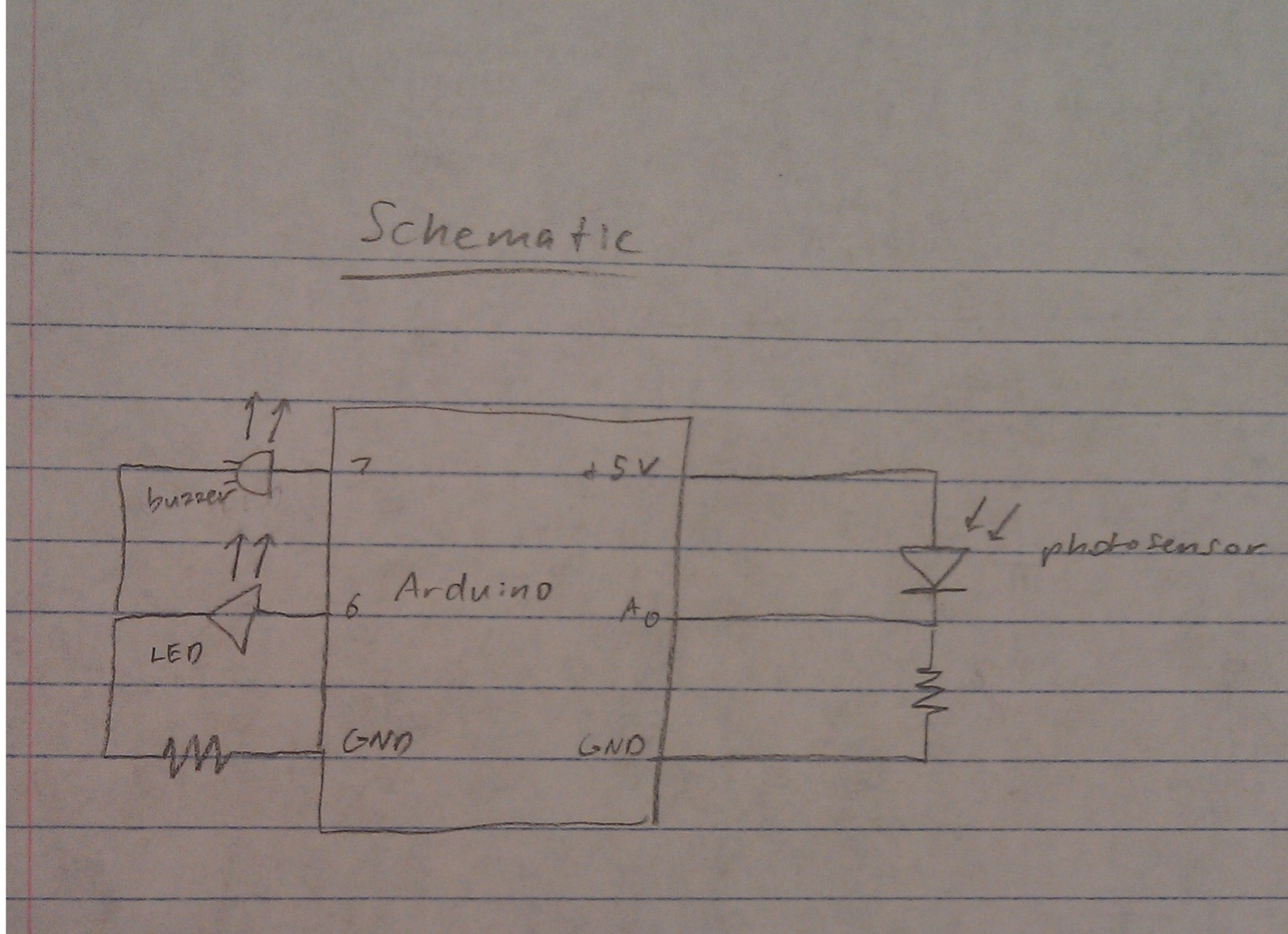
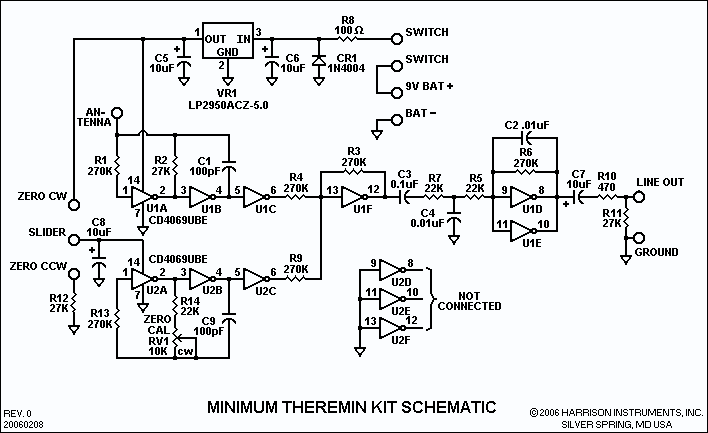
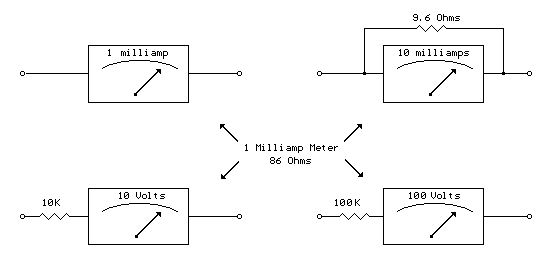
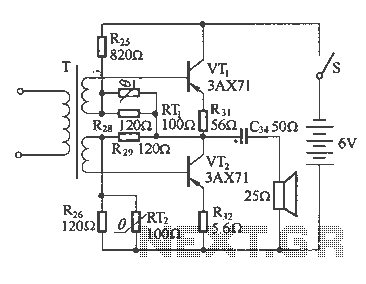
STK6327A application circuit
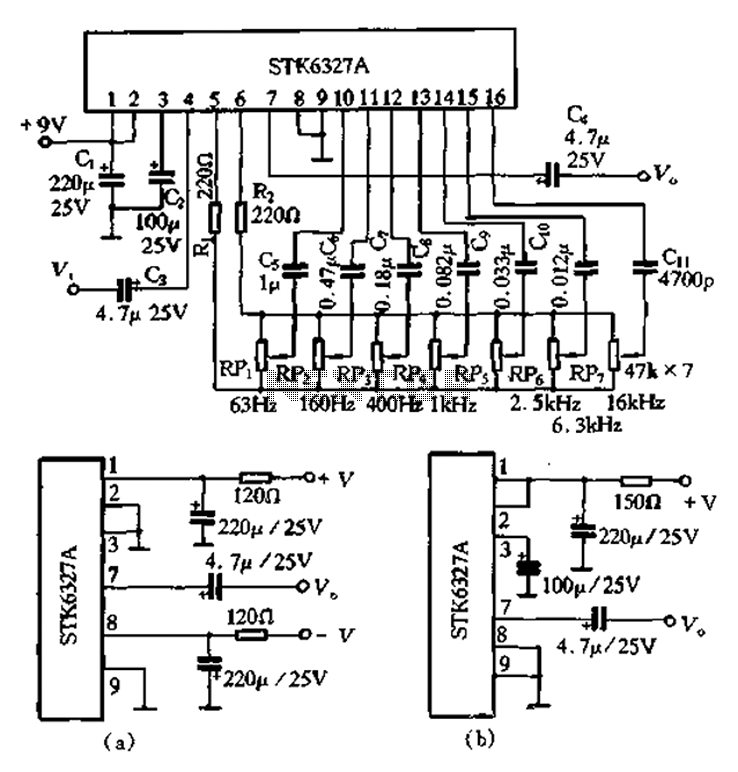
After the universal application of graphic equalizers, a new type of equalizer known as the parametric equalizer has emerged. This equalizer differs in its internal circuit structure and utilizes an external adjustment method that sets it apart from traditional tone regulation circuits. Unlike conventional tone control circuits, which typically adjust only two fixed frequencies within a narrow range, graphic equalizers adjust a few predetermined points. In contrast, parametric equalizers offer a wider frequency adjustment range, allowing for precise boosting or cutting of selected frequencies. The Nissan brand TEAC V-2RX and V-4RX decks both incorporate this equalizer. Whether used for recording or playback, it allows for arbitrary low-frequency adjustments between 60 Hz and 500 Hz, with a control range of up to 15 dB. Additionally, the domestic Huaqiang HQ-850 machines also feature this equalizer, employing a two-stage adjustment method. The first stage covers 70 Hz to 700 Hz, while the second stage spans 1 kHz to 10 kHz, enabling gain adjustments of up to 12 dB at any point within each band.
The parametric equalizer represents an advanced evolution in audio processing technology, characterized by its ability to manipulate sound frequencies with high precision. The core functionality of a parametric equalizer hinges on three primary controls: frequency selection, bandwidth (or Q factor), and gain.
1. **Frequency Selection**: This control allows the user to choose the specific frequency that requires adjustment. The parametric equalizer can target any frequency within its operational range, providing flexibility that is not available in fixed-frequency equalizers.
2. **Bandwidth (Q Factor)**: This parameter defines the range of frequencies around the selected frequency that will be affected by the gain adjustment. A lower Q factor results in a broader range of affected frequencies, while a higher Q factor narrows the adjustment to a specific frequency band. This allows for subtle tonal shaping or more pronounced alterations depending on the desired outcome.
3. **Gain Control**: This function adjusts the amplitude of the selected frequency. It can boost (amplify) or cut (attenuate) the signal by a specified amount, typically measured in decibels (dB). The ability to apply significant gain adjustments, as seen in the TEAC V-2RX and V-4RX models, enhances the versatility of the equalizer in both recording and playback scenarios.
The implementation of the parametric equalizer in audio devices such as the TEAC decks and Huaqiang HQ-850 exemplifies its practical application in real-world audio processing. By allowing adjustments across a wide frequency range and providing detailed control over the sound profile, parametric equalizers enable audio engineers and enthusiasts to achieve a tailored sound that meets specific requirements for various audio environments. This technology not only enhances the listening experience but also facilitates more precise sound engineering in professional and domestic settings.After the graphic equalizers are universally applied, and the emergence of a new kind of equalizer, called a parametric equalizer that amount of EQ, or from the internal circui t structure is different in terms of the use of external adjustment method the general tone regulation circuit, is also different from the preceding graphic equalizer circuit, it is a new equalizer circuit. The usual tone control circuit, only for the selected two fixed frequencies increase or decrease over the adjustment range is narrow.
Graphic equalizers are also only a few predetermined point increase or decrease the frequency adjustment, and the parametric equalizer and the two different ways o It can adjust in a wide range of frequencies of the control circuit choice, and then the frequency selection will be boost or cut fine adjustment. Nissan brand TEAC V-2RX and V-4RX Both decks are used in this equalizer. Use the equalizer Whether recording or playback, can be within 60 ~ 500Hz low frequency arbitrary point adjustment control of 15dB.
Domestic licensing Huaqiang HQ - 850 machines also use this equalizer, which uses a two-stage adjustment method, the first paragraph of 70 ~ 700H, second paragraph 1k ~ lOkHz, any point on each band could be used for 12. dB gain adjustment.
The parametric equalizer represents an advanced evolution in audio processing technology, characterized by its ability to manipulate sound frequencies with high precision. The core functionality of a parametric equalizer hinges on three primary controls: frequency selection, bandwidth (or Q factor), and gain.
1. **Frequency Selection**: This control allows the user to choose the specific frequency that requires adjustment. The parametric equalizer can target any frequency within its operational range, providing flexibility that is not available in fixed-frequency equalizers.
2. **Bandwidth (Q Factor)**: This parameter defines the range of frequencies around the selected frequency that will be affected by the gain adjustment. A lower Q factor results in a broader range of affected frequencies, while a higher Q factor narrows the adjustment to a specific frequency band. This allows for subtle tonal shaping or more pronounced alterations depending on the desired outcome.
3. **Gain Control**: This function adjusts the amplitude of the selected frequency. It can boost (amplify) or cut (attenuate) the signal by a specified amount, typically measured in decibels (dB). The ability to apply significant gain adjustments, as seen in the TEAC V-2RX and V-4RX models, enhances the versatility of the equalizer in both recording and playback scenarios.
The implementation of the parametric equalizer in audio devices such as the TEAC decks and Huaqiang HQ-850 exemplifies its practical application in real-world audio processing. By allowing adjustments across a wide frequency range and providing detailed control over the sound profile, parametric equalizers enable audio engineers and enthusiasts to achieve a tailored sound that meets specific requirements for various audio environments. This technology not only enhances the listening experience but also facilitates more precise sound engineering in professional and domestic settings.After the graphic equalizers are universally applied, and the emergence of a new kind of equalizer, called a parametric equalizer that amount of EQ, or from the internal circui t structure is different in terms of the use of external adjustment method the general tone regulation circuit, is also different from the preceding graphic equalizer circuit, it is a new equalizer circuit. The usual tone control circuit, only for the selected two fixed frequencies increase or decrease over the adjustment range is narrow.
Graphic equalizers are also only a few predetermined point increase or decrease the frequency adjustment, and the parametric equalizer and the two different ways o It can adjust in a wide range of frequencies of the control circuit choice, and then the frequency selection will be boost or cut fine adjustment. Nissan brand TEAC V-2RX and V-4RX Both decks are used in this equalizer. Use the equalizer Whether recording or playback, can be within 60 ~ 500Hz low frequency arbitrary point adjustment control of 15dB.
Domestic licensing Huaqiang HQ - 850 machines also use this equalizer, which uses a two-stage adjustment method, the first paragraph of 70 ~ 700H, second paragraph 1k ~ lOkHz, any point on each band could be used for 12. dB gain adjustment.