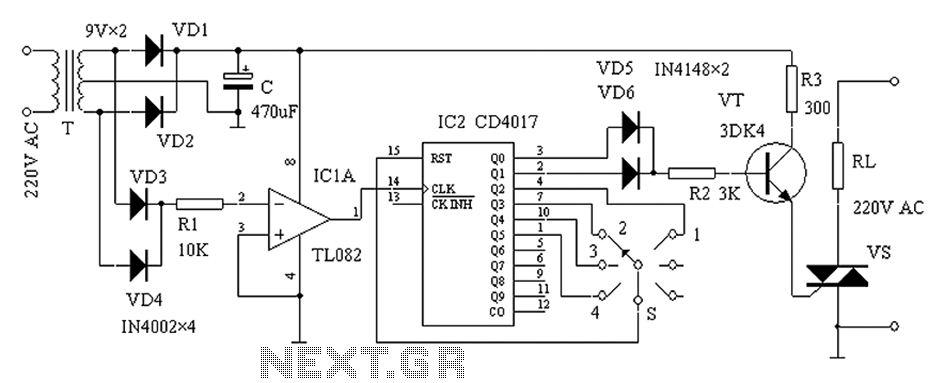
TDA3910 Internal Block Diagram
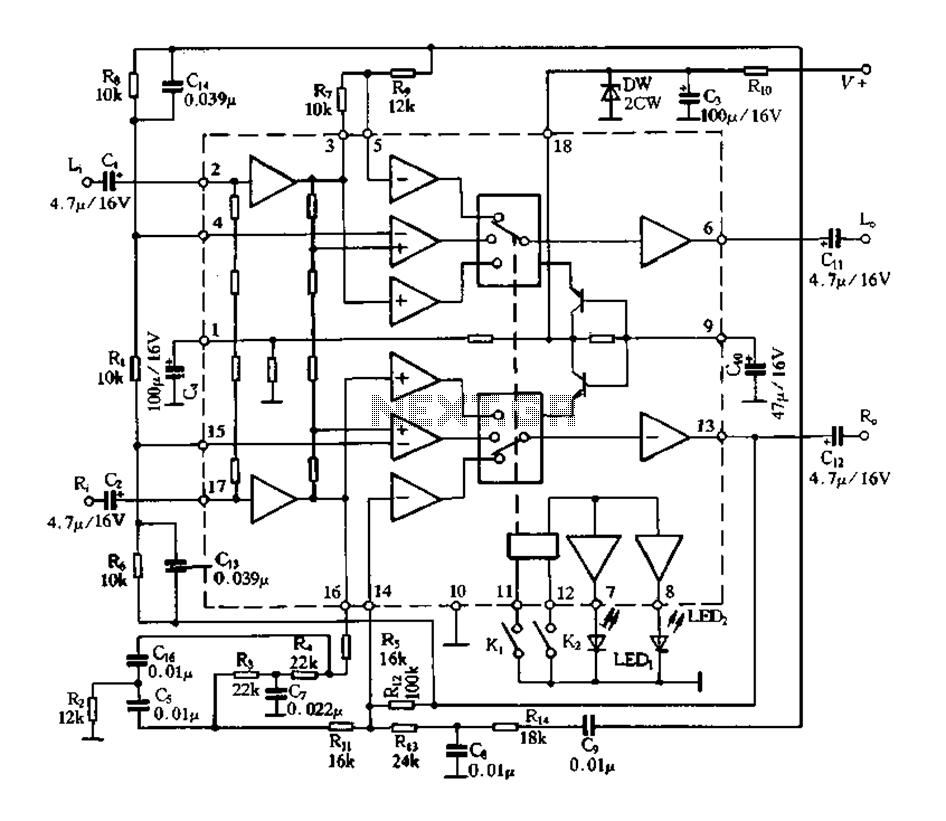
Figure 1-123 illustrates the internal block diagram of the TDA3810. The circuit is capable of functioning in three operational modes: (1) it can convert a mono channel stereo signal into an analog signal; (2) it can operate in stereo mode; and (3) it can function in stereo widening mode, also referred to as surround sound.
The TDA3810 is an integrated circuit designed for audio processing, specifically targeting applications that require versatile audio signal manipulation. The internal block diagram highlights the architecture that enables the device to switch between different modes of operation seamlessly, allowing for enhanced audio experiences.
In mono channel mode, the TDA3810 accepts a single audio input and processes it to produce a high-quality analog output. This mode is particularly useful in applications where stereo signals are not available, ensuring that audio playback remains clear and intelligible.
When operating in stereo mode, the circuit can handle two separate audio channels, allowing for a richer sound experience. This mode is ideal for applications that utilize standard stereo audio sources, enabling the TDA3810 to deliver precise audio reproduction with distinct left and right channel separation.
The stereo widening mode, or surround sound mode, is where the TDA3810 showcases its advanced capabilities. In this mode, the circuit employs various algorithms to enhance the spatial characteristics of the audio signal, creating an immersive listening experience that simulates surround sound environments. This is particularly advantageous in home theater systems and audio playback setups where users seek to replicate the acoustics of live performances or cinematic experiences.
Overall, the TDA3810's design and operational versatility make it a valuable component in modern audio applications, catering to a wide range of user needs while maintaining high fidelity and performance standards.Figure 1-123 is an internal block diagram of the TDA3810 o The circuit can operate in three modes of operation: (1) may be mono channel stereo signal into an analog signal; (2) can work in stereo status; (3) can work in stereo widening state or state called surround sound.
The TDA3810 is an integrated circuit designed for audio processing, specifically targeting applications that require versatile audio signal manipulation. The internal block diagram highlights the architecture that enables the device to switch between different modes of operation seamlessly, allowing for enhanced audio experiences.
In mono channel mode, the TDA3810 accepts a single audio input and processes it to produce a high-quality analog output. This mode is particularly useful in applications where stereo signals are not available, ensuring that audio playback remains clear and intelligible.
When operating in stereo mode, the circuit can handle two separate audio channels, allowing for a richer sound experience. This mode is ideal for applications that utilize standard stereo audio sources, enabling the TDA3810 to deliver precise audio reproduction with distinct left and right channel separation.
The stereo widening mode, or surround sound mode, is where the TDA3810 showcases its advanced capabilities. In this mode, the circuit employs various algorithms to enhance the spatial characteristics of the audio signal, creating an immersive listening experience that simulates surround sound environments. This is particularly advantageous in home theater systems and audio playback setups where users seek to replicate the acoustics of live performances or cinematic experiences.
Overall, the TDA3810's design and operational versatility make it a valuable component in modern audio applications, catering to a wide range of user needs while maintaining high fidelity and performance standards.Figure 1-123 is an internal block diagram of the TDA3810 o The circuit can operate in three modes of operation: (1) may be mono channel stereo signal into an analog signal; (2) can work in stereo status; (3) can work in stereo widening state or state called surround sound.

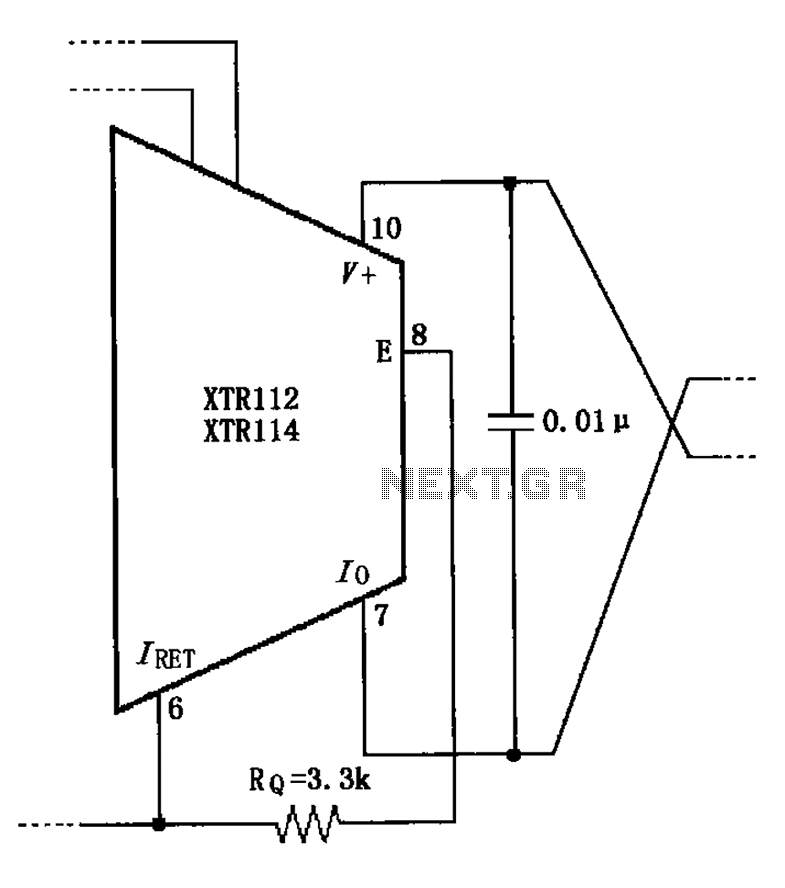
%2Bwith%2Banimation%2Bsimulation%2Bcircuit.png)