Simple Motorcycle AlarmCircuit by Ron J
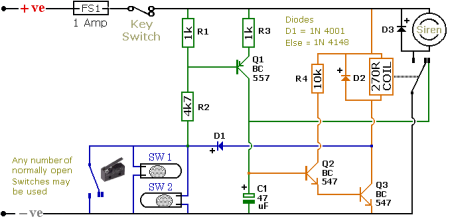
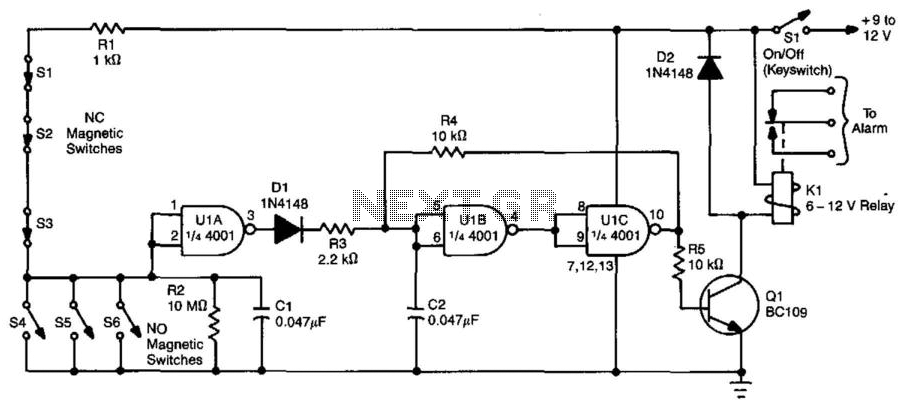
The schematic illustrates a Simple Motorcycle Alarm Circuit Diagram created by Ron J. It incorporates micro-switches to safeguard removable panels and...
The Simple Motorcycle Alarm Circuit Diagram is designed to enhance the security of motorcycles by utilizing a series of micro-switches strategically placed on removable panels. These micro-switches serve as sensors that detect unauthorized access to critical components, such as the seat or fuel tank, which are often targeted by thieves.
The circuit typically consists of a power supply, often a 9V battery, that powers the entire alarm system. The micro-switches are connected to a central control unit, which monitors their status. When a removable panel is disturbed, the corresponding micro-switch is activated, sending a signal to the control unit. This activation triggers an alarm, which can be an audible sound or a flashing LED light, alerting the owner and deterring potential thieves.
In addition to the micro-switches, the circuit may include a reset button that allows the user to deactivate the alarm after confirming that the panels are secure. It may also feature a delay timer to prevent false alarms caused by minor disturbances, such as vibrations from passing vehicles.
The schematic can be further enhanced by integrating a remote control system, allowing the user to arm or disarm the alarm from a distance. This feature adds convenience and additional layers of security, as it enables the owner to monitor the motorcycle without needing to approach it directly.
Overall, the Simple Motorcycle Alarm Circuit Diagram provides a practical solution for motorcycle security, utilizing basic electronic components to create an effective alarm system that can be easily implemented.The following schematic shows the Simple Motorcycle Alarm Circuit Diagram designed and drawn by Ron J. It uses micro-switches to protect removable panels and.. 🔗 External reference
The Simple Motorcycle Alarm Circuit Diagram is designed to enhance the security of motorcycles by utilizing a series of micro-switches strategically placed on removable panels. These micro-switches serve as sensors that detect unauthorized access to critical components, such as the seat or fuel tank, which are often targeted by thieves.
The circuit typically consists of a power supply, often a 9V battery, that powers the entire alarm system. The micro-switches are connected to a central control unit, which monitors their status. When a removable panel is disturbed, the corresponding micro-switch is activated, sending a signal to the control unit. This activation triggers an alarm, which can be an audible sound or a flashing LED light, alerting the owner and deterring potential thieves.
In addition to the micro-switches, the circuit may include a reset button that allows the user to deactivate the alarm after confirming that the panels are secure. It may also feature a delay timer to prevent false alarms caused by minor disturbances, such as vibrations from passing vehicles.
The schematic can be further enhanced by integrating a remote control system, allowing the user to arm or disarm the alarm from a distance. This feature adds convenience and additional layers of security, as it enables the owner to monitor the motorcycle without needing to approach it directly.
Overall, the Simple Motorcycle Alarm Circuit Diagram provides a practical solution for motorcycle security, utilizing basic electronic components to create an effective alarm system that can be easily implemented.The following schematic shows the Simple Motorcycle Alarm Circuit Diagram designed and drawn by Ron J. It uses micro-switches to protect removable panels and.. 🔗 External reference