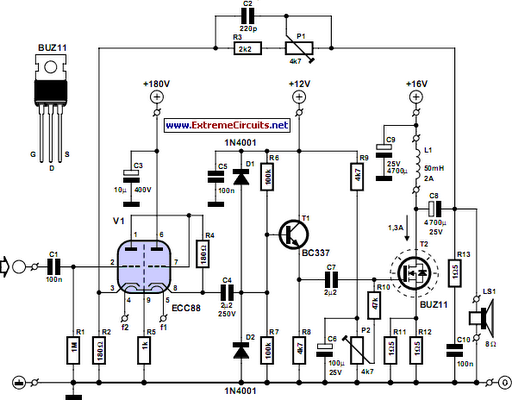
Pink Noise Generator for Audio Testing
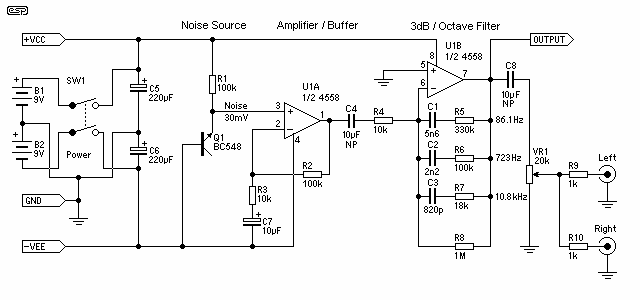
White noise (the sound you hear when a TV is tuned to a non-existent station) has a frequency characteristic which raises the power level by 3dB with each increasing octave, and is not suitable for response testing (and will probably blow your tweeters as well). By combining a 3dB / octave filter and a white noise source, we can get a very good approximation to "perfect" pink noise, where the power in the octave (for example) 40 to 80Hz is exactly the same as in the octave 10kHz to 20kHz.
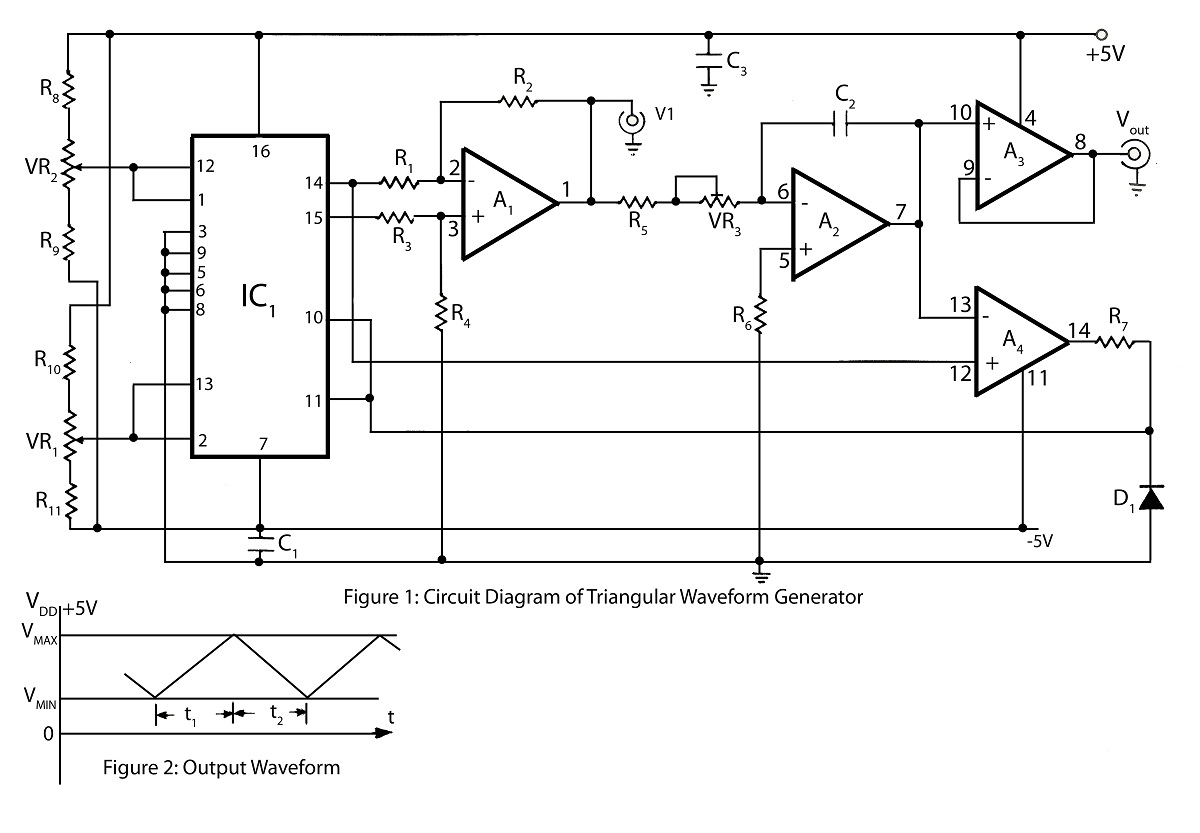
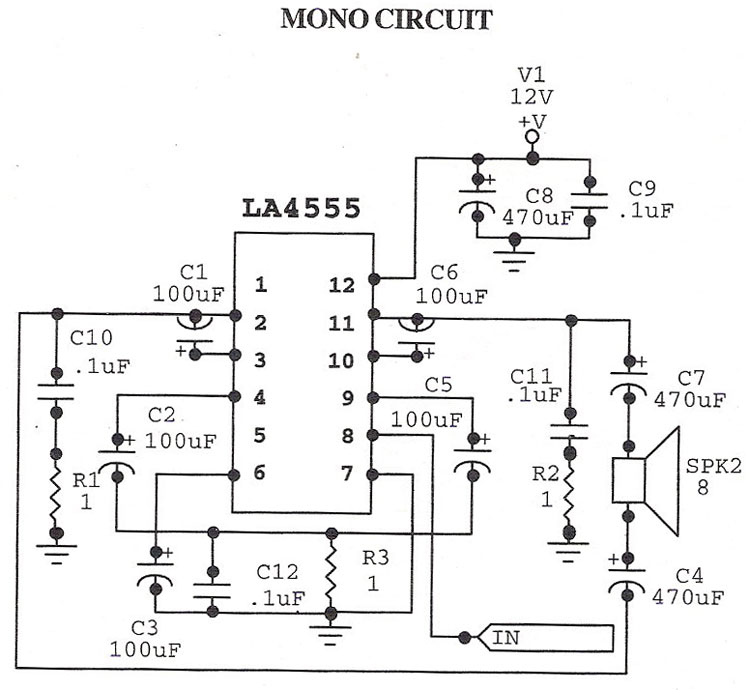
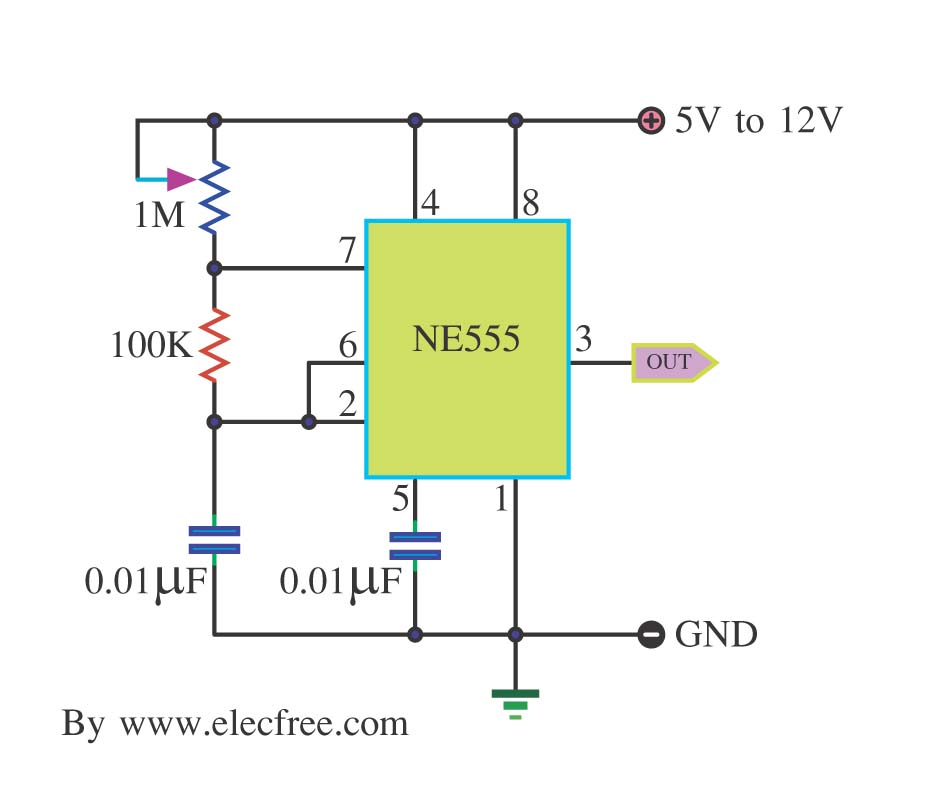
To create a circuit that generates pink noise from white noise, a combination of a white noise generator and a 3dB/octave filter is required. The white noise generator can be implemented using a simple transistor circuit or a dedicated noise IC, which produces a broadband noise signal. This signal exhibits a flat frequency response across a wide range, typically from 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
The filter circuit can be designed using operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured as low-pass filters. The filter should be designed to provide a roll-off of 3dB per octave, which can be achieved using multiple stages of RC (resistor-capacitor) filtering. Each stage of the filter will contribute to the overall frequency response, ensuring that the power level decreases by 3dB for each octave above the cutoff frequency.
For example, if the cutoff frequency is set at 1 kHz, the filter will allow frequencies below 1 kHz to pass while attenuating those above it. This ensures that the power levels in the lower frequency bands are equalized with those in higher frequency bands, thus approximating the pink noise characteristic.
The output of the filter can be monitored using an oscilloscope or a spectrum analyzer to verify the desired frequency response. Additionally, care should be taken to ensure that the output level is suitable for the connected audio equipment to prevent damage, particularly to tweeters, which are sensitive to high-frequency signals.
Overall, this circuit provides an effective means of generating pink noise for various applications, including audio testing and sound masking, by transforming the broadband white noise into a more balanced frequency output.White noise (the sound you hear when a TV is tuned to a non-existent station) has a frequency characteristic which raises the power level by 3dB with each increasing octave, and is not suitable for response testing (and will probably blow your tweeters as well). By combining a 3dB / octave filter and a white noise source, we can get a very good approximation to "perfect" pink noise, where the power in the octave (for example) 40 to 80Hz is exactly the same as in the octave 10kHz to 20kHz.
🔗 External reference
To create a circuit that generates pink noise from white noise, a combination of a white noise generator and a 3dB/octave filter is required. The white noise generator can be implemented using a simple transistor circuit or a dedicated noise IC, which produces a broadband noise signal. This signal exhibits a flat frequency response across a wide range, typically from 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
The filter circuit can be designed using operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured as low-pass filters. The filter should be designed to provide a roll-off of 3dB per octave, which can be achieved using multiple stages of RC (resistor-capacitor) filtering. Each stage of the filter will contribute to the overall frequency response, ensuring that the power level decreases by 3dB for each octave above the cutoff frequency.
For example, if the cutoff frequency is set at 1 kHz, the filter will allow frequencies below 1 kHz to pass while attenuating those above it. This ensures that the power levels in the lower frequency bands are equalized with those in higher frequency bands, thus approximating the pink noise characteristic.
The output of the filter can be monitored using an oscilloscope or a spectrum analyzer to verify the desired frequency response. Additionally, care should be taken to ensure that the output level is suitable for the connected audio equipment to prevent damage, particularly to tweeters, which are sensitive to high-frequency signals.
Overall, this circuit provides an effective means of generating pink noise for various applications, including audio testing and sound masking, by transforming the broadband white noise into a more balanced frequency output.White noise (the sound you hear when a TV is tuned to a non-existent station) has a frequency characteristic which raises the power level by 3dB with each increasing octave, and is not suitable for response testing (and will probably blow your tweeters as well). By combining a 3dB / octave filter and a white noise source, we can get a very good approximation to "perfect" pink noise, where the power in the octave (for example) 40 to 80Hz is exactly the same as in the octave 10kHz to 20kHz.
🔗 External reference