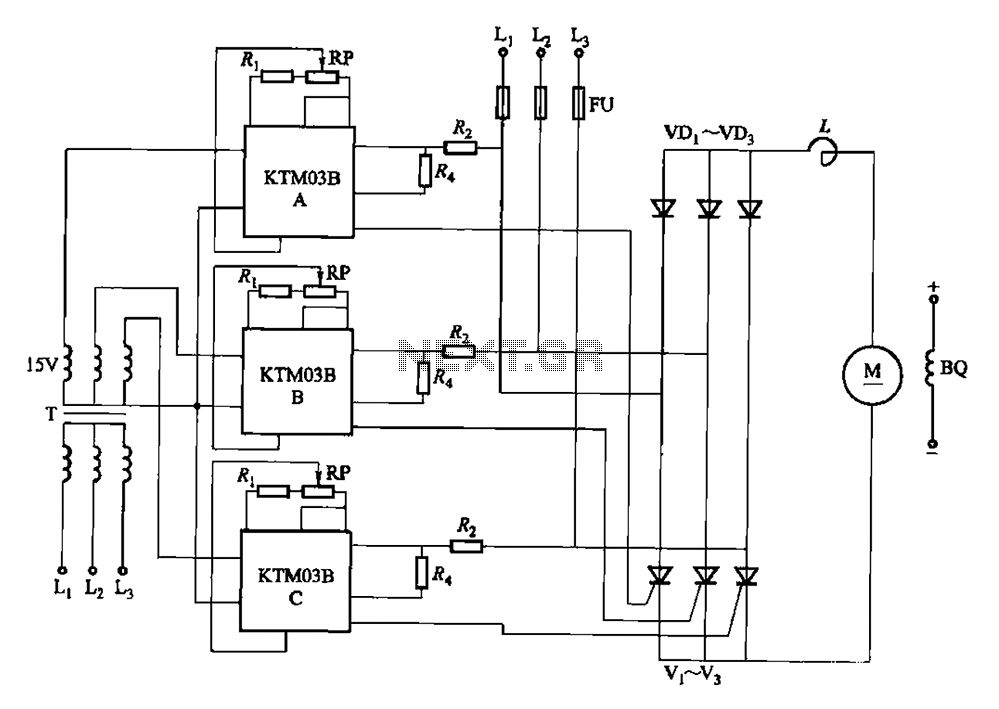
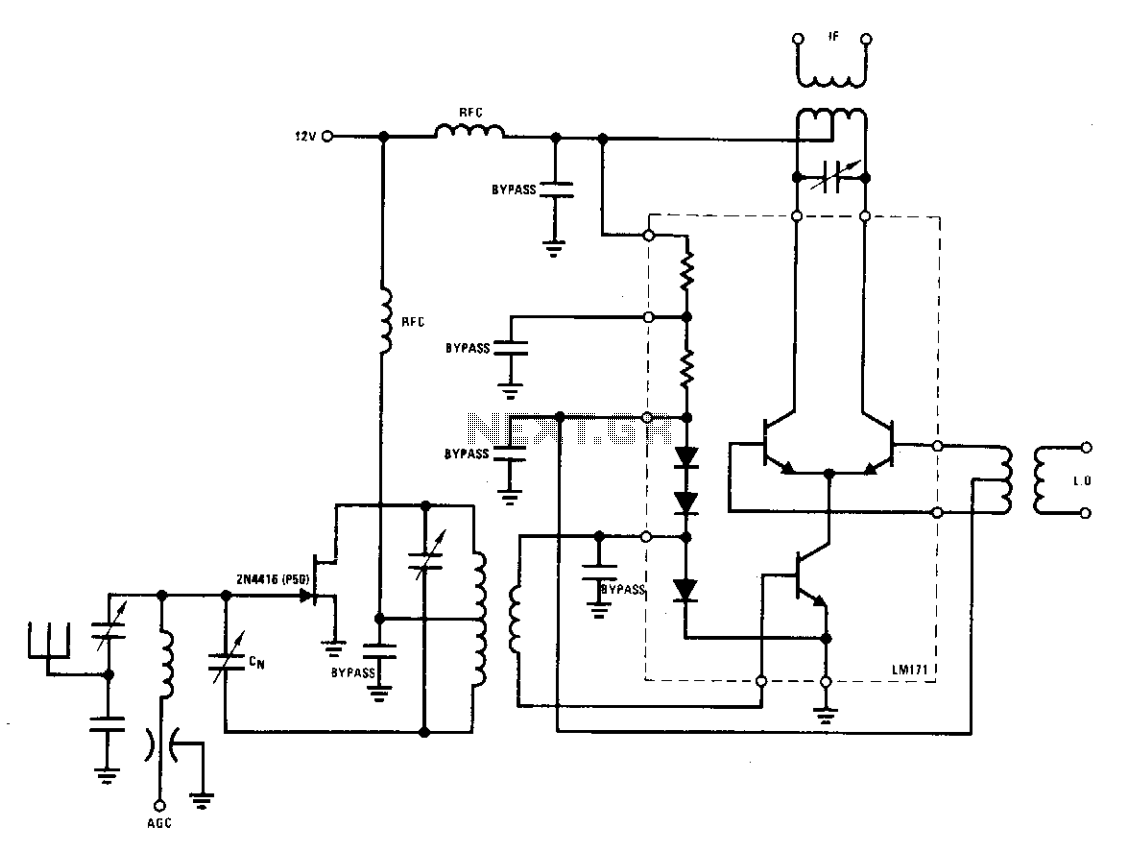
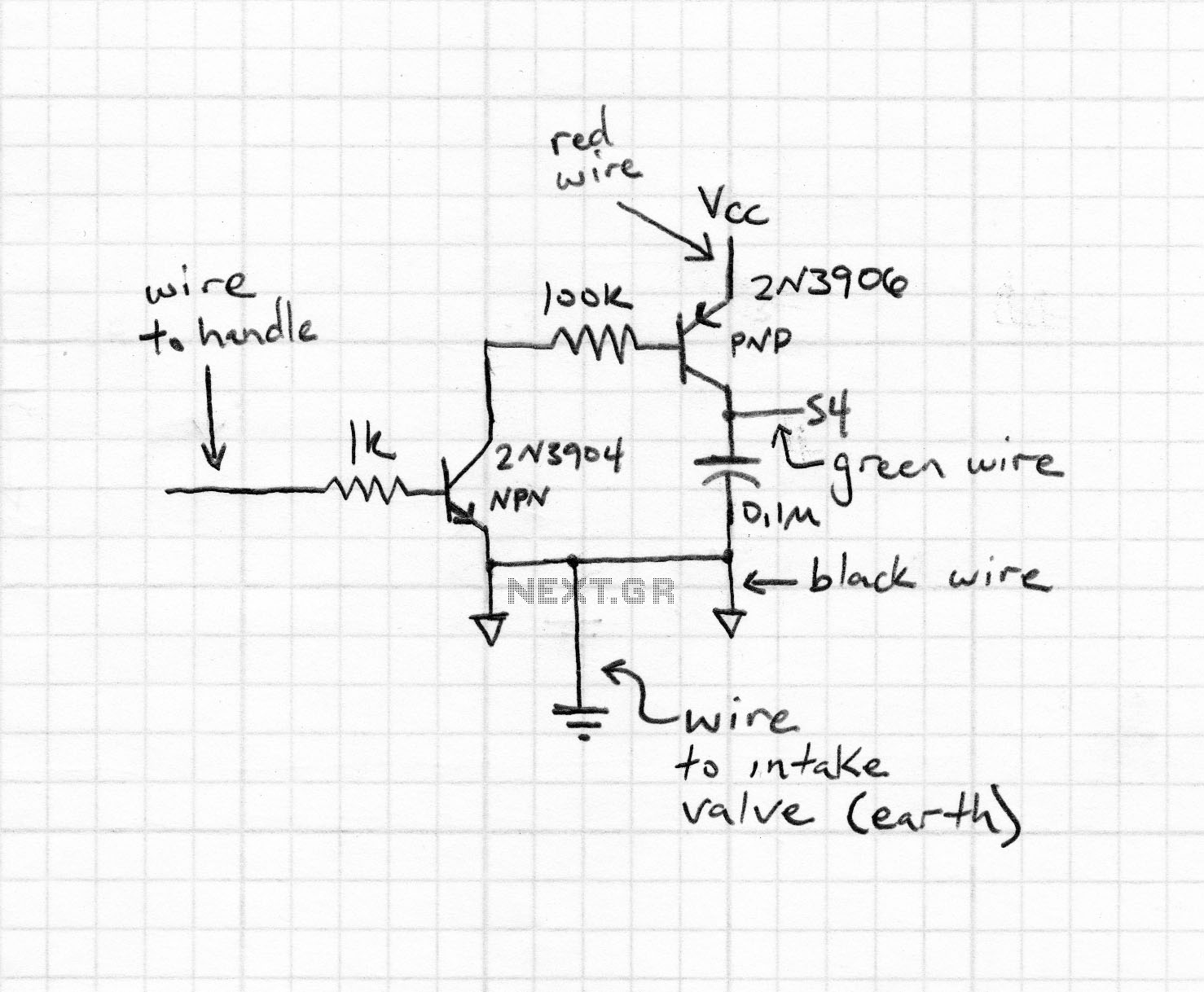
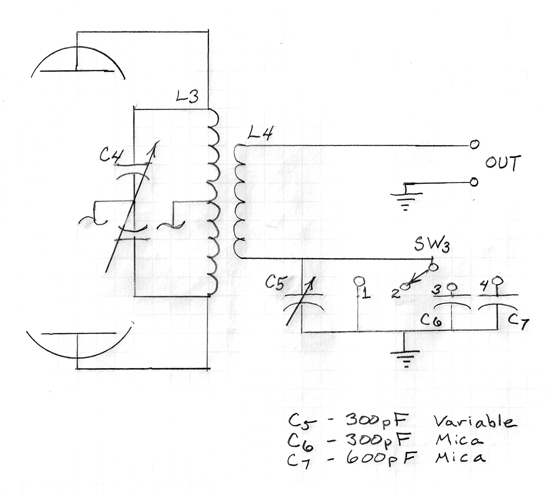
3V to 5V Converter Circuit
There are several methods to convert an AC voltage from a wall receptacle into the DC voltage required by a microcontroller. Traditionally, this has been accomplished using various types of power supply circuits.
To convert AC voltage to DC voltage effectively, a typical approach involves the use of a transformer, rectifier, and filter circuit. The transformer steps down the high voltage AC from the wall outlet to a lower AC voltage suitable for the microcontroller's requirements. The rectifier, which can be a diode bridge configuration, converts the AC voltage into pulsating DC. The filter, often a capacitor, smooths out the pulsating DC to provide a more stable voltage level.
In more advanced designs, additional components such as voltage regulators may be included to ensure that the output DC voltage remains constant despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. This is crucial for microcontroller operation, as they require a stable voltage to function correctly.
Furthermore, safety features such as fuses or circuit breakers may be incorporated to protect the circuit from overcurrent conditions. Additionally, proper isolation techniques should be employed to prevent any high voltage from reaching the low voltage side of the circuit, ensuring user safety and equipment reliability.
Overall, the design of an AC to DC converter for microcontroller applications must take into account efficiency, size, heat dissipation, and safety to meet the specific requirements of the intended application.There are several ways to convert an AC voltage at a wall receptacle into the DC voltage required by a microcontroller. Traditionally, this has been done w.. 🔗 External reference
To convert AC voltage to DC voltage effectively, a typical approach involves the use of a transformer, rectifier, and filter circuit. The transformer steps down the high voltage AC from the wall outlet to a lower AC voltage suitable for the microcontroller's requirements. The rectifier, which can be a diode bridge configuration, converts the AC voltage into pulsating DC. The filter, often a capacitor, smooths out the pulsating DC to provide a more stable voltage level.
In more advanced designs, additional components such as voltage regulators may be included to ensure that the output DC voltage remains constant despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. This is crucial for microcontroller operation, as they require a stable voltage to function correctly.
Furthermore, safety features such as fuses or circuit breakers may be incorporated to protect the circuit from overcurrent conditions. Additionally, proper isolation techniques should be employed to prevent any high voltage from reaching the low voltage side of the circuit, ensuring user safety and equipment reliability.
Overall, the design of an AC to DC converter for microcontroller applications must take into account efficiency, size, heat dissipation, and safety to meet the specific requirements of the intended application.There are several ways to convert an AC voltage at a wall receptacle into the DC voltage required by a microcontroller. Traditionally, this has been done w.. 🔗 External reference