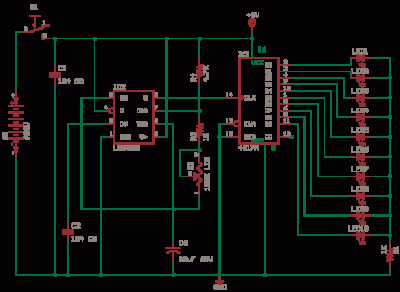
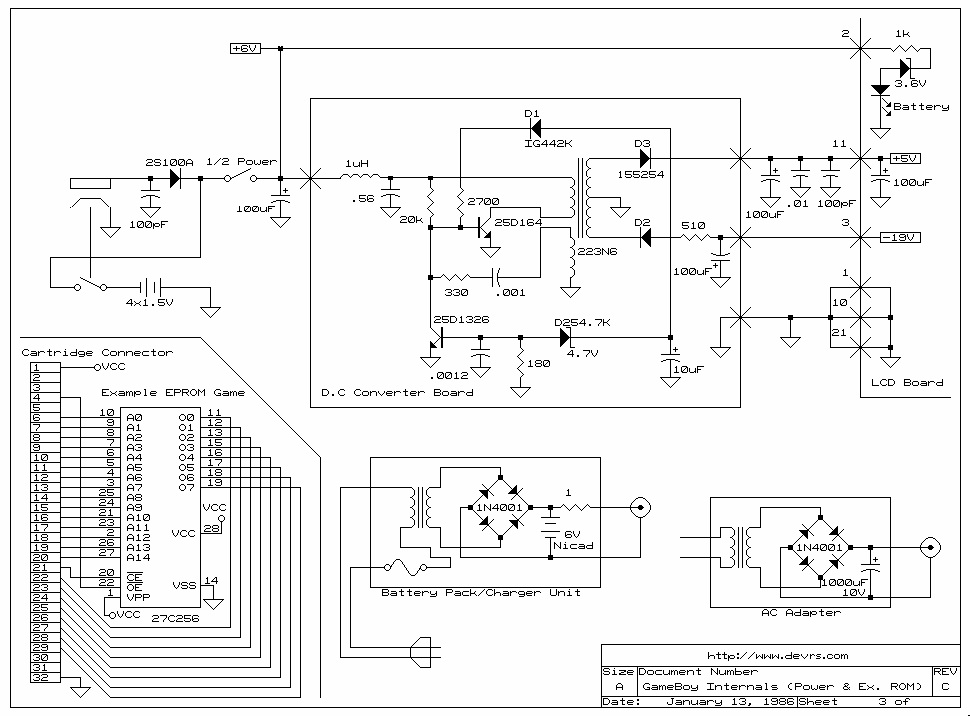
Seven blinker circuits
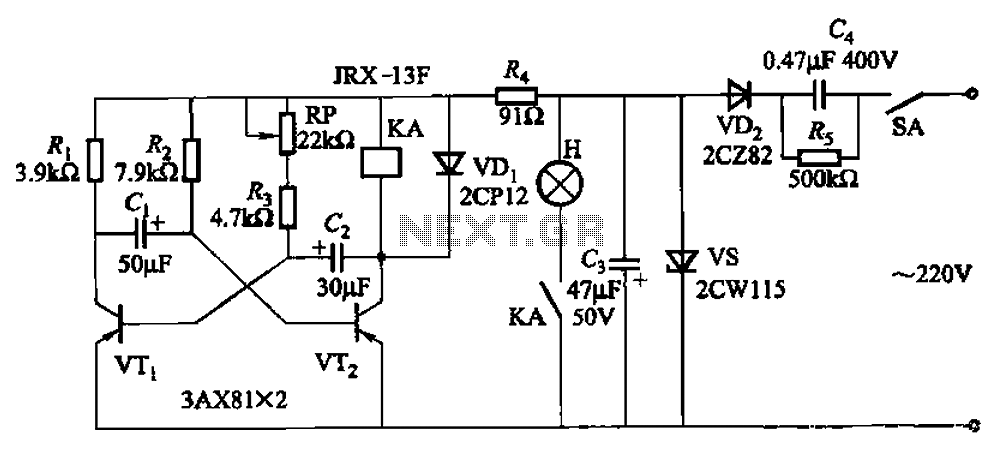
The circuit features a self-excited multivibrator composed of transistors VTi and VTZ. It includes an adjustment potentiometer RP and two RC networks that influence the transistors' parameters, specifically the timing for light activation and deactivation.
The described multivibrator circuit utilizes two transistors (VTi and VTZ) configured to create an astable multivibrator, which generates a continuous square wave output. This configuration is commonly employed in applications such as flashing lights or tone generation. The operation of the circuit hinges on the charging and discharging cycles of the capacitors within the RC networks, which dictate the frequency of oscillation.
The adjustment potentiometer RP plays a crucial role in fine-tuning the timing characteristics of the circuit. By varying its resistance, the time intervals for which the lights are turned on (high state) and off (low state) can be adjusted. This allows for customization of the light blinking rate, enhancing the versatility of the multivibrator in different applications.
The RC networks connected to each transistor help establish the necessary time constants for the oscillation. The resistors and capacitors can be selected based on the desired frequency range, with the time period of the output signal being determined by the formula T = 0.693 * (R1 + R2) * C, where R1 and R2 are the resistances in the RC networks and C is the capacitance. The output from the multivibrator can be connected to various load devices, such as LEDs or other light sources, to create visual indicators or alerts.
Overall, this self-excited multivibrator circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective design for generating timed signals, suitable for a variety of electronic applications. By the transistor VTi, VTZ composition self-excited multivibrator. Adjustment potentiometer RP and two RC transistors related parameters, time to change the lights and the ligh ts out time.
The described multivibrator circuit utilizes two transistors (VTi and VTZ) configured to create an astable multivibrator, which generates a continuous square wave output. This configuration is commonly employed in applications such as flashing lights or tone generation. The operation of the circuit hinges on the charging and discharging cycles of the capacitors within the RC networks, which dictate the frequency of oscillation.
The adjustment potentiometer RP plays a crucial role in fine-tuning the timing characteristics of the circuit. By varying its resistance, the time intervals for which the lights are turned on (high state) and off (low state) can be adjusted. This allows for customization of the light blinking rate, enhancing the versatility of the multivibrator in different applications.
The RC networks connected to each transistor help establish the necessary time constants for the oscillation. The resistors and capacitors can be selected based on the desired frequency range, with the time period of the output signal being determined by the formula T = 0.693 * (R1 + R2) * C, where R1 and R2 are the resistances in the RC networks and C is the capacitance. The output from the multivibrator can be connected to various load devices, such as LEDs or other light sources, to create visual indicators or alerts.
Overall, this self-excited multivibrator circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective design for generating timed signals, suitable for a variety of electronic applications. By the transistor VTi, VTZ composition self-excited multivibrator. Adjustment potentiometer RP and two RC transistors related parameters, time to change the lights and the ligh ts out time.