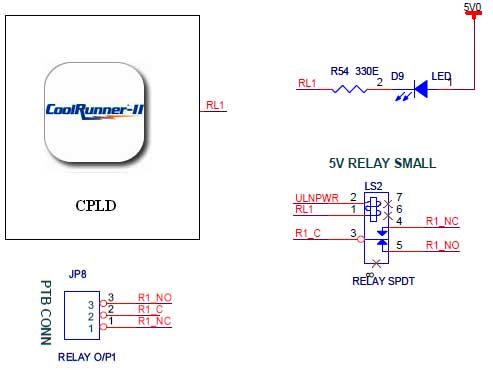
push button interfacing with spartan 3an fpga

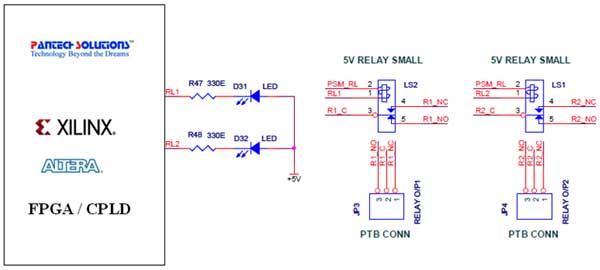
The Spartan-3an board features eight slide switches, as illustrated in the accompanying figure. The push button inputs are typically in a low state and transition to a high state only when the button is pressed. These push buttons are connected to the FPGA I/O lines.
The Spartan-3an board is designed to facilitate various input configurations through its eight slide switches and push button inputs. Each slide switch can be used to represent binary states, allowing for easy manual input of control signals. The push buttons, when activated, provide a momentary high signal to the FPGA, enabling it to respond to user interactions.
The push button inputs are connected to the FPGA's I/O lines, which are configured to detect the state changes. When a push button is pressed, the corresponding I/O line transitions from low to high, which can be used to trigger specific functions or processes within the FPGA. This functionality is critical for applications requiring user input, such as in development and testing environments.
In terms of circuit design, it is important to incorporate pull-down resistors for the push button inputs to ensure that the I/O lines remain in a defined low state when the buttons are not pressed. This prevents floating states that could lead to unpredictable behavior. The slide switches can similarly be connected with pull-up or pull-down resistors, depending on the desired logic level when the switch is in the off position.
Overall, the Spartan-3an board's input interface is versatile, allowing for a range of applications from simple user controls to complex signal processing tasks, making it a valuable tool for engineers and developers in the field of electronics.The Spartan-3an board has eight slide switches, indicated as in Figure. Push button inputs are normally low and driven high only when the push button is pressed. Push Buttons are interfaced with FPGA I/O lines. 🔗 External reference
The Spartan-3an board is designed to facilitate various input configurations through its eight slide switches and push button inputs. Each slide switch can be used to represent binary states, allowing for easy manual input of control signals. The push buttons, when activated, provide a momentary high signal to the FPGA, enabling it to respond to user interactions.
The push button inputs are connected to the FPGA's I/O lines, which are configured to detect the state changes. When a push button is pressed, the corresponding I/O line transitions from low to high, which can be used to trigger specific functions or processes within the FPGA. This functionality is critical for applications requiring user input, such as in development and testing environments.
In terms of circuit design, it is important to incorporate pull-down resistors for the push button inputs to ensure that the I/O lines remain in a defined low state when the buttons are not pressed. This prevents floating states that could lead to unpredictable behavior. The slide switches can similarly be connected with pull-up or pull-down resistors, depending on the desired logic level when the switch is in the off position.
Overall, the Spartan-3an board's input interface is versatile, allowing for a range of applications from simple user controls to complex signal processing tasks, making it a valuable tool for engineers and developers in the field of electronics.The Spartan-3an board has eight slide switches, indicated as in Figure. Push button inputs are normally low and driven high only when the push button is pressed. Push Buttons are interfaced with FPGA I/O lines. 🔗 External reference