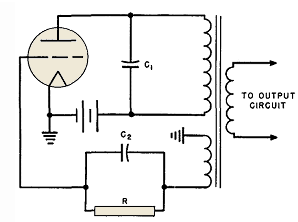
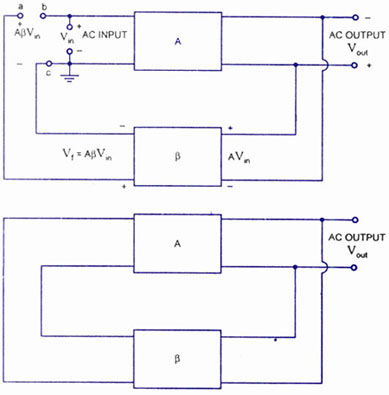
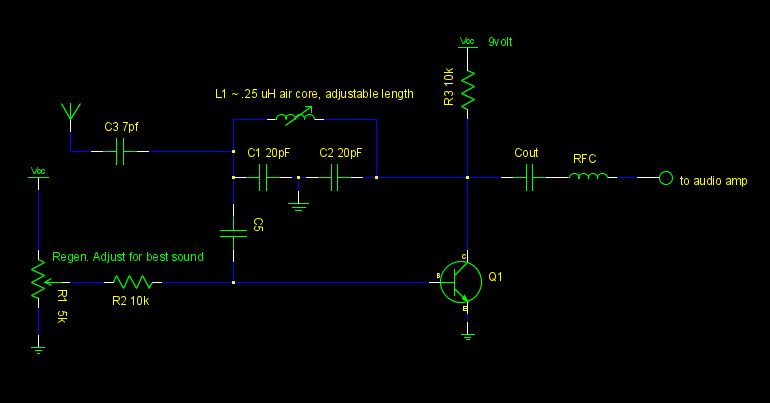
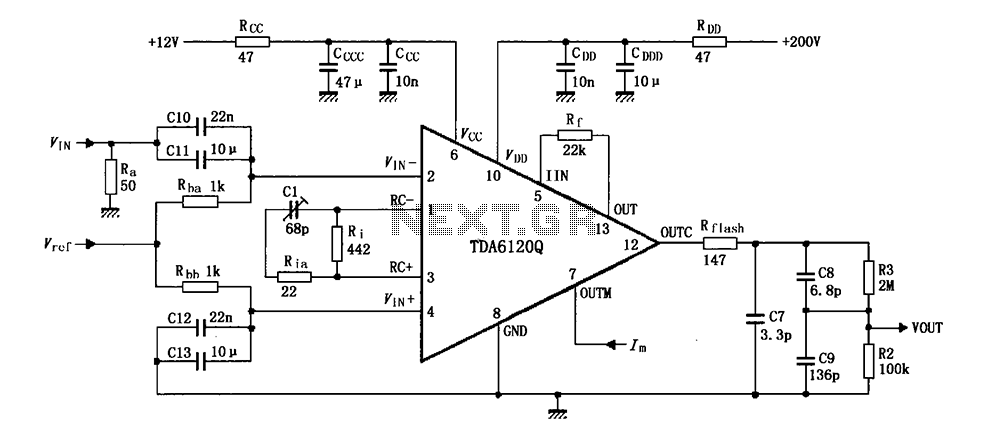
RC feedback oscillators
RC oscillators utilize resistors and capacitors to produce low or audio-frequency signals. Therefore, they are often referred to as audio-frequency (A.F) oscillators.
RC oscillators are fundamental circuit designs utilized in various applications for generating periodic waveforms, particularly in the audio frequency range. The basic principle of operation involves the charging and discharging of capacitors through resistors, which creates a time delay that ultimately determines the frequency of oscillation.
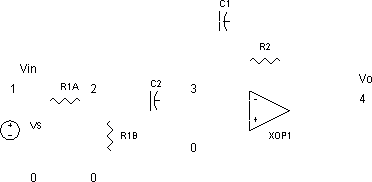
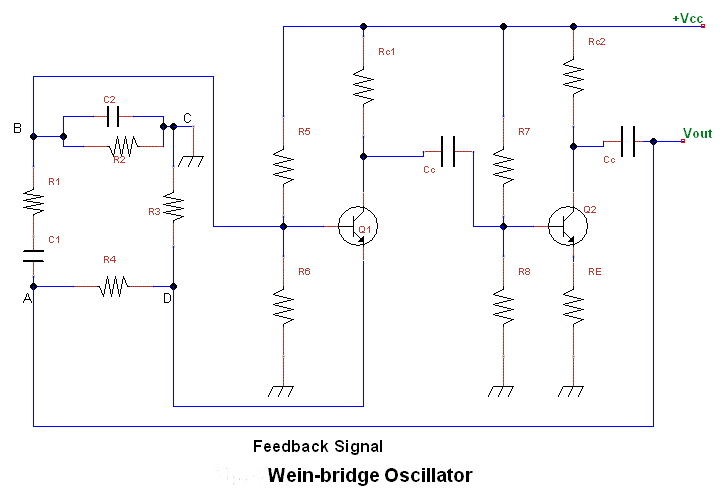
In a typical RC oscillator circuit, one of the most common configurations is the Wien Bridge oscillator. This configuration consists of a bridge circuit made up of two resistors and two capacitors arranged in such a way that it provides a feedback loop necessary for oscillation. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors in the circuit, specifically calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R C} \]
where \( f \) is the frequency, \( R \) is the resistance, and \( C \) is the capacitance.
Another popular type of RC oscillator is the phase-shift oscillator, which employs multiple RC networks to achieve the necessary phase shift for oscillation. Typically, three or more RC stages are used to provide a total phase shift of 180 degrees, combined with an additional 180-degree phase shift from an inverting amplifier, resulting in a total of 360 degrees or a full cycle.
RC oscillators are widely used in audio applications, signal generators, tone generators, and various timing circuits. They are valued for their simplicity, low cost, and ease of implementation. Furthermore, the frequency can be easily adjusted by changing the resistor or capacitor values, making them versatile for different applications.
In summary, RC oscillators are essential components in electronics, providing reliable and efficient means of generating audio-frequency signals through the interaction of resistors and capacitors in various configurations.RC oscillators employ resistors and capacitors and are used to generate low or audio-frequency signals. Hence they are also known as audio-frequency (A.F) oscillators.. 🔗 External reference
RC oscillators are fundamental circuit designs utilized in various applications for generating periodic waveforms, particularly in the audio frequency range. The basic principle of operation involves the charging and discharging of capacitors through resistors, which creates a time delay that ultimately determines the frequency of oscillation.
In a typical RC oscillator circuit, one of the most common configurations is the Wien Bridge oscillator. This configuration consists of a bridge circuit made up of two resistors and two capacitors arranged in such a way that it provides a feedback loop necessary for oscillation. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors in the circuit, specifically calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R C} \]
where \( f \) is the frequency, \( R \) is the resistance, and \( C \) is the capacitance.
Another popular type of RC oscillator is the phase-shift oscillator, which employs multiple RC networks to achieve the necessary phase shift for oscillation. Typically, three or more RC stages are used to provide a total phase shift of 180 degrees, combined with an additional 180-degree phase shift from an inverting amplifier, resulting in a total of 360 degrees or a full cycle.
RC oscillators are widely used in audio applications, signal generators, tone generators, and various timing circuits. They are valued for their simplicity, low cost, and ease of implementation. Furthermore, the frequency can be easily adjusted by changing the resistor or capacitor values, making them versatile for different applications.
In summary, RC oscillators are essential components in electronics, providing reliable and efficient means of generating audio-frequency signals through the interaction of resistors and capacitors in various configurations.RC oscillators employ resistors and capacitors and are used to generate low or audio-frequency signals. Hence they are also known as audio-frequency (A.F) oscillators.. 🔗 External reference