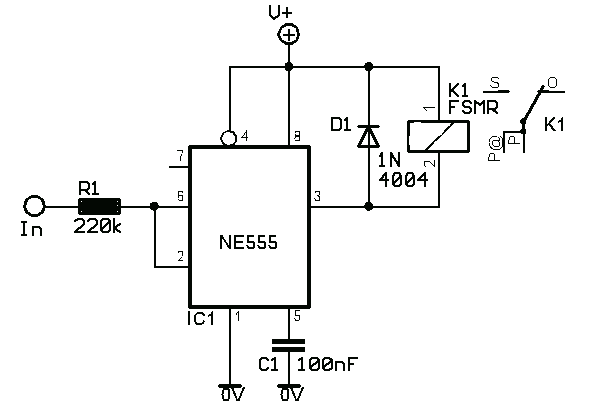
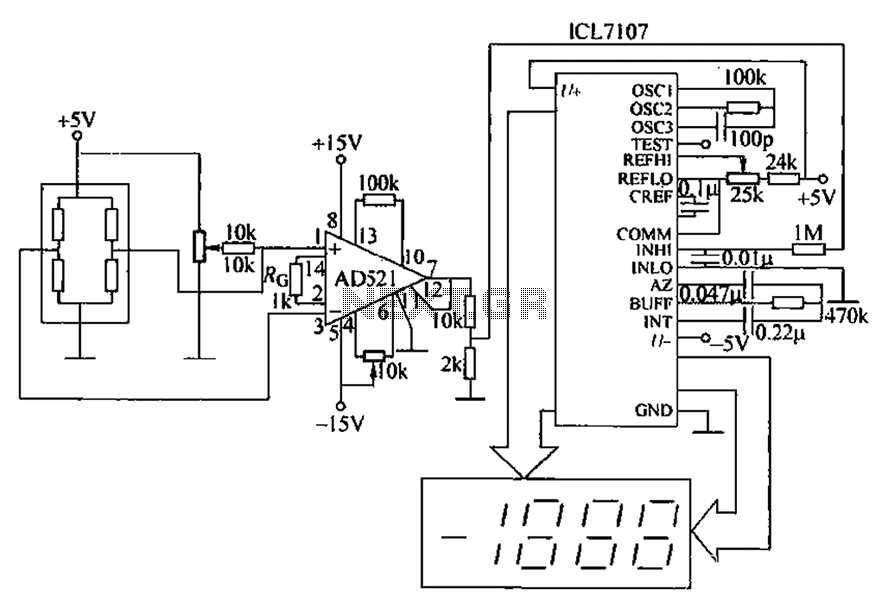
XTR108 reverse voltage and overvoltage protection circuit diagrams
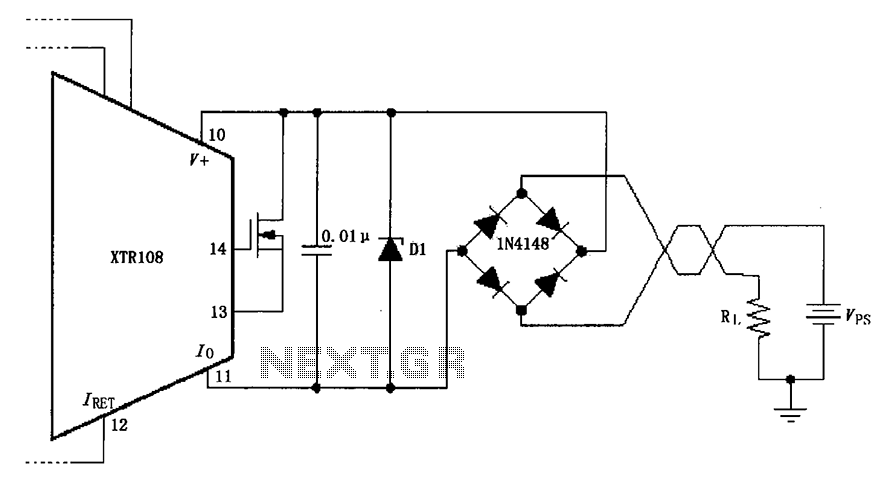
The circuit utilizes a Zener diode (D1) for overvoltage protection and a diode rectifier bridge for reverse voltage protection. The 1.4V drop across the diodes will result in a maximum voltage loss, meaning that the supply voltage (VPS) must be less than the minimum breakdown voltage of the Zener diode.
The circuit design incorporates a Zener diode configured to limit the voltage across sensitive components, ensuring that any voltage exceeding the specified threshold is clamped to a safe level. The Zener diode operates in reverse breakdown mode, where it maintains a constant output voltage even as the input voltage varies, thus providing reliable overvoltage protection.
In conjunction with the Zener diode, a diode rectifier bridge is employed to safeguard against reverse voltage conditions. This bridge consists of four diodes arranged in a configuration that allows current to flow in one direction while blocking reverse current, protecting the circuit from potential damage caused by incorrect polarity.
It is essential to consider the voltage drop across the diodes in the rectifier bridge, which typically amounts to approximately 1.4V for silicon diodes. This voltage drop must be factored into the circuit design, as it dictates that the supply voltage (VPS) should remain below the Zener diode's minimum breakdown voltage to avoid exceeding its limits and risking component failure.
In summary, the circuit effectively combines Zener diode overvoltage protection with a diode rectifier bridge to ensure robust performance and reliability, while careful attention to voltage specifications is critical for optimal operation. As shown, the circuit uses a zener diode D1 achieve overvoltage protection, a diode rectifier bridge to achieve reverse voltage protection. Diodes 1.4V loop will cause the maxi mum loss of voltage VPS must be lower than the minimum zener diode breakdown voltage.
The circuit design incorporates a Zener diode configured to limit the voltage across sensitive components, ensuring that any voltage exceeding the specified threshold is clamped to a safe level. The Zener diode operates in reverse breakdown mode, where it maintains a constant output voltage even as the input voltage varies, thus providing reliable overvoltage protection.
In conjunction with the Zener diode, a diode rectifier bridge is employed to safeguard against reverse voltage conditions. This bridge consists of four diodes arranged in a configuration that allows current to flow in one direction while blocking reverse current, protecting the circuit from potential damage caused by incorrect polarity.
It is essential to consider the voltage drop across the diodes in the rectifier bridge, which typically amounts to approximately 1.4V for silicon diodes. This voltage drop must be factored into the circuit design, as it dictates that the supply voltage (VPS) should remain below the Zener diode's minimum breakdown voltage to avoid exceeding its limits and risking component failure.
In summary, the circuit effectively combines Zener diode overvoltage protection with a diode rectifier bridge to ensure robust performance and reliability, while careful attention to voltage specifications is critical for optimal operation. As shown, the circuit uses a zener diode D1 achieve overvoltage protection, a diode rectifier bridge to achieve reverse voltage protection. Diodes 1.4V loop will cause the maxi mum loss of voltage VPS must be lower than the minimum zener diode breakdown voltage.
%2Busing%2Bop%2Bamp%2B741%2Bic%2B.png)