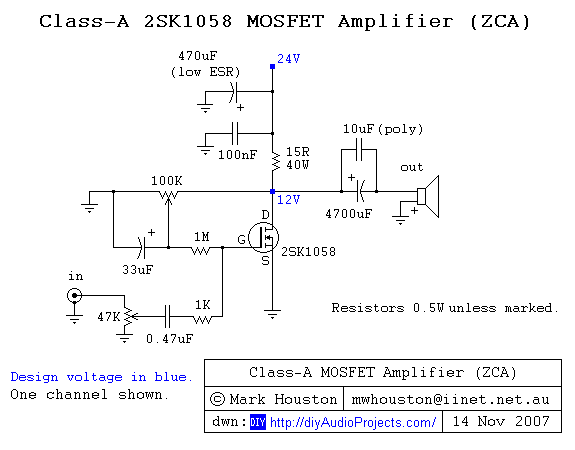
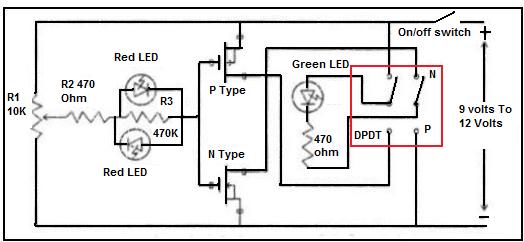
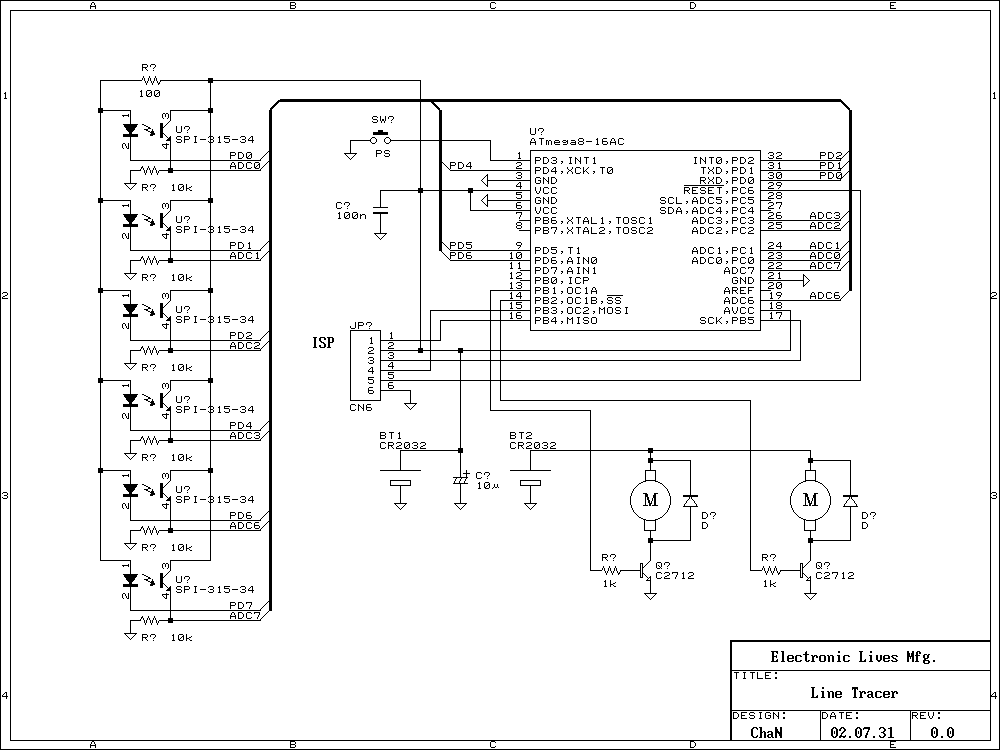
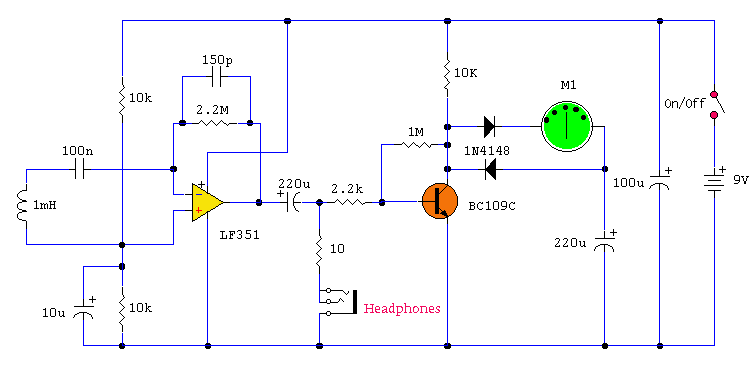
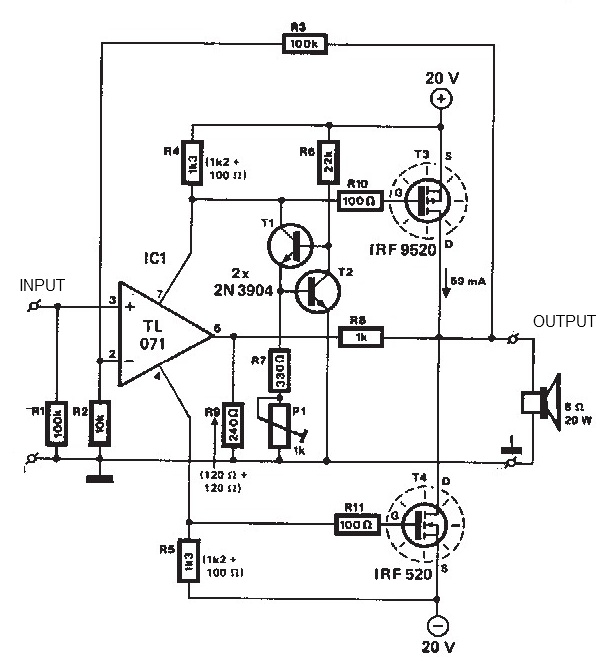
PMOS FET Following The Output for Soft-Start Mechanism

A PMOS FET switch regulator output is utilized in series with the regulator's load, as illustrated in the accompanying diagram. This represents a straightforward approach to circuit design.
The described configuration employs a PMOS FET as a switching element in a linear regulator circuit. In this setup, the PMOS FET is positioned in series with the load, allowing for efficient control of the output voltage and current delivered to the load. The PMOS FET operates by switching on and off based on the control signal, which modulates the power supplied to the load according to the desired output characteristics.
In this arrangement, the gate of the PMOS FET is driven by a control voltage that determines whether the FET is in the on-state or off-state. When a positive voltage is applied to the gate relative to the source, the PMOS FET turns off, interrupting the flow of current to the load. Conversely, when the gate voltage is pulled low, the FET turns on, allowing current to flow through to the load.
The simplicity of this design lies in its minimal component count and straightforward operation. It is particularly advantageous in applications where low-power switching is required, as it can efficiently handle varying load conditions while maintaining a stable output voltage. Additionally, the use of a PMOS FET allows for high-side switching, which is beneficial in certain circuit configurations where the load needs to be connected to the positive supply rail.
In summary, the PMOS FET switch regulator configuration offers an effective and uncomplicated method for regulating output voltage in electronic circuits, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in power management systems.Using the following PMOS FET switch regulator output, in series with the regulator`s load as shown in the picture below is the most simple method. Switch.. 🔗 External reference
The described configuration employs a PMOS FET as a switching element in a linear regulator circuit. In this setup, the PMOS FET is positioned in series with the load, allowing for efficient control of the output voltage and current delivered to the load. The PMOS FET operates by switching on and off based on the control signal, which modulates the power supplied to the load according to the desired output characteristics.
In this arrangement, the gate of the PMOS FET is driven by a control voltage that determines whether the FET is in the on-state or off-state. When a positive voltage is applied to the gate relative to the source, the PMOS FET turns off, interrupting the flow of current to the load. Conversely, when the gate voltage is pulled low, the FET turns on, allowing current to flow through to the load.
The simplicity of this design lies in its minimal component count and straightforward operation. It is particularly advantageous in applications where low-power switching is required, as it can efficiently handle varying load conditions while maintaining a stable output voltage. Additionally, the use of a PMOS FET allows for high-side switching, which is beneficial in certain circuit configurations where the load needs to be connected to the positive supply rail.
In summary, the PMOS FET switch regulator configuration offers an effective and uncomplicated method for regulating output voltage in electronic circuits, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in power management systems.Using the following PMOS FET switch regulator output, in series with the regulator`s load as shown in the picture below is the most simple method. Switch.. 🔗 External reference