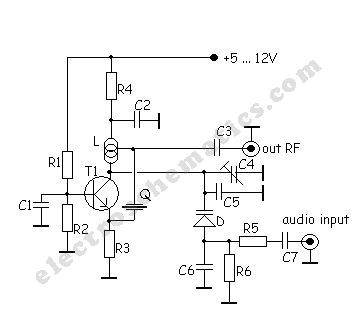
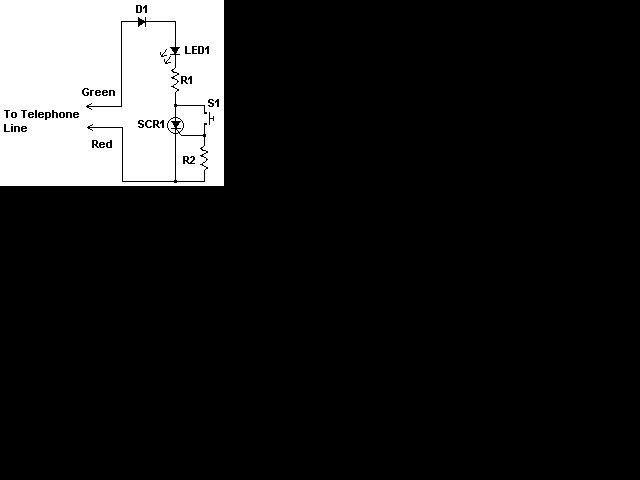
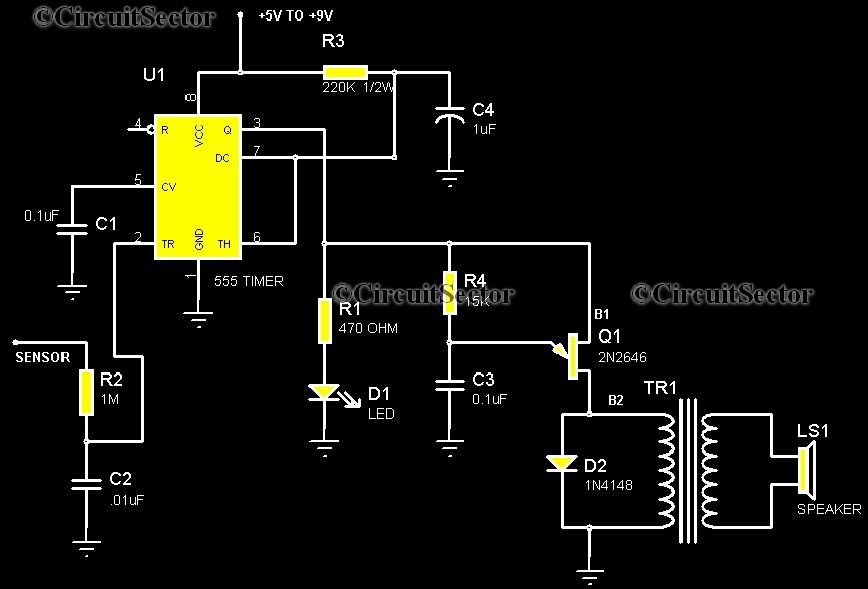
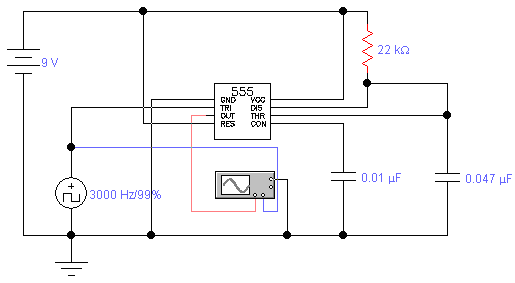
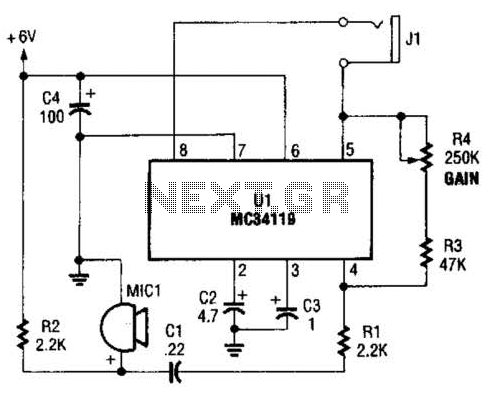
Reducing the power consumption of the circuit diagram ISO103
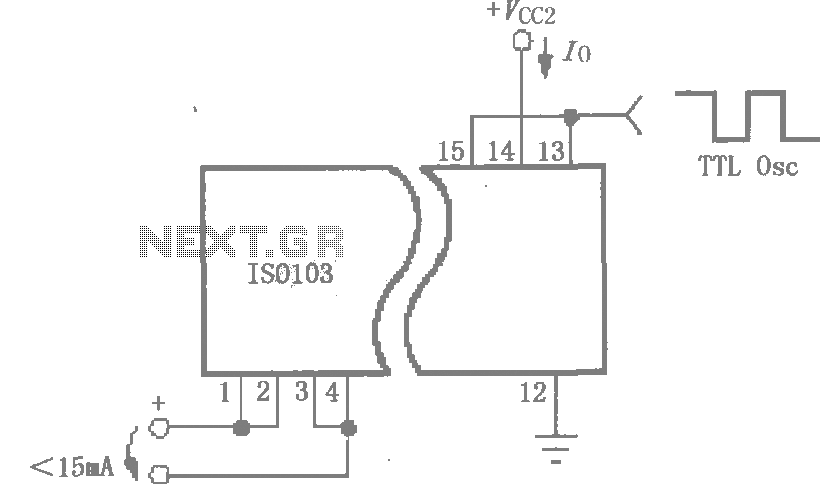
This circuit is designed to reduce power consumption in an ISO103 application. It operates with a Vcc1 current of less than 15mA for multi-channel synchronous applications. An oscillator, as illustrated in the figure, can be utilized to generate a TTL level signal to drive the synchronization input (pin 15) and the enable input (pin 13), thereby minimizing power consumption.
The ISO103 is an integrated circuit commonly used in applications requiring isolation and signal conditioning. In the described configuration, the circuit focuses on achieving low power operation, which is critical in battery-powered or energy-sensitive applications. The Vcc1 current specification of less than 15mA indicates that the device is optimized for efficiency, allowing it to be used in multi-channel systems without significantly increasing the overall power budget.
The oscillator circuit mentioned plays a vital role in generating the necessary TTL signal levels. The output from the oscillator is connected to the synchronization input on pin 15, which ensures that multiple channels can operate in harmony, reducing the likelihood of signal interference. Additionally, the enable input on pin 13 can be controlled by the same oscillator signal, allowing for a dynamic power management strategy. By turning off unused channels or sections of the circuit, further reductions in power consumption can be achieved.
In practical applications, careful consideration should be given to the selection of the oscillator frequency, as it will impact the performance of the ISO103. The oscillator should be designed to provide stable and reliable TTL signals that meet the timing requirements of the ISO103 inputs. Proper decoupling and filtering techniques should also be employed to minimize noise and ensure that the power supply remains stable under varying load conditions.
Overall, the design of this circuit emphasizes the importance of power efficiency in modern electronic systems, particularly in applications where multiple channels are synchronized. By leveraging low-power components and efficient signal generation techniques, the ISO103 circuit can achieve optimal performance while maintaining minimal power consumption.Shown for reducing power consumption ISO103 circuit. For multi-channel synchronous applications Vcc1 current of less than 15mA, as shown in FIG oscillator can be used to generate a TTL level, to drive the synchronization input (15 feet) and enable (13 feet) in order to reduce power consumption.
The ISO103 is an integrated circuit commonly used in applications requiring isolation and signal conditioning. In the described configuration, the circuit focuses on achieving low power operation, which is critical in battery-powered or energy-sensitive applications. The Vcc1 current specification of less than 15mA indicates that the device is optimized for efficiency, allowing it to be used in multi-channel systems without significantly increasing the overall power budget.
The oscillator circuit mentioned plays a vital role in generating the necessary TTL signal levels. The output from the oscillator is connected to the synchronization input on pin 15, which ensures that multiple channels can operate in harmony, reducing the likelihood of signal interference. Additionally, the enable input on pin 13 can be controlled by the same oscillator signal, allowing for a dynamic power management strategy. By turning off unused channels or sections of the circuit, further reductions in power consumption can be achieved.
In practical applications, careful consideration should be given to the selection of the oscillator frequency, as it will impact the performance of the ISO103. The oscillator should be designed to provide stable and reliable TTL signals that meet the timing requirements of the ISO103 inputs. Proper decoupling and filtering techniques should also be employed to minimize noise and ensure that the power supply remains stable under varying load conditions.
Overall, the design of this circuit emphasizes the importance of power efficiency in modern electronic systems, particularly in applications where multiple channels are synchronized. By leveraging low-power components and efficient signal generation techniques, the ISO103 circuit can achieve optimal performance while maintaining minimal power consumption.Shown for reducing power consumption ISO103 circuit. For multi-channel synchronous applications Vcc1 current of less than 15mA, as shown in FIG oscillator can be used to generate a TTL level, to drive the synchronization input (15 feet) and enable (13 feet) in order to reduce power consumption.