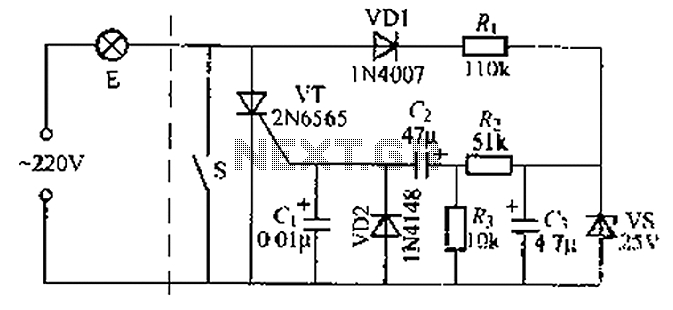
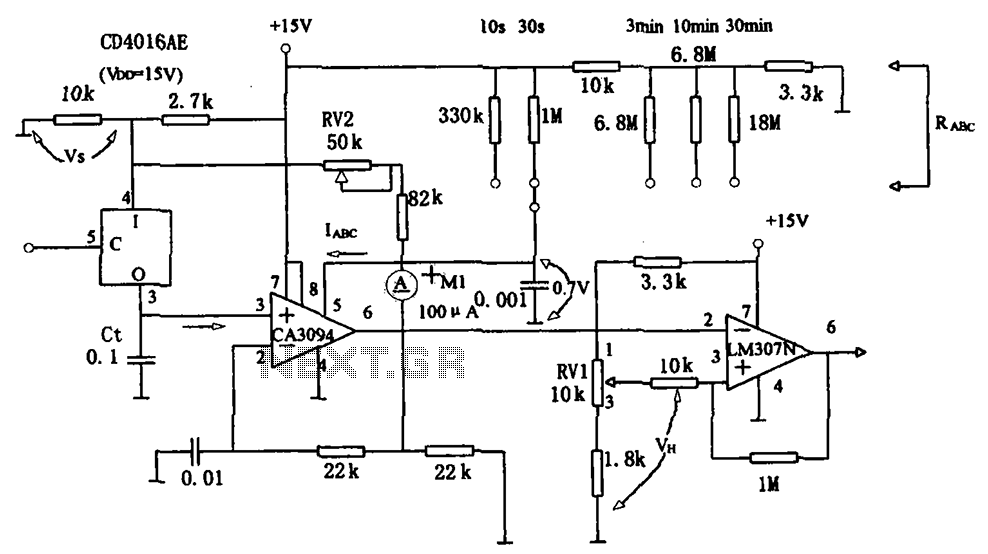
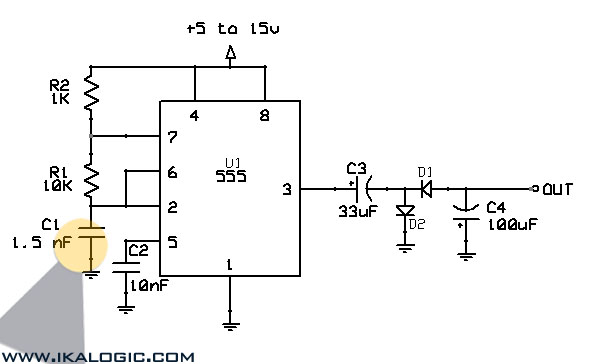
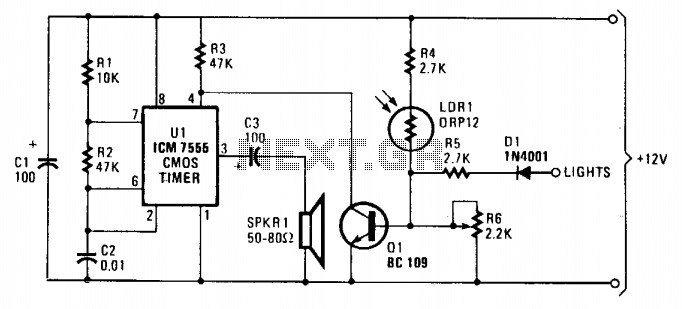
Temperature Controller with 555 Circuit
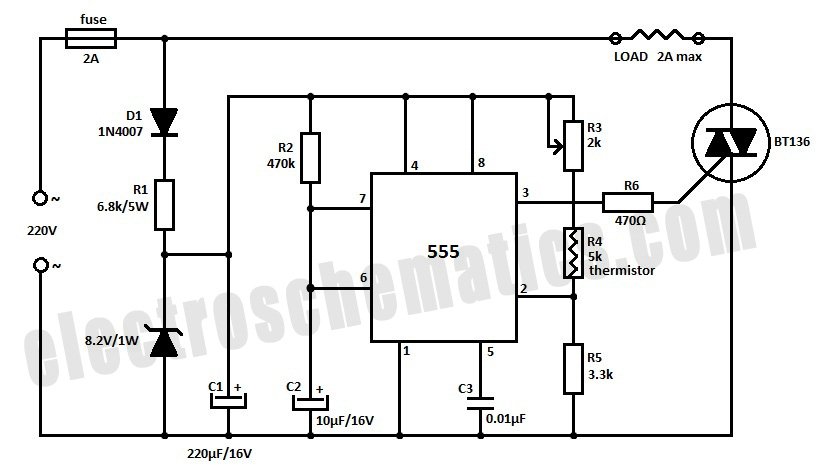
Construct a temperature controller circuit using the 555 integrated circuit (IC) in combination with a thermistor resistor divider. The benefit of this design is that it does not require a well-regulated power supply. The resistor divider network comprises an adjustable resistor (R3), a thermistor (R4), and another resistor (R5). When the temperature sensed by the thermistor falls below a predetermined threshold, the voltage at pin 2 of the 555 IC drops below one-third of Vcc. This activates a triac that controls the heater and initiates the timing cycle. If the temperature sensed by the thermistor exceeds the set point before the timing cycle concludes, the heater turns off at the end of the timing period; otherwise, the heater remains on.
The temperature controller circuit leverages the 555 timer IC, which operates in monostable mode to regulate the heating element based on the temperature readings from the thermistor. The thermistor's resistance decreases with an increase in temperature, creating a voltage divider with resistors R3 and R5. The adjustable resistor R3 allows for fine-tuning of the temperature set point, providing flexibility in the system's operation.
In this configuration, the 555 timer's pin 2 serves as the trigger input, which responds to the voltage level determined by the thermistor and the resistors. When the thermistor detects a temperature below the set threshold, the voltage at pin 2 drops, triggering the 555 timer. The timer's output at pin 3 goes high, activating the triac that controls the power to the heater. This action initiates the heating process.
The timing cycle duration is determined by the external components connected to the 555 timer, typically involving resistors and capacitors that set the timing interval. If the thermistor detects a temperature rise above the set point during this timing period, the circuit is designed to cut power to the heater at the end of the timing cycle, preventing overheating. Conversely, if the temperature does not exceed the threshold, the heater remains energized until the timing cycle concludes.
This circuit design is particularly advantageous for applications where a stable power supply is not feasible, as it operates effectively with a wide range of input voltages. Overall, the 555-based temperature controller provides a simple yet effective solution for temperature regulation in various electronic and heating applications.Build a temperature controller circuit with the 555 IC together with a thermistor resistor divider. The advantage is that a well regulated power supply is not needed. The dividing network consists of adjustable resistor R3, thermistor R4 and R5. When the thermistor temperature is below a set value the voltage at pin 2 of the 555 drops belo w 1/3 of Vcc. This turns on the triac controlled heater and also starts the timing cycle. If the thermistor temperature rises above the set point before the end of the timing cycle the heater shuts off at the end of the timing period. Otherwise the heater continues to stay on. 🔗 External reference
The temperature controller circuit leverages the 555 timer IC, which operates in monostable mode to regulate the heating element based on the temperature readings from the thermistor. The thermistor's resistance decreases with an increase in temperature, creating a voltage divider with resistors R3 and R5. The adjustable resistor R3 allows for fine-tuning of the temperature set point, providing flexibility in the system's operation.
In this configuration, the 555 timer's pin 2 serves as the trigger input, which responds to the voltage level determined by the thermistor and the resistors. When the thermistor detects a temperature below the set threshold, the voltage at pin 2 drops, triggering the 555 timer. The timer's output at pin 3 goes high, activating the triac that controls the power to the heater. This action initiates the heating process.
The timing cycle duration is determined by the external components connected to the 555 timer, typically involving resistors and capacitors that set the timing interval. If the thermistor detects a temperature rise above the set point during this timing period, the circuit is designed to cut power to the heater at the end of the timing cycle, preventing overheating. Conversely, if the temperature does not exceed the threshold, the heater remains energized until the timing cycle concludes.
This circuit design is particularly advantageous for applications where a stable power supply is not feasible, as it operates effectively with a wide range of input voltages. Overall, the 555-based temperature controller provides a simple yet effective solution for temperature regulation in various electronic and heating applications.Build a temperature controller circuit with the 555 IC together with a thermistor resistor divider. The advantage is that a well regulated power supply is not needed. The dividing network consists of adjustable resistor R3, thermistor R4 and R5. When the thermistor temperature is below a set value the voltage at pin 2 of the 555 drops belo w 1/3 of Vcc. This turns on the triac controlled heater and also starts the timing cycle. If the thermistor temperature rises above the set point before the end of the timing cycle the heater shuts off at the end of the timing period. Otherwise the heater continues to stay on. 🔗 External reference