Telephone Hold Circuit Circuit

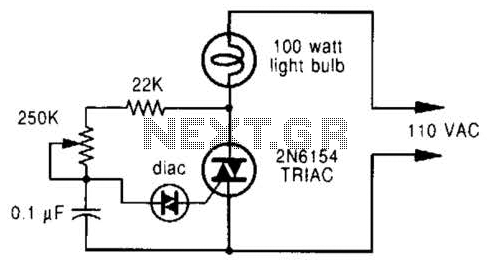
When the switch SI is pressed, the silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) is activated, connecting LED1 and resistor R1 across the telephone line. This action causes the line voltage to drop to approximately 20 volts, which maintains the connection to the central office of the telephone company.
The described circuit utilizes a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) to control the connection between an LED and a resistor across a telephone line. When the switch SI is engaged, the SCR is triggered into a conductive state. This allows current to flow through LED1 and resistor R1, which are connected in parallel to the telephone line.
The activation of the SCR results in a significant voltage drop across the line, stabilizing at around 20 volts. This voltage level is critical as it ensures that the necessary signaling and communication with the telephone company's central office is maintained. The LED serves as an indicator that the circuit is active, while resistor R1 limits the current to prevent damage to the components.
In practical applications, this configuration can be used in various telecommunication systems where visual indication of line status is required. The use of an SCR allows for efficient control of the circuit, ensuring that the LED lights up only when the switch is pressed, thus providing a clear visual cue while maintaining the integrity of the telephone line connection. Additionally, careful selection of R1 is essential to ensure proper current flow through the LED without exceeding its rated specifications. When SI is pressed, the SCR fires, and places LED1 and Rl across the phone line. The line voltage drops to about 20 V, which holds the connection to the phone company`s central office.
The described circuit utilizes a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) to control the connection between an LED and a resistor across a telephone line. When the switch SI is engaged, the SCR is triggered into a conductive state. This allows current to flow through LED1 and resistor R1, which are connected in parallel to the telephone line.
The activation of the SCR results in a significant voltage drop across the line, stabilizing at around 20 volts. This voltage level is critical as it ensures that the necessary signaling and communication with the telephone company's central office is maintained. The LED serves as an indicator that the circuit is active, while resistor R1 limits the current to prevent damage to the components.
In practical applications, this configuration can be used in various telecommunication systems where visual indication of line status is required. The use of an SCR allows for efficient control of the circuit, ensuring that the LED lights up only when the switch is pressed, thus providing a clear visual cue while maintaining the integrity of the telephone line connection. Additionally, careful selection of R1 is essential to ensure proper current flow through the LED without exceeding its rated specifications. When SI is pressed, the SCR fires, and places LED1 and Rl across the phone line. The line voltage drops to about 20 V, which holds the connection to the phone company`s central office.