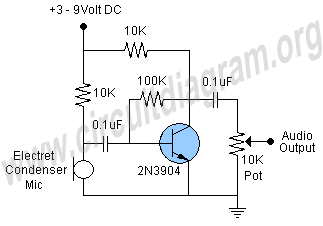
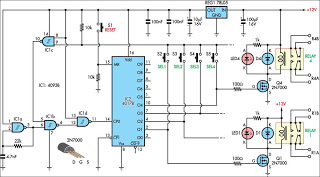
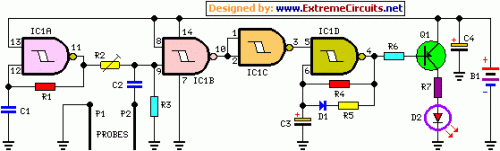
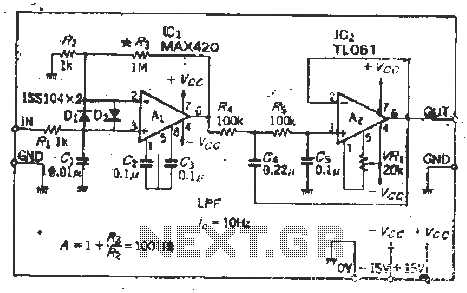
RTD Amplifier Circuit (A/D)

RTD sensors are measured using a precision 24-bit analog-to-digital converter (A/D) that includes a built-in programmable gain amplifier. The connections for 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire RTDs are illustrated. This setup facilitates the connection and measurement of RTDs with amplifiers and data acquisition systems, ensuring precision in RTD resistance measurement.
RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) sensors are widely utilized for temperature measurement due to their accuracy and stability. The precision 24-bit A/D converter enhances the resolution of the measured signals, allowing for fine detection of temperature changes. The built-in programmable gain amplifier is crucial as it adjusts the signal level to optimize the A/D conversion process, particularly when dealing with low-level signals that may be generated by RTDs.
In terms of wiring configurations, RTDs can be connected in three different ways: 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire. The 2-wire configuration is the simplest but is prone to errors due to lead resistance. The 3-wire configuration compensates for lead resistance, making it more accurate than the 2-wire setup. The 4-wire configuration is the most accurate, as it eliminates the effects of lead resistance entirely by using separate pairs of wires for the current supply and voltage measurement.
The integration of amplifiers and data acquisition systems with RTD sensors allows for enhanced measurement capabilities. Amplifiers can boost the output signal from the RTD to a level suitable for processing by the A/D converter, while data acquisition systems can digitize the signal for further analysis and monitoring. This combination is essential in applications where precision temperature measurement is critical, such as in industrial processes, HVAC systems, and laboratory environments.
Overall, the use of a precision 24-bit A/D converter, along with a programmable gain amplifier and various RTD connection configurations, provides a robust solution for accurate temperature measurement and monitoring in diverse applications.RTD sensors are measured with a precision 24-bit A/D (analog to digital converter) with built-in programmable gain amplifier. Connections for 2-wire RTDs, 3-wire RTDs, and 4-wire RTDs are shown. Connecting and measuring RTDs with amplifiers and data acquisition systems. Precision RTD resistance measurement.. 🔗 External reference
RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) sensors are widely utilized for temperature measurement due to their accuracy and stability. The precision 24-bit A/D converter enhances the resolution of the measured signals, allowing for fine detection of temperature changes. The built-in programmable gain amplifier is crucial as it adjusts the signal level to optimize the A/D conversion process, particularly when dealing with low-level signals that may be generated by RTDs.
In terms of wiring configurations, RTDs can be connected in three different ways: 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire. The 2-wire configuration is the simplest but is prone to errors due to lead resistance. The 3-wire configuration compensates for lead resistance, making it more accurate than the 2-wire setup. The 4-wire configuration is the most accurate, as it eliminates the effects of lead resistance entirely by using separate pairs of wires for the current supply and voltage measurement.
The integration of amplifiers and data acquisition systems with RTD sensors allows for enhanced measurement capabilities. Amplifiers can boost the output signal from the RTD to a level suitable for processing by the A/D converter, while data acquisition systems can digitize the signal for further analysis and monitoring. This combination is essential in applications where precision temperature measurement is critical, such as in industrial processes, HVAC systems, and laboratory environments.
Overall, the use of a precision 24-bit A/D converter, along with a programmable gain amplifier and various RTD connection configurations, provides a robust solution for accurate temperature measurement and monitoring in diverse applications.RTD sensors are measured with a precision 24-bit A/D (analog to digital converter) with built-in programmable gain amplifier. Connections for 2-wire RTDs, 3-wire RTDs, and 4-wire RTDs are shown. Connecting and measuring RTDs with amplifiers and data acquisition systems. Precision RTD resistance measurement.. 🔗 External reference