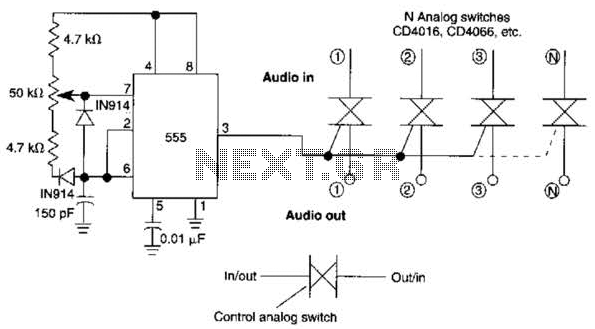
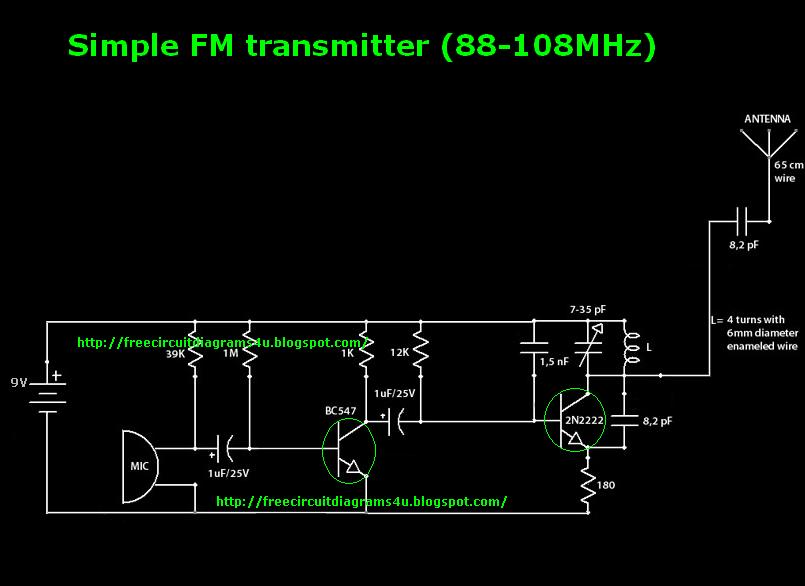
RF Wireless Data Transfer communication Circuit diagram
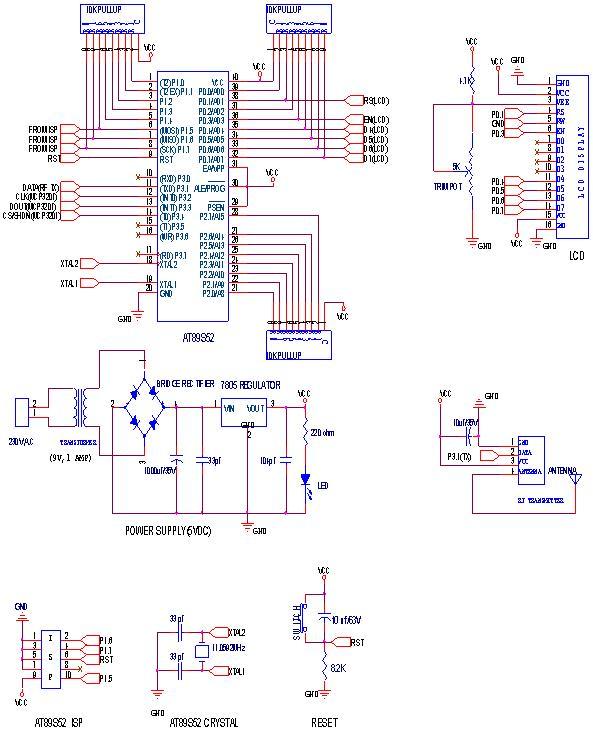
RF Wireless Data Transfer communication circuit diagram. A wireless communication interface was implemented to facilitate data transfer from one point to another using RF technology.
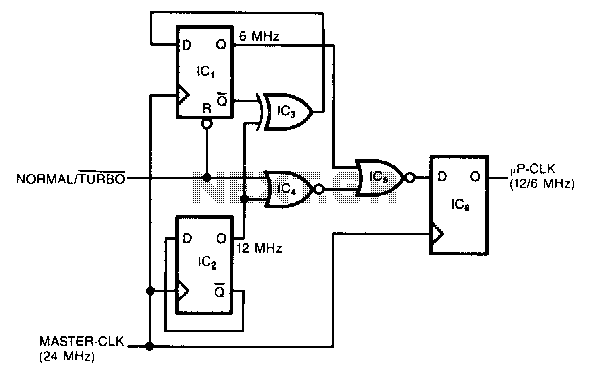
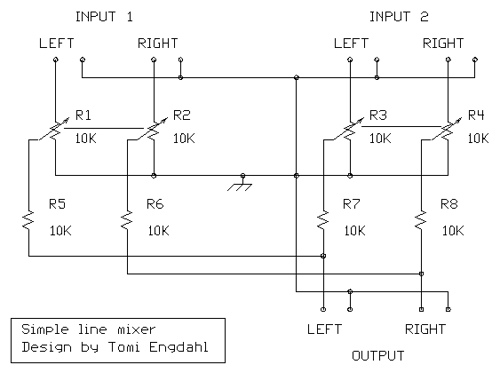
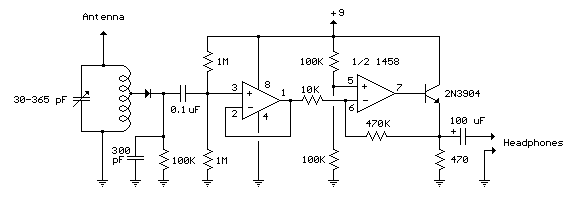
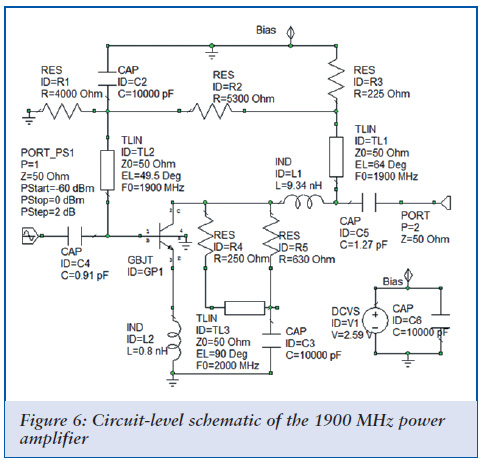
The RF Wireless Data Transfer communication circuit utilizes radio frequency (RF) technology to establish a wireless link for transmitting data between two points. The core components of this circuit typically include a transmitter module, a receiver module, an antenna, and associated circuitry for modulation and demodulation.
The transmitter module converts the data signal into a radio frequency signal using modulation techniques such as Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) or Frequency Shift Keying (FSK). The modulated RF signal is then transmitted through an antenna, which radiates the signal into the surrounding environment.
At the receiving end, the receiver module captures the RF signal using its antenna. The received signal is then demodulated to retrieve the original data. This demodulation process involves filtering and amplifying the signal to ensure that it is clean and free from noise. The output of the receiver module is then connected to a microcontroller or another processing unit, which interprets the received data for further action.
Power supply considerations are crucial in RF circuits, as both the transmitter and receiver require stable voltage levels for optimal performance. Additionally, the design may include features such as error detection and correction mechanisms to enhance the reliability of data transmission.
Overall, the RF Wireless Data Transfer communication circuit is designed for applications requiring short to medium-range data communication, making it suitable for various uses such as remote control systems, wireless sensor networks, and telemetry applications.RF Wireless Data Transfer communication Circuit diagram.we implemented a wireless communication interface one point to another by means of RF technology. 🔗 External reference
The RF Wireless Data Transfer communication circuit utilizes radio frequency (RF) technology to establish a wireless link for transmitting data between two points. The core components of this circuit typically include a transmitter module, a receiver module, an antenna, and associated circuitry for modulation and demodulation.
The transmitter module converts the data signal into a radio frequency signal using modulation techniques such as Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) or Frequency Shift Keying (FSK). The modulated RF signal is then transmitted through an antenna, which radiates the signal into the surrounding environment.
At the receiving end, the receiver module captures the RF signal using its antenna. The received signal is then demodulated to retrieve the original data. This demodulation process involves filtering and amplifying the signal to ensure that it is clean and free from noise. The output of the receiver module is then connected to a microcontroller or another processing unit, which interprets the received data for further action.
Power supply considerations are crucial in RF circuits, as both the transmitter and receiver require stable voltage levels for optimal performance. Additionally, the design may include features such as error detection and correction mechanisms to enhance the reliability of data transmission.
Overall, the RF Wireless Data Transfer communication circuit is designed for applications requiring short to medium-range data communication, making it suitable for various uses such as remote control systems, wireless sensor networks, and telemetry applications.RF Wireless Data Transfer communication Circuit diagram.we implemented a wireless communication interface one point to another by means of RF technology. 🔗 External reference