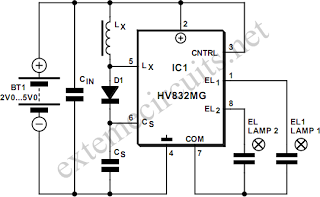
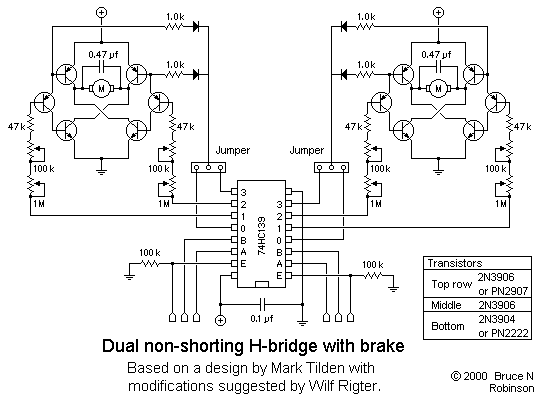
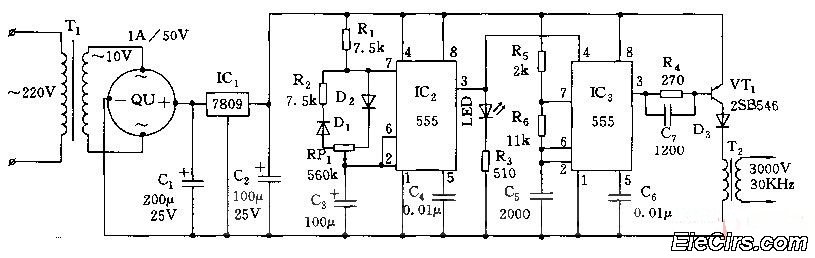
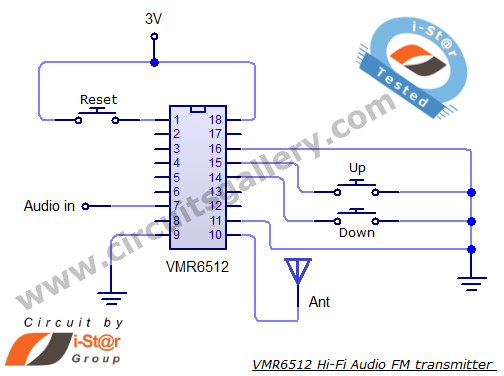
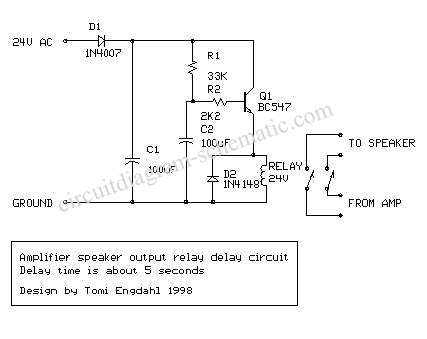
Programmable bandpass using twin-t bridge
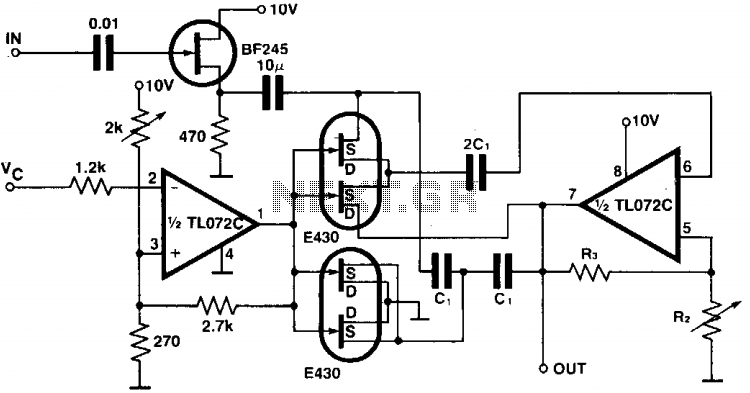
The circuit provides a programmable bandpass filter where both the cutoff frequency and gain (A) can be controlled independently. In the twin-T bridge configuration, the resistors R and R/2 are replaced by two double FETs, with the channel resistance of the first FET in series and the channel resistances of the second FET in parallel to simulate the resistance R/2. Both of these resistors are controlled by a voltage (Vc) that ranges from 0 V to approximately 1 V. The gain of the circuit is determined by the resistors R2 and R3.
The described circuit employs a programmable bandpass filter architecture, utilizing a twin-T bridge configuration for effective frequency selection. The independent control of the cutoff frequency and gain is a significant advantage, allowing for versatile applications in signal processing.
The twin-T bridge typically consists of a combination of resistors and capacitors that determine the frequency response. In this design, traditional resistors R and R/2 are substituted with double FETs, enhancing the circuit's programmability and responsiveness. The first FET operates in series, contributing to the overall resistance, while the second FET is configured in a parallel arrangement to emulate the desired resistance of R/2. This arrangement allows for finer control over the circuit's characteristics.
The control voltage (Vc), varying between 0 V and 1 V, directly influences the channel resistances of the FETs, thereby adjusting the cutoff frequency of the bandpass filter. This feature enables the circuit to adapt to different signal conditions and requirements dynamically.
The gain of the circuit is managed through resistors R2 and R3, which are critical in setting the amplification level of the output signal. By selecting appropriate values for these resistors, the user can achieve the desired gain, further enhancing the circuit's flexibility. This design is particularly useful in applications where precise control over frequency and gain is essential, such as in audio processing, communication systems, and instrumentation.
In summary, this programmable bandpass filter circuit represents an advanced approach to signal processing, leveraging FET technology for improved performance and adaptability. The ability to independently control both cutoff frequency and gain makes it an invaluable tool in various electronic applications.The circuit gives a programmable bandpass where both the cut-over frequency and the gain, A, are controlled independently. In the twin-T bridge the resistors R and R/2 are replaced by two double FETs, 430, the channel resistance of the first one in the series, the channel resistances of the second one are in parallel as to stimulate the resistance R/2.
Both these resistors are controlled by Vc which ranges from 0 V to about 1 V. The gain of the circuit is set by means of the resistors R2 and R3.
The described circuit employs a programmable bandpass filter architecture, utilizing a twin-T bridge configuration for effective frequency selection. The independent control of the cutoff frequency and gain is a significant advantage, allowing for versatile applications in signal processing.
The twin-T bridge typically consists of a combination of resistors and capacitors that determine the frequency response. In this design, traditional resistors R and R/2 are substituted with double FETs, enhancing the circuit's programmability and responsiveness. The first FET operates in series, contributing to the overall resistance, while the second FET is configured in a parallel arrangement to emulate the desired resistance of R/2. This arrangement allows for finer control over the circuit's characteristics.
The control voltage (Vc), varying between 0 V and 1 V, directly influences the channel resistances of the FETs, thereby adjusting the cutoff frequency of the bandpass filter. This feature enables the circuit to adapt to different signal conditions and requirements dynamically.
The gain of the circuit is managed through resistors R2 and R3, which are critical in setting the amplification level of the output signal. By selecting appropriate values for these resistors, the user can achieve the desired gain, further enhancing the circuit's flexibility. This design is particularly useful in applications where precise control over frequency and gain is essential, such as in audio processing, communication systems, and instrumentation.
In summary, this programmable bandpass filter circuit represents an advanced approach to signal processing, leveraging FET technology for improved performance and adaptability. The ability to independently control both cutoff frequency and gain makes it an invaluable tool in various electronic applications.The circuit gives a programmable bandpass where both the cut-over frequency and the gain, A, are controlled independently. In the twin-T bridge the resistors R and R/2 are replaced by two double FETs, 430, the channel resistance of the first one in the series, the channel resistances of the second one are in parallel as to stimulate the resistance R/2.
Both these resistors are controlled by Vc which ranges from 0 V to about 1 V. The gain of the circuit is set by means of the resistors R2 and R3.