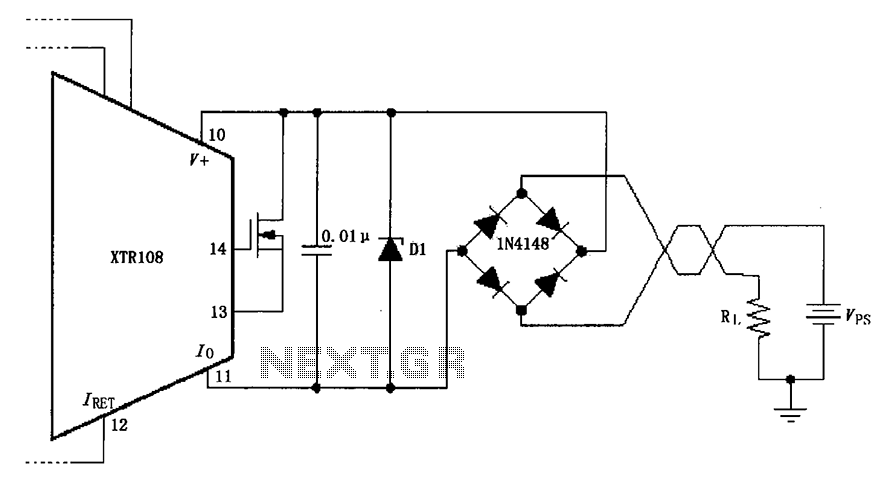
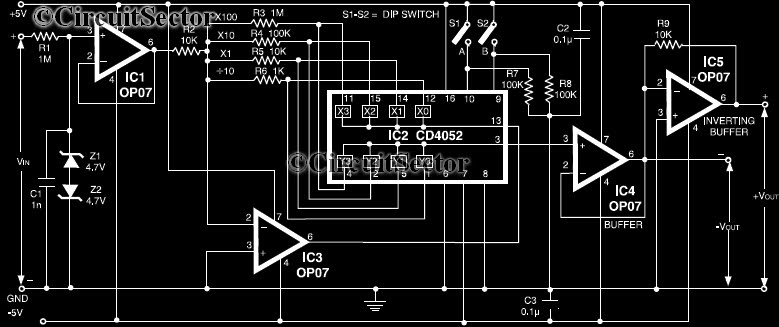
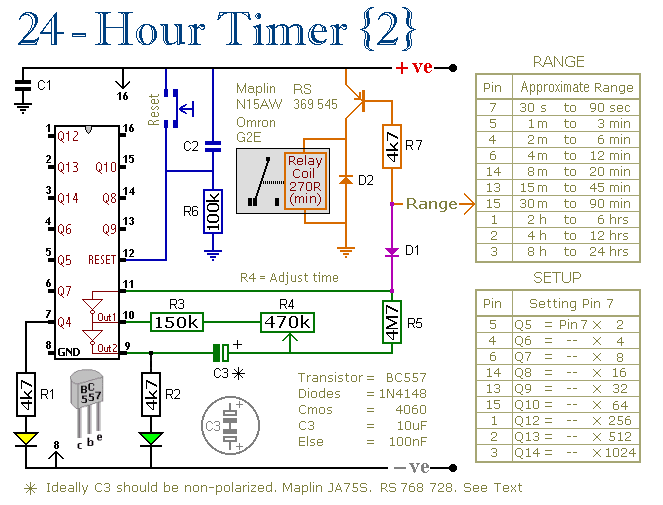
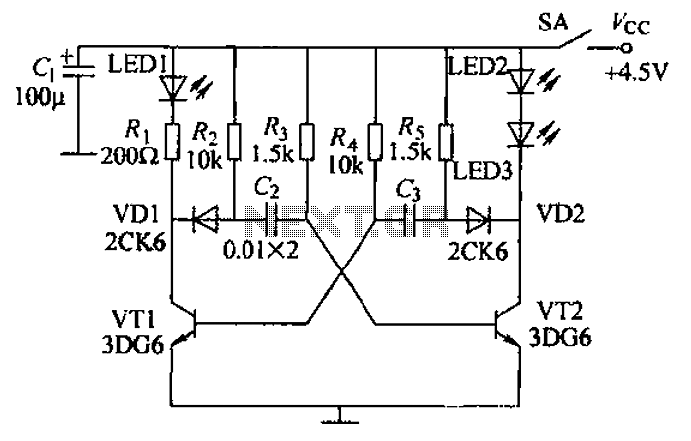
TDA1022 Audio Reverberator Circuit
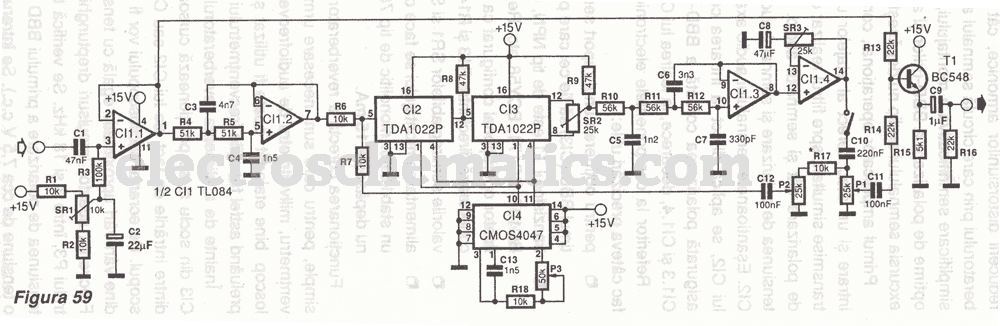
The first reverberator presented is based on the TDA1022, which is the most commonly used BBD (Bucket Brigade Device). Adjustments for proper functionality of the reverberator are required before connecting the power supply.
The TDA1022 is a versatile BBD that operates effectively in audio processing applications, particularly for creating reverb effects. It is designed to handle low-frequency signals, making it suitable for musical instruments and vocal processing. The reverberator circuit using the TDA1022 typically includes several key components: the BBD itself, a clock generator for timing control, and various passive components such as resistors and capacitors that dictate the delay time and feedback characteristics.
To ensure proper functionality, the circuit should be configured with the appropriate power supply voltage as specified in the TDA1022 datasheet, usually around 9V to 15V. Additionally, adjustments may include setting the input and output levels to prevent distortion or clipping, as well as tuning the feedback loop to achieve the desired reverberation effect. The integration of potentiometers in the feedback path can allow for real-time adjustments of the reverb depth.
The schematic will typically feature an input stage where the audio signal is fed into the TDA1022. The output stage will then convert the processed signal back to a suitable level for further amplification or mixing. Care should be taken to layout the PCB to minimize noise and interference, especially in the clock circuit, as timing inaccuracies can adversely affect the reverb quality.
Overall, the TDA1022-based reverberator design exemplifies a classic approach to audio effects, combining analog components to produce a rich, spacious sound that enhances musical performances. Proper tuning and adjustments are essential for optimal performance, ensuring that the reverberation effect complements the source material effectively.The first reverberator we present is based on TDA1022, the most used BBD. Reverberator adjustements for proper functionality Before we connect the power su.. 🔗 External reference
The TDA1022 is a versatile BBD that operates effectively in audio processing applications, particularly for creating reverb effects. It is designed to handle low-frequency signals, making it suitable for musical instruments and vocal processing. The reverberator circuit using the TDA1022 typically includes several key components: the BBD itself, a clock generator for timing control, and various passive components such as resistors and capacitors that dictate the delay time and feedback characteristics.
To ensure proper functionality, the circuit should be configured with the appropriate power supply voltage as specified in the TDA1022 datasheet, usually around 9V to 15V. Additionally, adjustments may include setting the input and output levels to prevent distortion or clipping, as well as tuning the feedback loop to achieve the desired reverberation effect. The integration of potentiometers in the feedback path can allow for real-time adjustments of the reverb depth.
The schematic will typically feature an input stage where the audio signal is fed into the TDA1022. The output stage will then convert the processed signal back to a suitable level for further amplification or mixing. Care should be taken to layout the PCB to minimize noise and interference, especially in the clock circuit, as timing inaccuracies can adversely affect the reverb quality.
Overall, the TDA1022-based reverberator design exemplifies a classic approach to audio effects, combining analog components to produce a rich, spacious sound that enhances musical performances. Proper tuning and adjustments are essential for optimal performance, ensuring that the reverberation effect complements the source material effectively.The first reverberator we present is based on TDA1022, the most used BBD. Reverberator adjustements for proper functionality Before we connect the power su.. 🔗 External reference