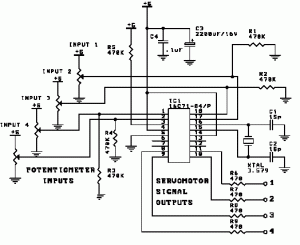
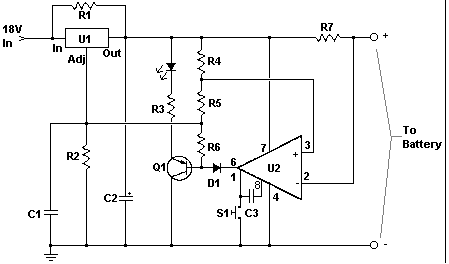
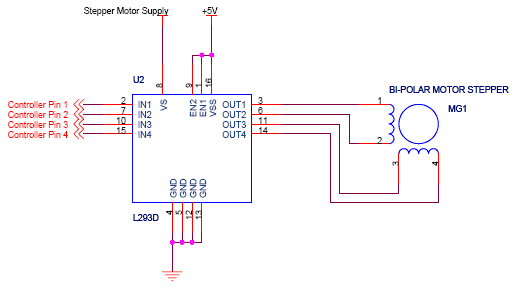
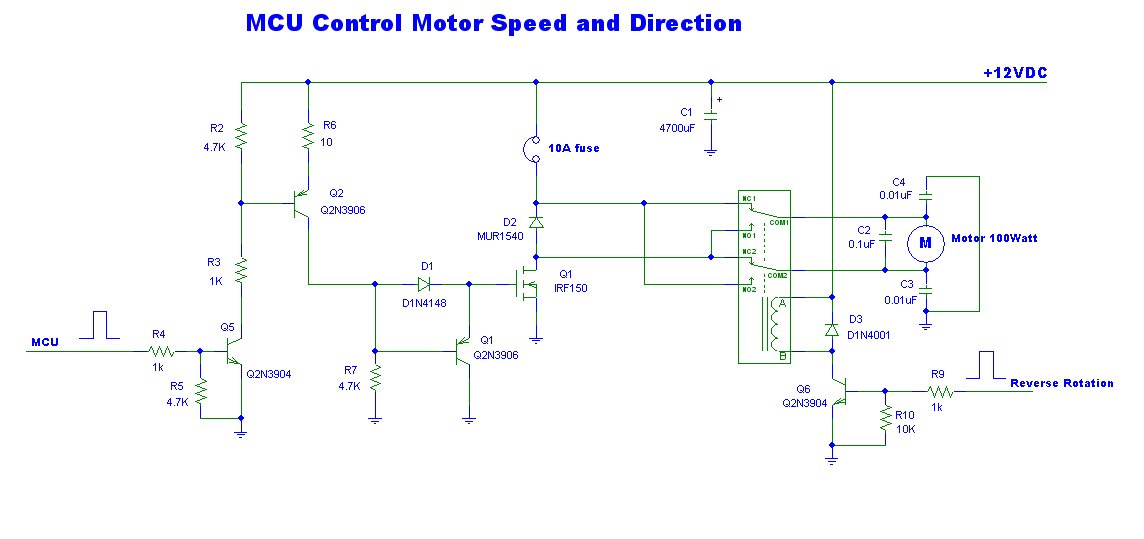
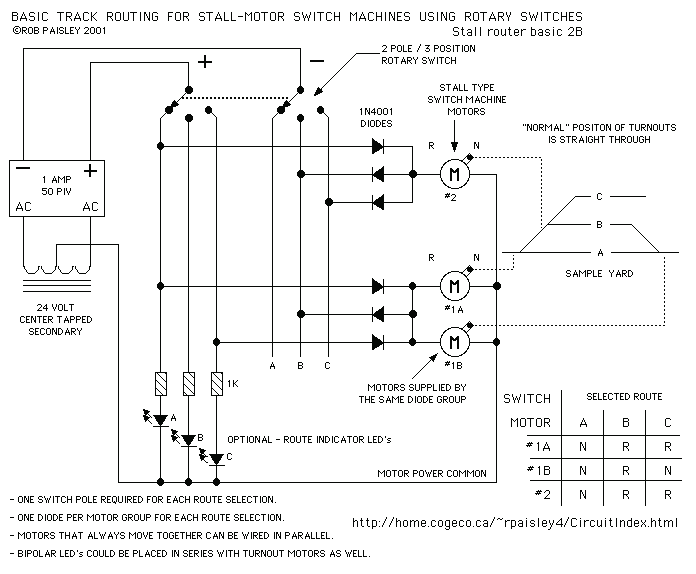
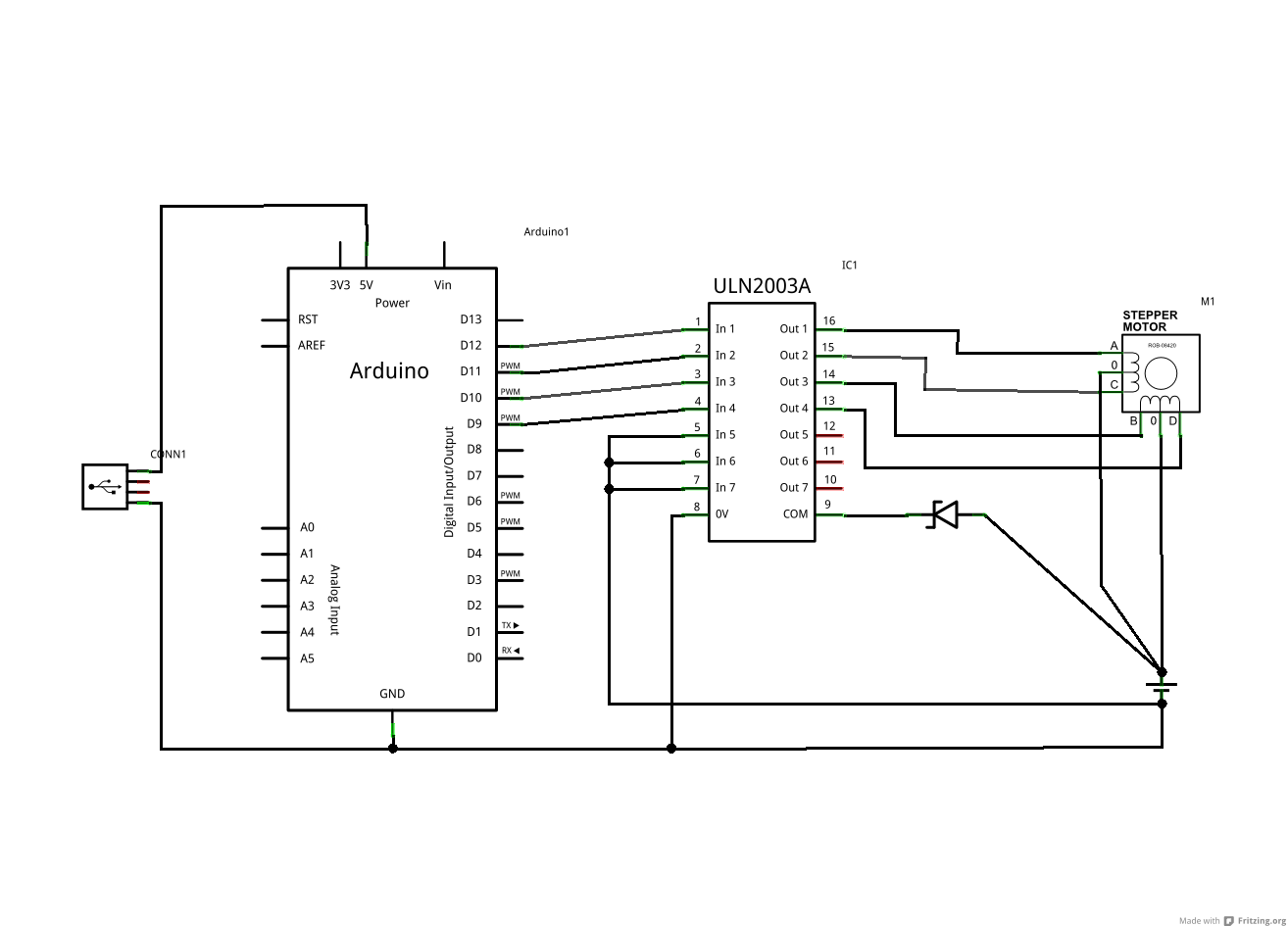
Speed-Control for Small Asynchronous Induction Motor
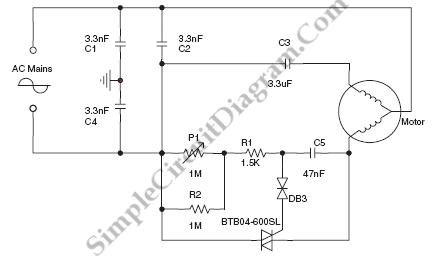
The circuit diagram below illustrates a schematic designed to control the speed of a low-power induction motor, commonly found in fans.
The schematic for controlling the speed of a low-power induction motor typically incorporates several key components that work together to adjust the motor's operational speed effectively. The primary method of speed control in such motors involves varying the voltage or frequency supplied to the motor.
One common approach is the use of a variable resistor or potentiometer connected to a triac or a solid-state relay. The variable resistor allows the user to adjust the resistance in the circuit, which in turn alters the voltage reaching the motor. This change in voltage results in a corresponding change in the speed of the motor.
In more sophisticated designs, a pulse-width modulation (PWM) controller may be employed. This method involves switching the motor's power supply on and off at a high frequency, effectively controlling the average voltage and current supplied to the motor. The duty cycle of the PWM signal can be adjusted to vary the speed of the motor, providing a smooth and efficient operation.
Additionally, the circuit may include protective components such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent damage due to overload conditions. Capacitors may also be present to filter out electrical noise and ensure stable operation.
The schematic will typically include a power supply section that provides the necessary voltage to the motor, a control interface for user input, and a motor driver section that translates the control signals into motor operation. The integration of these components allows for effective speed control of low-power induction motors used in various applications, including household fans.On the circuit diagram below show us a schematic which is used to set the speed of a low-power induction motor, such as those which can be found in fan.. 🔗 External reference
The schematic for controlling the speed of a low-power induction motor typically incorporates several key components that work together to adjust the motor's operational speed effectively. The primary method of speed control in such motors involves varying the voltage or frequency supplied to the motor.
One common approach is the use of a variable resistor or potentiometer connected to a triac or a solid-state relay. The variable resistor allows the user to adjust the resistance in the circuit, which in turn alters the voltage reaching the motor. This change in voltage results in a corresponding change in the speed of the motor.
In more sophisticated designs, a pulse-width modulation (PWM) controller may be employed. This method involves switching the motor's power supply on and off at a high frequency, effectively controlling the average voltage and current supplied to the motor. The duty cycle of the PWM signal can be adjusted to vary the speed of the motor, providing a smooth and efficient operation.
Additionally, the circuit may include protective components such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent damage due to overload conditions. Capacitors may also be present to filter out electrical noise and ensure stable operation.
The schematic will typically include a power supply section that provides the necessary voltage to the motor, a control interface for user input, and a motor driver section that translates the control signals into motor operation. The integration of these components allows for effective speed control of low-power induction motors used in various applications, including household fans.On the circuit diagram below show us a schematic which is used to set the speed of a low-power induction motor, such as those which can be found in fan.. 🔗 External reference