Servo System
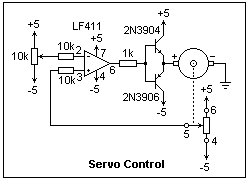
This study utilizes a motor potentiometer available from All Electronics at a low cost of $4.00. The catalog number is MPOT-10K, manufactured by Alps, with the motor marked MD157320 and the body labeled 725t 10BX2. The potentiometer is a dual 10k type, allowing one potentiometer to provide feedback on the position while the other serves as the output. The goal is to create a remote-controlled potentiometer that replicates the settings of the control potentiometer. This setup represents a typical feedback system, referred to as a servomechanism or servo due to its mechanical component. The output can indicate the shaft position or the electrical output of the controlled potentiometer, with most servos producing mechanical outputs. The motor potentiometer comprises a small DC motor, gearing that actuates the sliders, a support structure for the potentiometer resistances, and a shaft. The connections are illustrated on the right side, with the motor located at one end and the shaft at the opposite end. Although the potentiometers are interconnected, which limits their independence, this is not a significant issue for the intended application. A clockwise rotation of the shaft, viewed from the shaft end, increases the resistance between the common end and the sliders. Applying voltage to the motor terminals in the specified polarity rotates the shaft counterclockwise, bringing the sliders closer to the common ends. The motor requires slightly over 2 V to initiate movement, making 5 V a suitable maximum voltage. The motor draws approximately 30 mA or slightly more. There are two connection pins on the shaft side of the potentiometer that illuminate a red LED visible through a hole in the shaft, with the anode positioned on the right. Pins 1 and 8 appear to be unconnected. An elementary servo circuit is depicted on the left. The LF411 op-amp used in the circuit cannot drive the motor directly and requires assistance from transistors. A complementary pair, such as the 2N3904 and 2N3906, is suitable for this task, although any small complementary pair could suffice. The LF411 functions as a comparator, operating within its common-mode range. The output saturates in one direction or the other to activate the motor. With a ±5 V supply, the motor voltage will range between 3.5 and 4 V, eliminating the need for further arrangements. In this basic configuration, the motor is driven in one direction or the other at full voltage. A more complex circuit could offer enhanced control. The circuit quickly locates the appropriate position, tracking the control potentiometer, and then oscillates around the correct position at a frequency of approximately 5 Hz. Observing the output voltage of the op-amp with an oscilloscope set to the slowest sweep speed is recommended. If the feedback signal has the incorrect sign during testing, reversing the connections to the op-amp inputs will correct the issue. Addressing the problem of hunting is more complex than anticipated. Reducing the voltage supplied to the motor as the equilibrium position is approached (proportional control) may result in the motor stopping short of the desired position. If this outcome is acceptable, the issue is resolved; however, some hysteresis will occur due to the minimum voltage required for movement. Integrating the error signal (integral control) leads the motor to approach a more accurate position until the error is eliminated. While these refinements are not the focus of this exercise, they are discussed extensively in control systems literature. Initial attempts may lead to misunderstandings regarding connections, potentially damaging the potentiometer if it rotates to its limit. Such experiences can provide insights into the internal workings of the system, clarifying connections and revealing components such as the LED. The gear mechanism is intricate, featuring a worm gear on the motor that drives a spur gear, which connects to a hypoid right-angle drive with a ring gear featuring inclined teeth driven by a unique worm gear. A friction connection allows manual rotation of the shaft, while the motor gear does not reverse. The entire assembly is well-manufactured, likely costing significantly more than the $4.00 surplus price.This study is made possible by the availability of a motor potentiometer from All Electronics at small cost. The item is catalog number MPOT-10K, and costs $4. 00. It is manufactured by Alps, and the motor is marked MD157320, the body 725t 10BX2. The potentiometer is dual 10k, so one potentiometer can be used for feedback of the position, while the
other serves as the output. What we are going to do here is to make a remote-controlled potentiometer that repeats the setting of the control potentiometer. This is a typical feedback system, but since it involves a mechanical element, it is called aservomechanism, orservo, for short.
The output could be the shaft position, as well as the electrical output of the controlled potentiometer. In fact, the output of most servos is mechanical. The motor pot consists of a small DC motor, gearing that drives the sliders, the support for the potentiometer resistances, and a shaft.
The connections are shown at the right. We are looking at the motor end; the shaft is at the other end. It is slightly disappointing that the potentiometers are Siamese twins, so they are not completely independent, but that is little matter for our purposes. A clockwise rotation of the shaft, looking from the shaft end, increases the resistance between the common end and the sliders.
A voltage applied to the motor terminals with the marked polarity turns the shaft anticlockwise, bringing the sliders toward the common ends. The motor requires a little more than 2 V to begin turning, so that 5 V is a reasonable maximum. The motor draws about 30 mA or a bit more. There are two connection pins (not shown) on the shaft side of the potentiometer connections that light a red LED that shines through the hole in the shaft.
As you face the shaft, the anode is at the right. Pins 1 and 8 appear to be connected to nothing. An elementary servo circuit is shown at the left. The usual op-amp, here an LF411, cannot drive the motor by itself, and must be helped by transistors. The complementary 2N3904 and 2N3906 can do the job nicely, but, of course, any small complementary pair could be used.
The LF411 is used as a comparator here, which is allowed by its common-mode range. The output saturates one direction or the other to drive the motor. With a ±5 V supply, the motor voltage will be between 3. 5 and 4 V, so no further arrangments are necessary. In this simple circuit, the motor is driven one way or the other at full voltage. A more complicated circuit could provide more sophisticated control. This circuit finds the proper position rapidly, following the control potentiometer. It then oscillates on either side of the correct position at a frequency of about 5 Hz. Observe the output voltage of the op-amp with the oscilloscope on the slowest speed sweep. If the feedback has the wrong sign when you test the circuit, simply exchange the connections to the op-amp inputs. The elimination of the hunting is a more challenging problem than would appear at first sight. If the voltage applied to the motor is decreased as the equilibrium position is approached (proportional control), the motor will stop short at some point.
If this is satisfactory, then the problem is solved, but there will be a little annoying hysteresis because of the finite voltage required for movement. If the error signal is integrated (integral control), it will cause the motor to approach a more correct position until the error is zero.
These refinements are not (at this time) within the scope of this exercise, which is to illustrate basic servo control, but are discussed at length in any text on control systems. On my first try, a quick, erroneous understanding of the connections ruined the potentiometer immediately, when it rotated to one limit.
This, however, gave me the opportunity to disassemble the system and find out what it looked like inside, especially to clarify the connections. The LED was discovered in this way, which had been something of a mystery. The gearing is ingenious. A worm gear on the motor drives a spur gear which is connected to a hypoid right-angle drive, with a ring gear with inclined teeth driven by a curious worm gear.
There is a friction connection to the shaft, so that the shaft can be rotated manually. Of course, the motor gear does not reverse. The whole is nicely manufactured, and probably cost considerably more than the $4. 00 it brings as surplus. 🔗 External reference
other serves as the output. What we are going to do here is to make a remote-controlled potentiometer that repeats the setting of the control potentiometer. This is a typical feedback system, but since it involves a mechanical element, it is called aservomechanism, orservo, for short.
The output could be the shaft position, as well as the electrical output of the controlled potentiometer. In fact, the output of most servos is mechanical. The motor pot consists of a small DC motor, gearing that drives the sliders, the support for the potentiometer resistances, and a shaft.
The connections are shown at the right. We are looking at the motor end; the shaft is at the other end. It is slightly disappointing that the potentiometers are Siamese twins, so they are not completely independent, but that is little matter for our purposes. A clockwise rotation of the shaft, looking from the shaft end, increases the resistance between the common end and the sliders.
A voltage applied to the motor terminals with the marked polarity turns the shaft anticlockwise, bringing the sliders toward the common ends. The motor requires a little more than 2 V to begin turning, so that 5 V is a reasonable maximum. The motor draws about 30 mA or a bit more. There are two connection pins (not shown) on the shaft side of the potentiometer connections that light a red LED that shines through the hole in the shaft.
As you face the shaft, the anode is at the right. Pins 1 and 8 appear to be connected to nothing. An elementary servo circuit is shown at the left. The usual op-amp, here an LF411, cannot drive the motor by itself, and must be helped by transistors. The complementary 2N3904 and 2N3906 can do the job nicely, but, of course, any small complementary pair could be used.
The LF411 is used as a comparator here, which is allowed by its common-mode range. The output saturates one direction or the other to drive the motor. With a ±5 V supply, the motor voltage will be between 3. 5 and 4 V, so no further arrangments are necessary. In this simple circuit, the motor is driven one way or the other at full voltage. A more complicated circuit could provide more sophisticated control. This circuit finds the proper position rapidly, following the control potentiometer. It then oscillates on either side of the correct position at a frequency of about 5 Hz. Observe the output voltage of the op-amp with the oscilloscope on the slowest speed sweep. If the feedback has the wrong sign when you test the circuit, simply exchange the connections to the op-amp inputs. The elimination of the hunting is a more challenging problem than would appear at first sight. If the voltage applied to the motor is decreased as the equilibrium position is approached (proportional control), the motor will stop short at some point.
If this is satisfactory, then the problem is solved, but there will be a little annoying hysteresis because of the finite voltage required for movement. If the error signal is integrated (integral control), it will cause the motor to approach a more correct position until the error is zero.
These refinements are not (at this time) within the scope of this exercise, which is to illustrate basic servo control, but are discussed at length in any text on control systems. On my first try, a quick, erroneous understanding of the connections ruined the potentiometer immediately, when it rotated to one limit.
This, however, gave me the opportunity to disassemble the system and find out what it looked like inside, especially to clarify the connections. The LED was discovered in this way, which had been something of a mystery. The gearing is ingenious. A worm gear on the motor drives a spur gear which is connected to a hypoid right-angle drive, with a ring gear with inclined teeth driven by a curious worm gear.
There is a friction connection to the shaft, so that the shaft can be rotated manually. Of course, the motor gear does not reverse. The whole is nicely manufactured, and probably cost considerably more than the $4. 00 it brings as surplus. 🔗 External reference