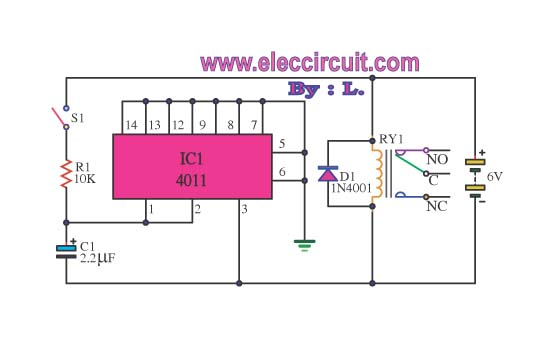
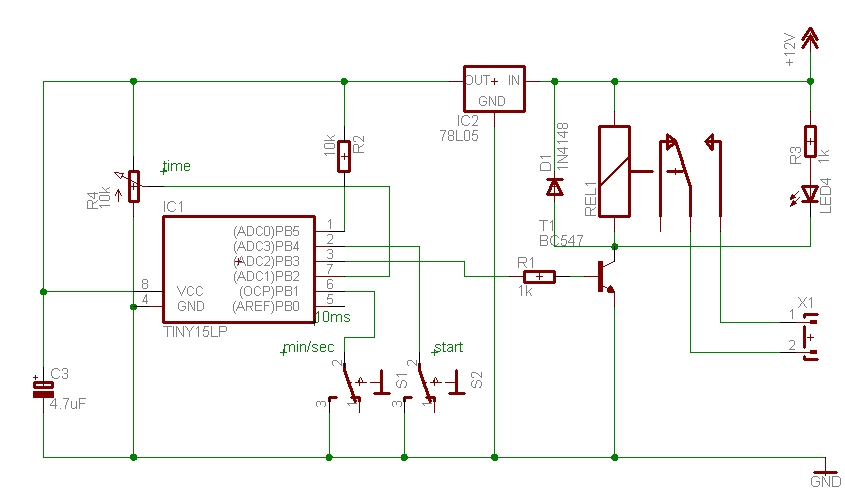
speaker to microphone circuit converter
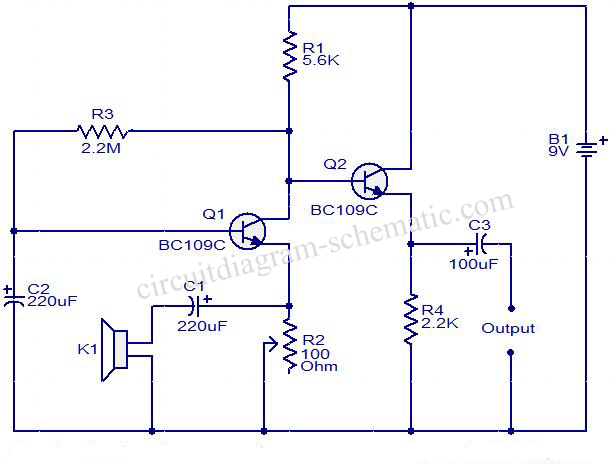
This circuit diagram illustrates the conversion of a speaker into a microphone. When sound waves impact the diaphragm of a speaker, fluctuations occur in the coil, generating an induced voltage. This induced voltage is typically substantial but low in output. In this design, a low voltage circuit employs a transistor to amplify the signal and produce a suitable output.
The circuit operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the movement of the speaker diaphragm in response to sound waves creates variations in the magnetic field surrounding the coil. This results in an alternating current (AC) voltage that can be harnessed as an audio signal. The speaker, originally designed to convert electrical signals into sound, is repurposed to perform the opposite function—capturing sound and converting it back into electrical signals.
The key components of the circuit include the speaker, a transistor, and passive components such as resistors and capacitors. The speaker acts as the input transducer, while the transistor functions as the amplifier, boosting the weak audio signal generated by the speaker.
The circuit may utilize a common-emitter configuration for the transistor, which provides significant voltage gain. A resistor is connected to the collector of the transistor to set the operating point and ensure proper biasing. Additionally, a coupling capacitor may be employed to block any DC component from the output, allowing only the amplified AC audio signal to pass through.
To enhance performance, a power supply circuit is included to provide the necessary voltage for the transistor's operation. The overall design must consider the impedance matching between the speaker and the transistor to maximize signal transfer and minimize distortion.
This circuit can be used in various applications, such as audio recording, communication devices, and sound sensing systems, showcasing the versatility of converting a speaker into a functional microphone through careful circuit design.This circuit is a circuit diagram to convert the speaker into the microphone. In principle When sound waves fall on the diaphragm of a speaker, there will be fluctuations in the coil and the induced voltage will be no small proportion. This induced voltage is usually very large and useful low. Here, the low voltage circuit using a transistor amplified to produce a reasonable output 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the movement of the speaker diaphragm in response to sound waves creates variations in the magnetic field surrounding the coil. This results in an alternating current (AC) voltage that can be harnessed as an audio signal. The speaker, originally designed to convert electrical signals into sound, is repurposed to perform the opposite function—capturing sound and converting it back into electrical signals.
The key components of the circuit include the speaker, a transistor, and passive components such as resistors and capacitors. The speaker acts as the input transducer, while the transistor functions as the amplifier, boosting the weak audio signal generated by the speaker.
The circuit may utilize a common-emitter configuration for the transistor, which provides significant voltage gain. A resistor is connected to the collector of the transistor to set the operating point and ensure proper biasing. Additionally, a coupling capacitor may be employed to block any DC component from the output, allowing only the amplified AC audio signal to pass through.
To enhance performance, a power supply circuit is included to provide the necessary voltage for the transistor's operation. The overall design must consider the impedance matching between the speaker and the transistor to maximize signal transfer and minimize distortion.
This circuit can be used in various applications, such as audio recording, communication devices, and sound sensing systems, showcasing the versatility of converting a speaker into a functional microphone through careful circuit design.This circuit is a circuit diagram to convert the speaker into the microphone. In principle When sound waves fall on the diaphragm of a speaker, there will be fluctuations in the coil and the induced voltage will be no small proportion. This induced voltage is usually very large and useful low. Here, the low voltage circuit using a transistor amplified to produce a reasonable output 🔗 External reference