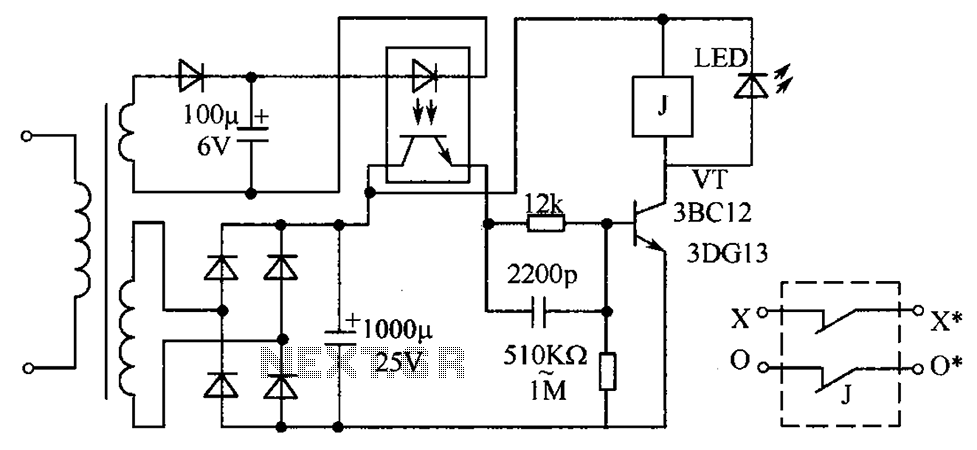
In the circuit's resting (dark) state, current flows through the electromagnet M. When light shines on the phototransistor, it turns on, causing the final stage transistor to enter the OFF state, which releases the solenoid. A 1M ohm feedback to the photosensitive base of the transistor ensures that even when light is absent, the time-sensitive transistor remains activated. The system resets to its initial state by pressing the reset button T. A Darlington transistor can be utilized in place of an amplifier for greater magnification.
The described circuit operates on a principle of light sensitivity and feedback control. Initially, in the dark state, the electromagnet M is energized, allowing a current to flow that keeps the system in a ready state. The phototransistor acts as a light sensor; when illuminated, it activates, which subsequently deactivates the final stage transistor. This deactivation results in the solenoid being released, indicating a change in the circuit state from active to inactive.
The inclusion of a 1M ohm feedback resistor plays a crucial role in maintaining the transistor’s state. This feedback mechanism allows the circuit to retain its activated state even after the light source is removed. The time-sensitive nature of the transistor is critical for ensuring that the circuit remains responsive to transient changes in light conditions.
The reset mechanism is straightforward; pressing the reset button T reverts the circuit back to its original state, allowing for repeated operation. This functionality is essential for applications where the circuit needs to be reset frequently without manual intervention in the light detection process.
Furthermore, the option to use a Darlington transistor as an amplifier enhances the circuit's performance by providing a higher current gain. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications requiring substantial amplification of the input signal from the phototransistor, thereby improving overall sensitivity and responsiveness of the circuit.
Overall, this circuit design effectively integrates phototransistor operation, feedback mechanisms, and amplification to create a versatile system suitable for various electronic applications. Circuit at rest (dark) state operation the electromagnet M current flows, once there is sufficient strength so that light shines on the phototransistor is turned on, that is th e final stage transistor is in the OFF state, the solenoid release. Because by 1M ohm feedback to the photosensitive base of the transistor effect, so that even light cancel time-sensitive transistor is still turned on. Until press the reset button T, in order to return to the initial state. Darlington transistor which can be used in place of an amplifier greater magnification.
The described circuit operates on a principle of light sensitivity and feedback control. Initially, in the dark state, the electromagnet M is energized, allowing a current to flow that keeps the system in a ready state. The phototransistor acts as a light sensor; when illuminated, it activates, which subsequently deactivates the final stage transistor. This deactivation results in the solenoid being released, indicating a change in the circuit state from active to inactive.
The inclusion of a 1M ohm feedback resistor plays a crucial role in maintaining the transistor’s state. This feedback mechanism allows the circuit to retain its activated state even after the light source is removed. The time-sensitive nature of the transistor is critical for ensuring that the circuit remains responsive to transient changes in light conditions.
The reset mechanism is straightforward; pressing the reset button T reverts the circuit back to its original state, allowing for repeated operation. This functionality is essential for applications where the circuit needs to be reset frequently without manual intervention in the light detection process.
Furthermore, the option to use a Darlington transistor as an amplifier enhances the circuit's performance by providing a higher current gain. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications requiring substantial amplification of the input signal from the phototransistor, thereby improving overall sensitivity and responsiveness of the circuit.
Overall, this circuit design effectively integrates phototransistor operation, feedback mechanisms, and amplification to create a versatile system suitable for various electronic applications. Circuit at rest (dark) state operation the electromagnet M current flows, once there is sufficient strength so that light shines on the phototransistor is turned on, that is th e final stage transistor is in the OFF state, the solenoid release. Because by 1M ohm feedback to the photosensitive base of the transistor effect, so that even light cancel time-sensitive transistor is still turned on. Until press the reset button T, in order to return to the initial state. Darlington transistor which can be used in place of an amplifier greater magnification.