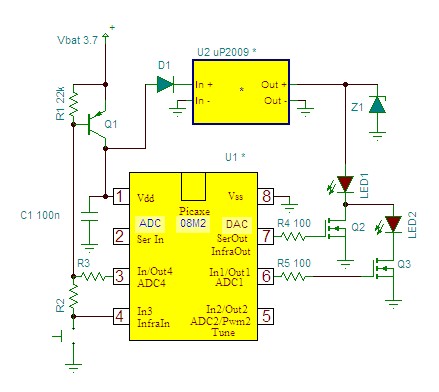
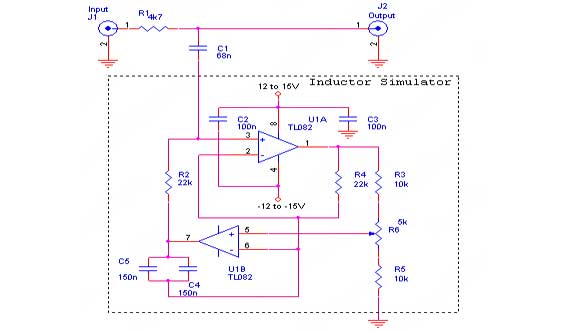
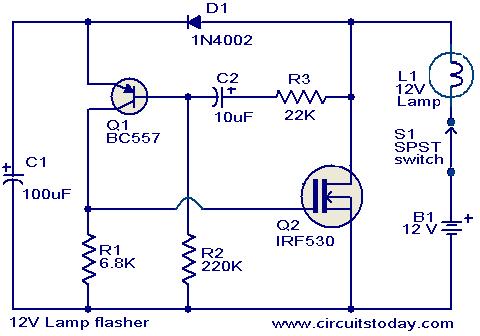
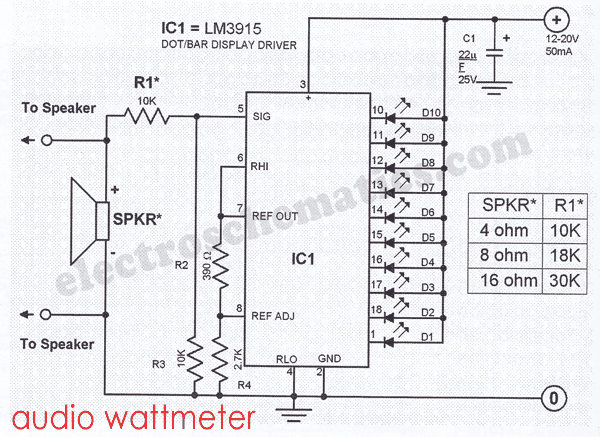
transducer current limiter circuit
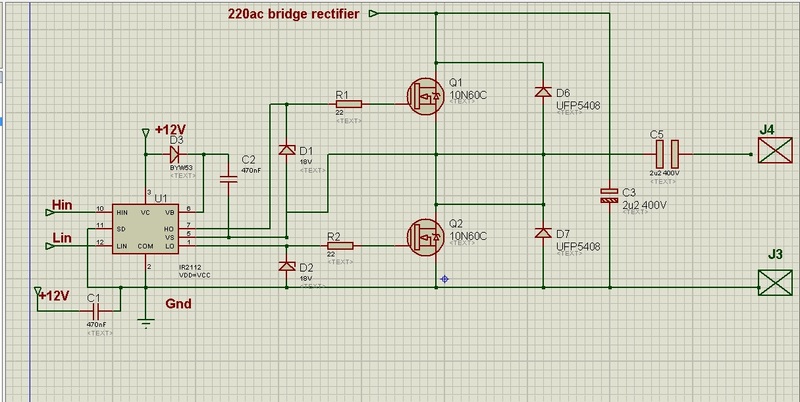
This circuit is designed to drive an ultrasonic transducer. A question has arisen regarding how to limit the output current, as a 60W transducer may be at risk of damage due to excessive current. Guidance or examples for integrating a current limiter circuit would be appreciated. Applications include high-power ultrasonic uses such as ultrasonic cleaning tanks, ultrasonic plastic welding, ground sonar transducers, biodiesel mixer transducers, solid separation transducers, prevention of organism growth on boat hulls, and high-torque traveling wave ultrasonic motors. For a ring transducer with a thickness of 5.5 mm, the maximum input voltage is 1,650V, but the power output should not exceed 70W for a single transducer or 50W for a parallel setup. If the temperature exceeds 120°C, the transducer risks depolarization and potential fracture. Therefore, an operating voltage of 450-500V is recommended.
To effectively drive an ultrasonic transducer while ensuring its protection, a driver circuit must be designed with a current limiting feature. The circuit typically includes a power source capable of delivering the required voltage and current, along with a suitable driver stage that can handle high-frequency signals.
A common approach to limit the output current involves the use of a current sensing resistor in series with the transducer. This resistor allows for the measurement of the current flowing through the circuit. The voltage drop across this resistor is proportional to the current, and it can be monitored using an operational amplifier configured as a comparator. When the current exceeds a predefined threshold, the comparator output can trigger a control mechanism, such as a transistor or a relay, to reduce the drive signal or shut off the output to prevent damage to the transducer.
In addition to the current limiting feature, it is crucial to consider the voltage ratings. For the specified ring transducer, the driver circuit should be able to handle input voltages up to 1,650V, while ensuring that the output power remains within safe limits. The circuit design should incorporate high-voltage components capable of withstanding these conditions without failure.
Thermal management is another critical aspect. Since the transducer can become damaged if the temperature exceeds 120°C, a thermal cutoff or sensor may be integrated into the circuit to monitor the temperature. If it approaches the critical threshold, the circuit can be designed to reduce the output power or shut down entirely.
Lastly, the applications for this ultrasonic driver circuit are diverse, ranging from industrial cleaning processes to biomedical applications. Each application may have specific requirements for frequency, power, and control, which should be taken into account during the design phase to ensure optimal performance and reliability.Drive an ultrasonic transducer by using this driver circuit. I have a quesiton for this operation. How can I limit my output current I am using a 60W transducer and maybe it can be damaged because of the output current. Could you direct me, or share sample to add this limiter circuit Applications: High-power ultrasonic applications such as ultrasonic cleaning tanks,
ultrasonic plastic welding, ground sonar transducer, Bio Diesel mixer transducer, Solid separation transducer, stop organism growth on boat hull, Biodiesel mixing transducer, High-Torque Traveling Wave Ultrasonic Motor and others. Notes: For the thickness of the ring transducer used (5. 5mm), the maximum input voltage is 1, 650V but the power output should not exceed 70W for single transducer or 50W for parallel setup.
If the temperature is higher than 120C the transducer will depolarize and maybe fracture. So the operating voltage suggested is between 450-500V. 🔗 External reference
To effectively drive an ultrasonic transducer while ensuring its protection, a driver circuit must be designed with a current limiting feature. The circuit typically includes a power source capable of delivering the required voltage and current, along with a suitable driver stage that can handle high-frequency signals.
A common approach to limit the output current involves the use of a current sensing resistor in series with the transducer. This resistor allows for the measurement of the current flowing through the circuit. The voltage drop across this resistor is proportional to the current, and it can be monitored using an operational amplifier configured as a comparator. When the current exceeds a predefined threshold, the comparator output can trigger a control mechanism, such as a transistor or a relay, to reduce the drive signal or shut off the output to prevent damage to the transducer.
In addition to the current limiting feature, it is crucial to consider the voltage ratings. For the specified ring transducer, the driver circuit should be able to handle input voltages up to 1,650V, while ensuring that the output power remains within safe limits. The circuit design should incorporate high-voltage components capable of withstanding these conditions without failure.
Thermal management is another critical aspect. Since the transducer can become damaged if the temperature exceeds 120°C, a thermal cutoff or sensor may be integrated into the circuit to monitor the temperature. If it approaches the critical threshold, the circuit can be designed to reduce the output power or shut down entirely.
Lastly, the applications for this ultrasonic driver circuit are diverse, ranging from industrial cleaning processes to biomedical applications. Each application may have specific requirements for frequency, power, and control, which should be taken into account during the design phase to ensure optimal performance and reliability.Drive an ultrasonic transducer by using this driver circuit. I have a quesiton for this operation. How can I limit my output current I am using a 60W transducer and maybe it can be damaged because of the output current. Could you direct me, or share sample to add this limiter circuit Applications: High-power ultrasonic applications such as ultrasonic cleaning tanks,
ultrasonic plastic welding, ground sonar transducer, Bio Diesel mixer transducer, Solid separation transducer, stop organism growth on boat hull, Biodiesel mixing transducer, High-Torque Traveling Wave Ultrasonic Motor and others. Notes: For the thickness of the ring transducer used (5. 5mm), the maximum input voltage is 1, 650V but the power output should not exceed 70W for single transducer or 50W for parallel setup.
If the temperature is higher than 120C the transducer will depolarize and maybe fracture. So the operating voltage suggested is between 450-500V. 🔗 External reference