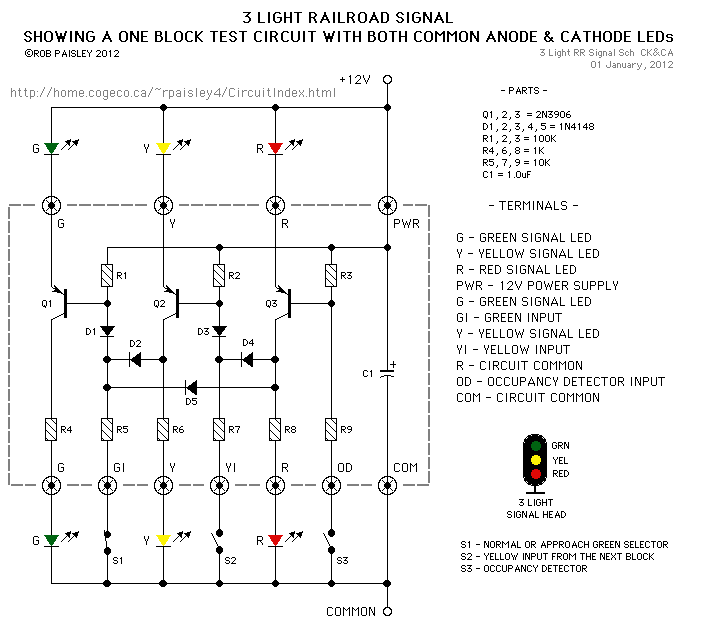
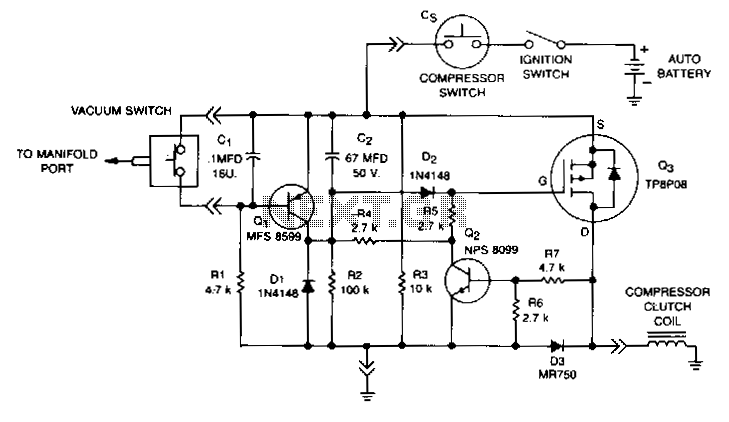
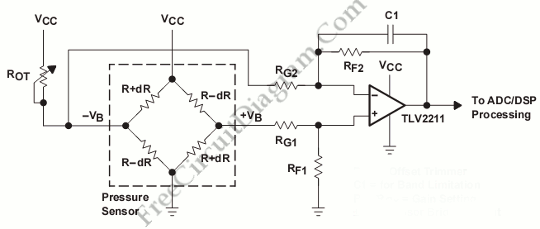
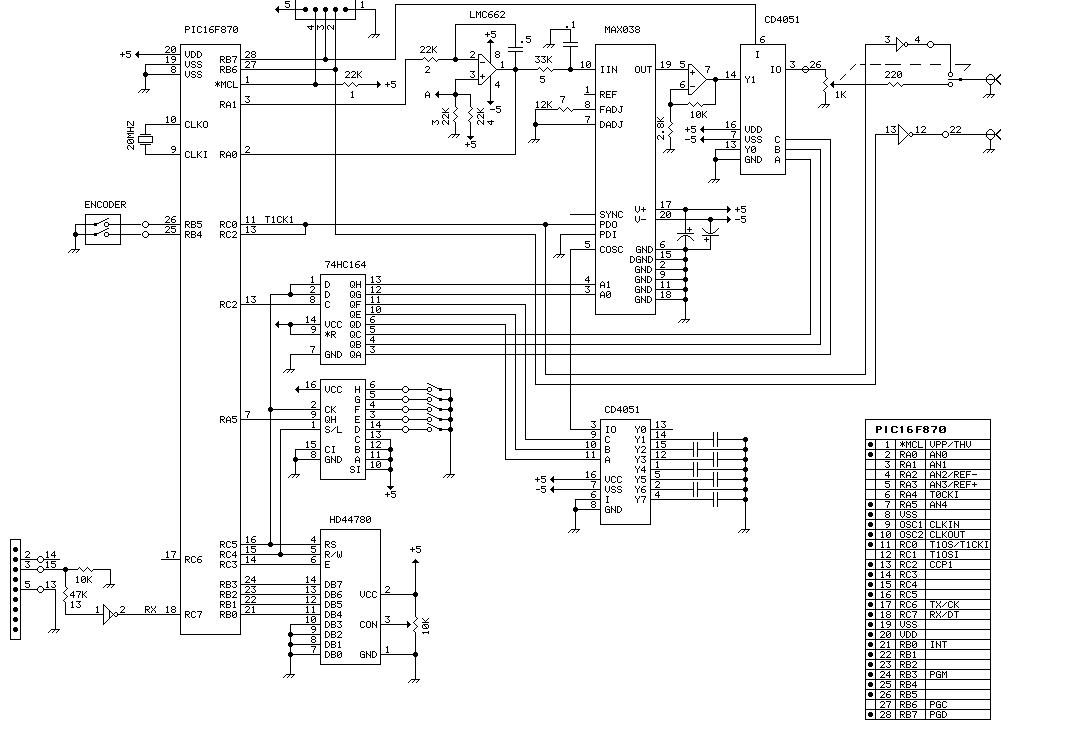
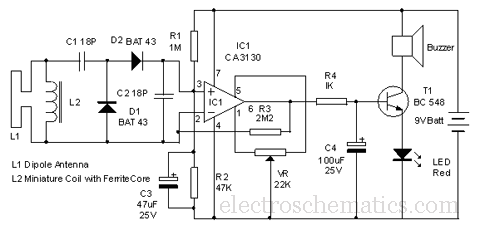
Signal Conditioner
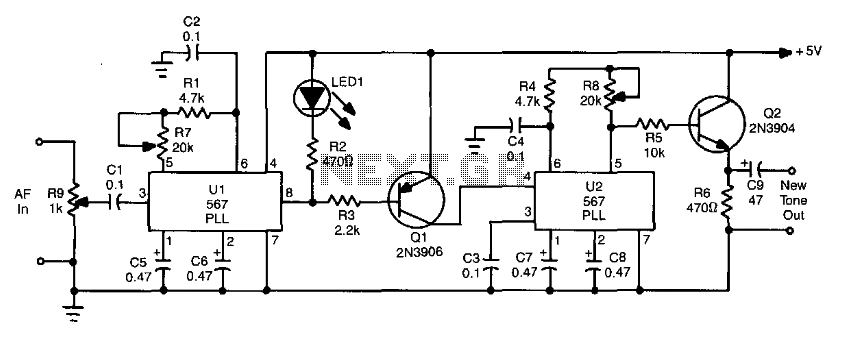
This circuit takes audio from a receiver that may have a weak continuous wave (CW) or tone signal and utilizes a phase-locked loop (PLL) to recover the weak signal. The PLL generates a low output when it detects a tone or note of a specific frequency, which is determined by resistors R1, R7, and capacitor C2. The output from the PLL (pin 8) goes low, activating tone generator U2 to produce a new tone. This circuit is beneficial for improving CW reception in the presence of static, noise, and other interferences.
The circuit operates by first receiving an audio signal that may be compromised due to weak signal strength or interference. The phase-locked loop (PLL), designated as U1, plays a crucial role in signal processing by locking onto the frequency of the incoming tone. The frequency detection is achieved through the configuration of resistors R1 and R7 and capacitor C2, which set the PLL's reference frequency. When the PLL successfully detects a tone, it generates a low signal at pin 8.
This low output serves as a control signal that activates tone generator U2. The tone generator is responsible for producing a clean, consistent tone that can replace the original weak signal. The output of U2 can then be used for further processing or directly fed to a speaker or other audio output device. The overall design significantly enhances the clarity of CW signals by filtering out unwanted noise and static, making it a valuable tool for amateur radio operators and audio signal processing applications.
In summary, the circuit effectively recovers and enhances weak CW signals by utilizing a PLL for frequency detection and a tone generator for signal improvement, resulting in clearer audio output. This circuit takes audio from a receiver that might have a weak CW or tone signal and uses a PLL (Ul) to recover the wea k signal. Ul produces a low on receipt of a tone or note of frequency, determined by Rl, R7, and C2. The output of Ul (pin 8) goes low, keys tone generator U2, and produces a new tone. The circuit is useful in cleaning up CW reception in static, noise, etc.
The circuit operates by first receiving an audio signal that may be compromised due to weak signal strength or interference. The phase-locked loop (PLL), designated as U1, plays a crucial role in signal processing by locking onto the frequency of the incoming tone. The frequency detection is achieved through the configuration of resistors R1 and R7 and capacitor C2, which set the PLL's reference frequency. When the PLL successfully detects a tone, it generates a low signal at pin 8.
This low output serves as a control signal that activates tone generator U2. The tone generator is responsible for producing a clean, consistent tone that can replace the original weak signal. The output of U2 can then be used for further processing or directly fed to a speaker or other audio output device. The overall design significantly enhances the clarity of CW signals by filtering out unwanted noise and static, making it a valuable tool for amateur radio operators and audio signal processing applications.
In summary, the circuit effectively recovers and enhances weak CW signals by utilizing a PLL for frequency detection and a tone generator for signal improvement, resulting in clearer audio output. This circuit takes audio from a receiver that might have a weak CW or tone signal and uses a PLL (Ul) to recover the wea k signal. Ul produces a low on receipt of a tone or note of frequency, determined by Rl, R7, and C2. The output of Ul (pin 8) goes low, keys tone generator U2, and produces a new tone. The circuit is useful in cleaning up CW reception in static, noise, etc.