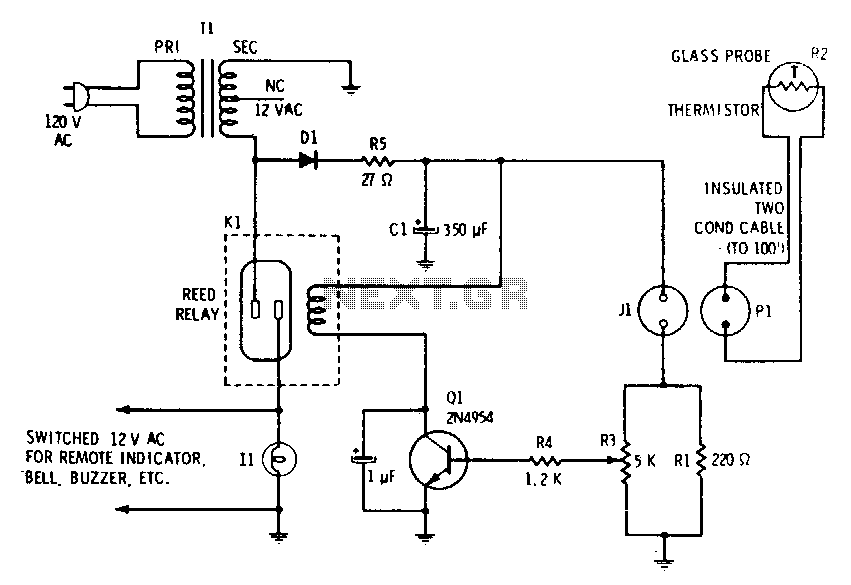
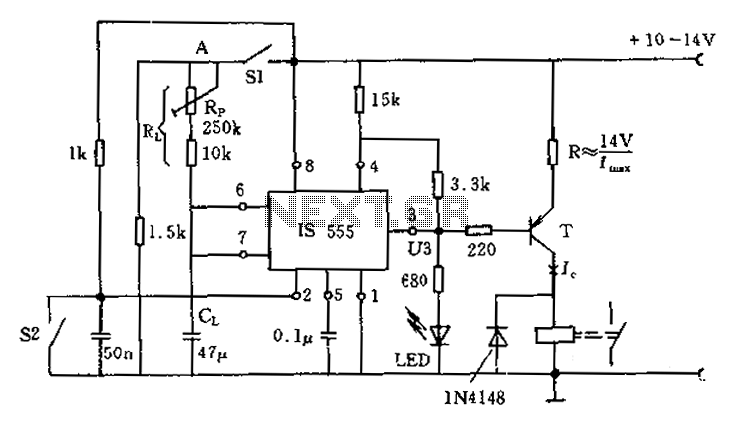
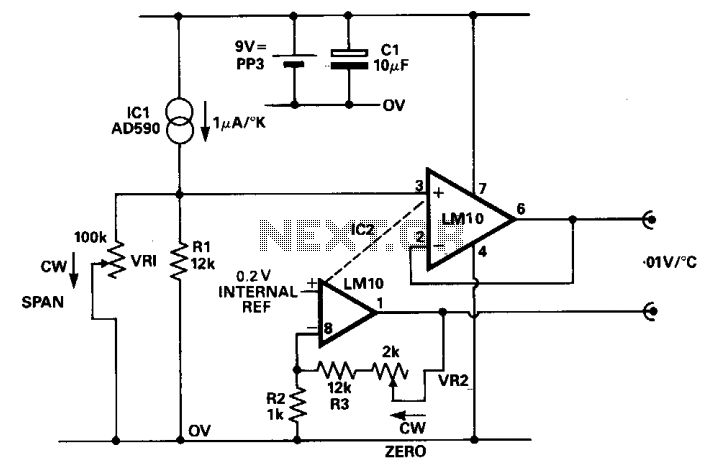
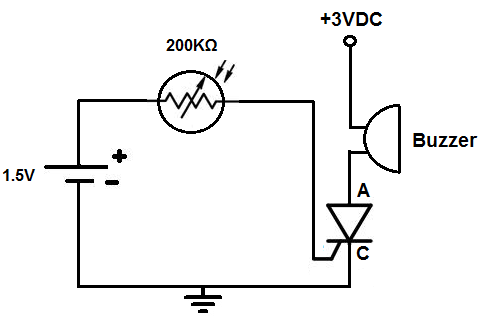
Temperature Alarm with Op-Amp Comparator
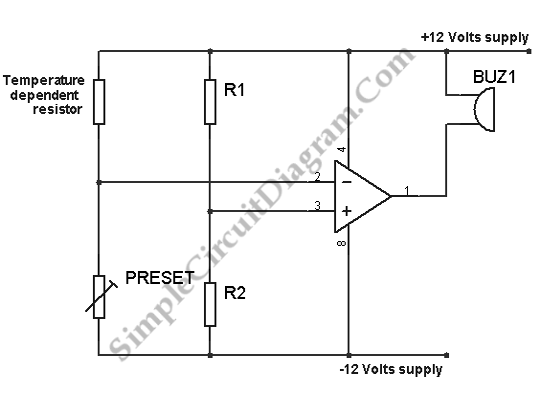
The circuit below is configured as a comparator. A fixed reference voltage at the non-inverting input is provided by resistors R1 and R2. The inverting input voltage is...
The comparator circuit functions by comparing two input voltages and producing a digital output that indicates which input is higher. In this configuration, the non-inverting input receives a fixed reference voltage determined by the resistor divider formed by R1 and R2. This reference voltage is crucial for setting the threshold at which the comparator toggles its output state.
The inverting input voltage is typically derived from a variable source, allowing the circuit to respond to changes in this input. The output of the comparator will switch states when the voltage at the inverting input exceeds the reference voltage at the non-inverting input. This characteristic makes the comparator useful in various applications, such as zero-crossing detectors, level shifters, and signal conditioning circuits.
To ensure stable operation, it is important to select appropriate resistor values for R1 and R2, considering the desired reference voltage and the input voltage range. Additionally, the circuit may benefit from hysteresis to prevent rapid switching in the presence of noise, which can be implemented by adding positive feedback through a resistor connected from the output back to the non-inverting input.
Overall, the comparator circuit is a fundamental building block in electronic design, enabling precise voltage comparisons and control in a wide array of applications.The circuit below is configured as a comparator. A fixed reference voltage at the non inverting input is provided by R1 and R2. The inverting input voltage is.. 🔗 External reference
The comparator circuit functions by comparing two input voltages and producing a digital output that indicates which input is higher. In this configuration, the non-inverting input receives a fixed reference voltage determined by the resistor divider formed by R1 and R2. This reference voltage is crucial for setting the threshold at which the comparator toggles its output state.
The inverting input voltage is typically derived from a variable source, allowing the circuit to respond to changes in this input. The output of the comparator will switch states when the voltage at the inverting input exceeds the reference voltage at the non-inverting input. This characteristic makes the comparator useful in various applications, such as zero-crossing detectors, level shifters, and signal conditioning circuits.
To ensure stable operation, it is important to select appropriate resistor values for R1 and R2, considering the desired reference voltage and the input voltage range. Additionally, the circuit may benefit from hysteresis to prevent rapid switching in the presence of noise, which can be implemented by adding positive feedback through a resistor connected from the output back to the non-inverting input.
Overall, the comparator circuit is a fundamental building block in electronic design, enabling precise voltage comparisons and control in a wide array of applications.The circuit below is configured as a comparator. A fixed reference voltage at the non inverting input is provided by R1 and R2. The inverting input voltage is.. 🔗 External reference