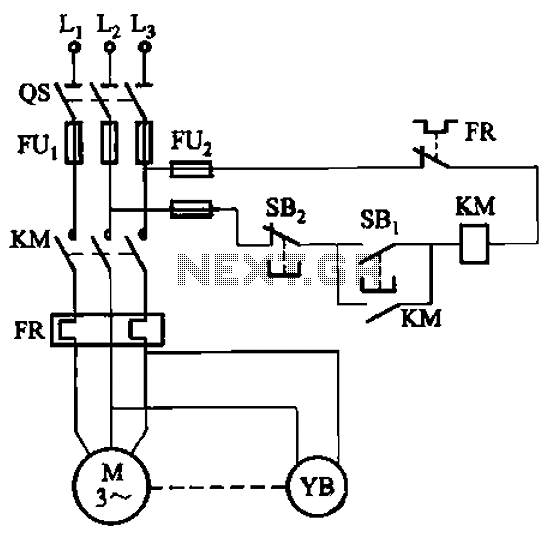
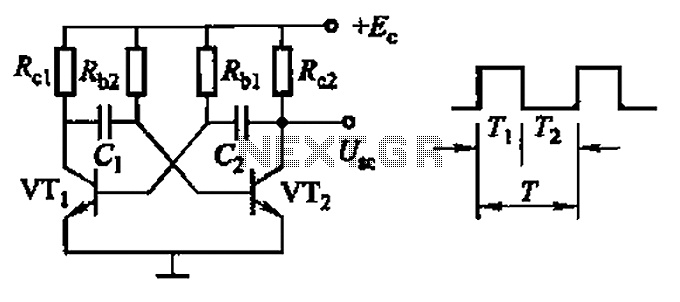
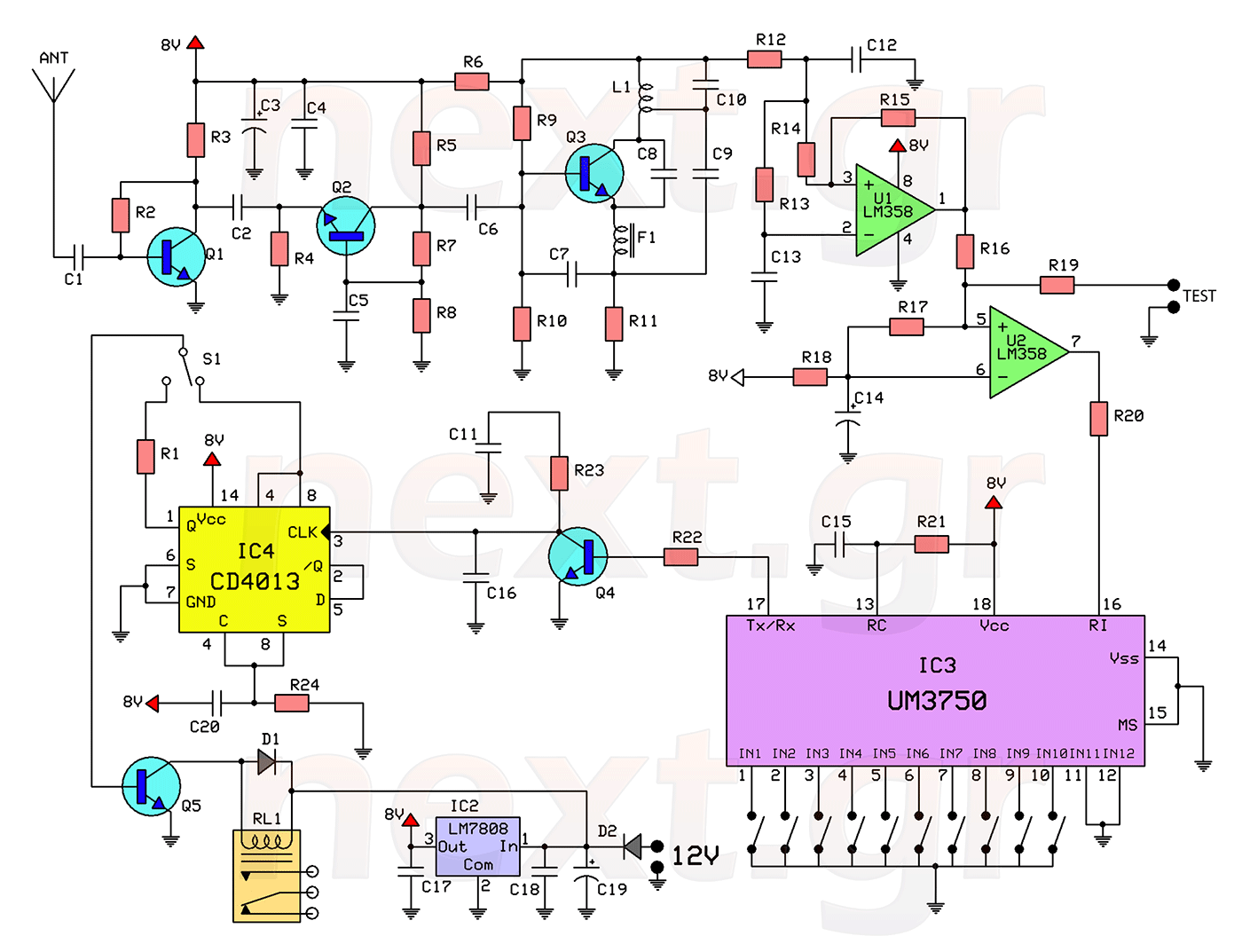
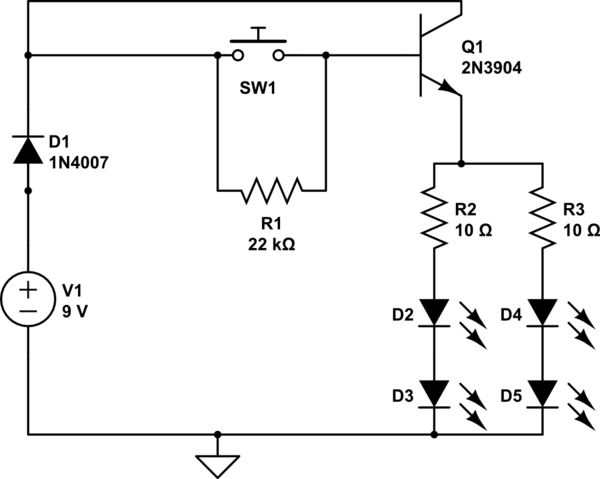
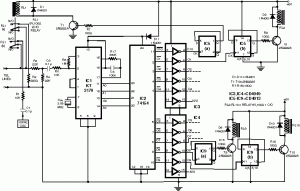
Sony KV-S29MHl TV switching power supply (SIR a 80145A) circuit diagram
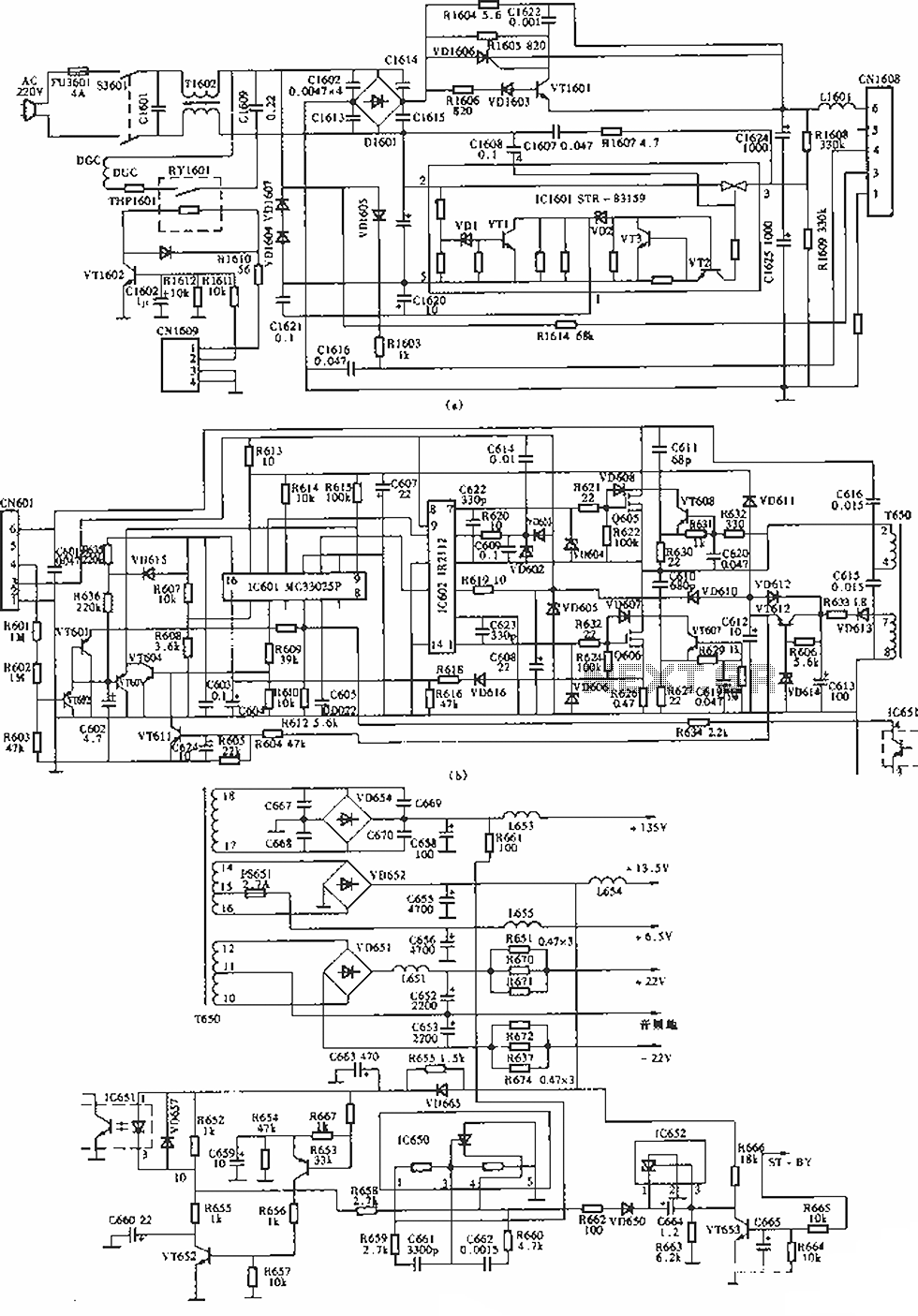
The circuit of the Sony KV-S29MHl (S Movement series) TV switching power supply (SIR a 80145A) consists of three main sections: (A) the power oscillation part, (B) the regulator part, and (C) the output section.
The Sony KV-S29MHl TV switching power supply utilizes a SIR a 80145A integrated circuit to manage power conversion efficiently. The power oscillation section (A) is responsible for generating the high-frequency AC voltage necessary for the operation of the power supply. This section typically includes components such as a transformer, switching transistors, and associated feedback mechanisms to maintain stability and efficiency during operation.
The regulator section (B) ensures that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in load or input voltage. This is achieved through various control strategies, which may involve pulse-width modulation (PWM) or linear regulation techniques. Components in this section often include operational amplifiers, error amplifiers, and additional filtering capacitors to smooth out the voltage output.
The output section (C) delivers the regulated voltage to the TV circuitry. It is designed to provide adequate current while minimizing ripple and noise, which is crucial for maintaining the performance of the television. This section may also incorporate protective features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, and short-circuit protection to ensure the reliability and safety of the power supply.
Overall, the design and functionality of the Sony KV-S29MHl TV switching power supply reflect a well-engineered approach to power management, ensuring that the television operates efficiently and reliably under various conditions.As shown in the Sony KV-S29MHl (S movement series) TV switching power supply (SIR a 80145A) circuit; (A) is the power oscillation part; (b) is the regulator part; (c) is the output section.
The Sony KV-S29MHl TV switching power supply utilizes a SIR a 80145A integrated circuit to manage power conversion efficiently. The power oscillation section (A) is responsible for generating the high-frequency AC voltage necessary for the operation of the power supply. This section typically includes components such as a transformer, switching transistors, and associated feedback mechanisms to maintain stability and efficiency during operation.
The regulator section (B) ensures that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in load or input voltage. This is achieved through various control strategies, which may involve pulse-width modulation (PWM) or linear regulation techniques. Components in this section often include operational amplifiers, error amplifiers, and additional filtering capacitors to smooth out the voltage output.
The output section (C) delivers the regulated voltage to the TV circuitry. It is designed to provide adequate current while minimizing ripple and noise, which is crucial for maintaining the performance of the television. This section may also incorporate protective features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, and short-circuit protection to ensure the reliability and safety of the power supply.
Overall, the design and functionality of the Sony KV-S29MHl TV switching power supply reflect a well-engineered approach to power management, ensuring that the television operates efficiently and reliably under various conditions.As shown in the Sony KV-S29MHl (S movement series) TV switching power supply (SIR a 80145A) circuit; (A) is the power oscillation part; (b) is the regulator part; (c) is the output section.